Hematuria Is The Presence Of Blood In The Urine This Can Be Caused By A Number Of Different Conditions
Most of the time, the cause is not serious and will quickly self-resolve. Strenuous exercise is a cause of hematuria that is not serious. Certain foods can give the urine a red, blood-like appearance that is nothing to worry about. An enlarged prostate or vaginal dryness can cause blood to be found in a urine test. However, hematuria can also be a symptom of a urinary tract infection or a more serious disorder, including urinary tract cancers, so hematuria should never be ignored. If you have blood in the urine, it is important to see a doctor.
Classifications Of Urinary Tract Infections:
Uncomplicated UTI: mild UTI, without complications, occur in normal urinary tracts
Complicated : abnormality in urinary system or individual has a health problem that compromises hosts defenses
Recurrent UTI: three or more UTIs in 12 months or 2 or more occurrences within 6 month
-Relapse: a second UTI caused by the same pathogen within 2 weeks of first treatment
-Reinfection: a UTI that occurs greater than 2 weeks after completing treatment for same or a different pathogen
Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection
Uncomplicated UTI is a UTI in a patient without structural or functional abnormalities within the urinary tract or kidney parenchyma, without relevant comorbidities that place the patient at risk for more serious adverse outcome, and not associated with GU tract instrumentation.9,10 This classification is thus limited to young, healthy, nonpregnant women with normal anatomic and functioning urinary tracts. Women are more susceptible than men to UTI due to a shorter urethra for uropathogenic bacteria to ascend. The traditional diagnostic criterion dating from 1960 had been a positive urine culture of 105 CFU/mL however, in symptomatic patients, low-colony-count infections with â¥102 to 103 CFU/mL are clinically valid.8,9,10
You May Like: Diet To Prevent Urinary Tract Infection
What Could Be Mistaken For A Uti
There are several conditions whose symptoms mimic UTIs. Sexually transmitted infections cause symptoms also common in UTIs, such as painful urination and discharge.
Vaginitis, caused by bacteria or yeast, can result in a burning sensation when urinating and similar discomfort that may mimic a UTI.
Often mistaken for a UTI, interstitial cystitis , or painful bladder condition, is a chronic condition affecting the bladder that does not improve with antibiotic treatment. Symptoms of IC include increased urgency and more frequent urination as well as pain in the pelvic area.
Other conditions to rule out are overactive bladder, pregnancy, prostatitis, diabetes, cancer, and kidney stones.
How To Treat Acute Cystitis With Hematuria
Since hematuria in acute cystitis is technically a symptom, rather than a condition, there is no direct treatment. Instead, your doctor will focus on its underlying cause. That may mean prescribing a regimen of antibiotics for a bladder infection or adjusting existing medications for bladder or kidney cancer.
If you notice blood in your urine, its important to ask your doctor for a diagnosis before taking any steps. The approach to treatment depends heavily on the type of infection you have. Kidney infections, for example, are much more complex than bladder infections. They need intensive medication to kill the bacteria, and particularly severe cases might even require dialysis.
You May Like: How To Get Rid Of A Urinary Tract Infection Male
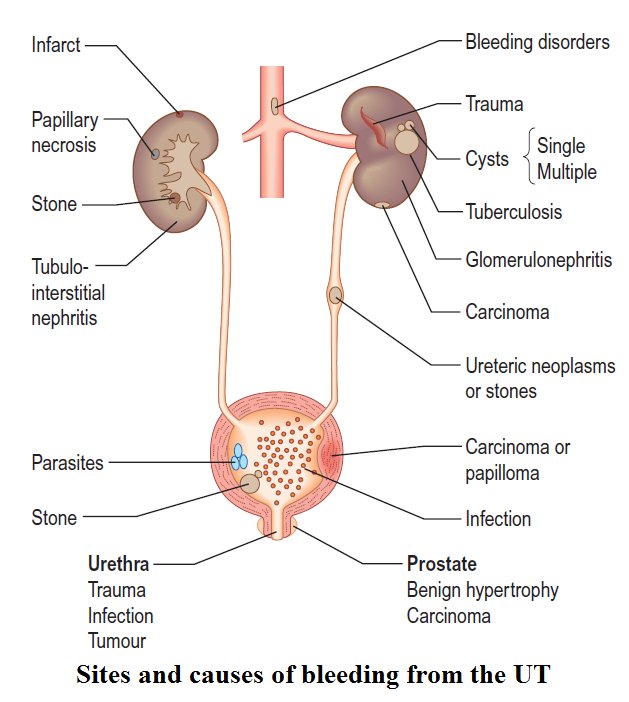
What Are The Causes Of Blood In Urine
There are many causes of blood in your urine, including:
- An infection, such as a UTI or virus
Anyone can have blood in their urine, but it is more likely if you:
- Have a family history of kidney disease
- Have an enlarged prostate
- Have a history of kidney stones
- Are taking certain medicines, such as pain relievers, blood thinners and antibiotics
- Have or recently had certain types of infections
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Hematuria
Microscopic hematuria has no visible signs. Doctors will only know someone has it if a urine test finds it.
Gross hematuria is seen because it changes the color of urine, which can happen with only a little bit of blood. Often, red or tea-colored urine is the only symptom.
In some cases, hematuria can be one of many symptoms of another condition. For example, if a bladder infection is causing the hematuria, other symptoms might include fever, pain while peeing, and lower belly pain.
Recommended Reading: Frequent Urinary Tract Infections Icd 10
Four Common Causes Of Hematuria
Written by Sarah Thebarge, Physician Assistant
Hematuria is a condition in which red blood cells are found in the urine. Hematuria can be macroscopic , where blood is visible with the naked eye, or it can be microscopic, only visible when examined under a microscope.
Here are four of the most common causes of this condition.
Other Disorders Of Urinary System
- 2016201720182019202020212022Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
- Acute lower urinary tract infection
- Acute upper urinary tract infection
- Acute urinary tract infection
- 689 Kidney and urinary tract infections with mcc
- 690 Kidney and urinary tract infections without mcc
- 791 Prematurity with major problems
- 793 Full term neonate with major problems
You May Like: Fibroids And Urinary Tract Infections
Acute Cystitis With Hematuria: How It Can Be Treated
Blood in your urine can be frightening, and at times, a telltale sign of acute cystitis with hematuria. Read on for a comprehensive guide to this medical condition, how it affects you, and the steps you should take to treat it.
How Does Boston Childrens Treat A Hematuria
Your childs pediatric urologist will determine which treatment is appropriate for your child based on what’s causing the hematuria.
- Hematuria caused by urinary stones is generally treated by removal of the stones.
- Hematuria caused by urinary tract infections is treated with antibiotic therapy to eradicate the infection.
The doctor will also consider the extent of the condition, your childs tolerance for specific medicines and procedures, and your preferences. In many cases, the hematuria goes away by itself and does not return in this case, your child wouldnt require any specific therapy other than observation.
Read Also: Can Obesity Cause Urinary Incontinence
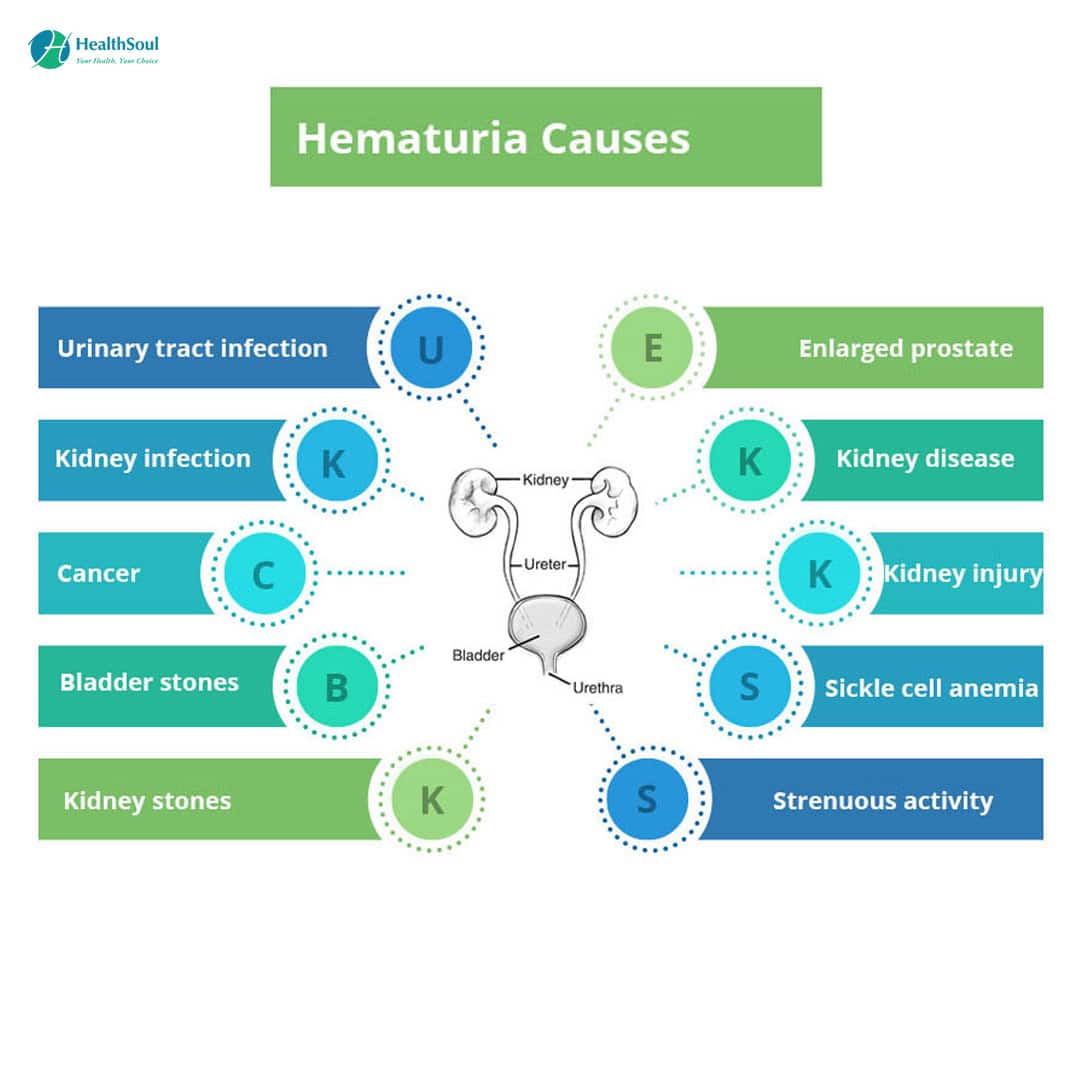
What Causes Blood In The Urine
There are several possible causes for this symptom, explains Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center surgeon and urologic cancer specialist Eugene Pietzak.
- Urinary tract infections. UTIs are more common in women than men, explains Dr. Pietzak, because a womans urethra is shorter than a mans. This makes it easier for bacteria to get into the bladder or kidney. Occasionally, a UTI can cause an increase of white blood cells in the urine, a condition known as pyuria. This can cause the urine to appear cloudy, but it is not what most people think of as blood in the urine.
- Bladder or kidney stones. Solid masses that form from chemicals in the urine might scrape the lining of the bladder or kidney and damage blood vessels, causing them to leak.
- Cancer of the bladder, kidney, or prostate. A tumormay grow, and the blood vessels within it become fragile so that they rupture and bleed, Dr. Pietzak says. Ive heard people tell vivid stories of having normal urine and then suddenly it becomes completely red.
- Often, the person has had no other symptoms before the blood appears. The most likely cancer is bladder cancer, although the blood also could be a sign or kidney cancer or prostate cancer.
- Blood in the urine is more likely to be cancer in men than in women, mainly because men develop bladder cancer at a much higher rate about four times as much than women. Unfortunately, this often leads women to dismiss this cancer warning sign when the disease is at an early stage.
What Is The Treatment For Blood In Urine

The treatment depends on the cause of the blood in your urine. To find out the cause, your doctor may ask about your family history and test your urine. A lab will test the urine sample for signs of an infection, kidney disease or other problems.
If an infection is causing the blood in your urine, your doctor may give you antibiotic medicine. Other causes may need different treatments.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Rid Of A Urinary Tract Infection
Prostatitis Epididymitis Urethritis And Orchitis
In contrast to UTI, prostatitis affects men of all ages and, from 1990-1994, accounted for almost 2 million office visits per year in the United States. Prostatitis syndromes account for 25% of male office visits for genitourinary complaints, 8% of visits to urologists, and 1% of visits to primary care physicians. Of these men, 5% have bacterial prostatitis, 64% have nonbacterial prostatitis, and 31% have prostatodynia. Digital examination of the prostate in the setting of probable or possible UTI should be avoided to prevent the risk of inciting bacteremia.
Epididymitis has a bimodal distribution, corresponding to different age groups and pathogens. Most cases in men younger than 35 years are due to sexually transmitted pathogens. Older patients are more likely to have obstructive prostatism or a history of instrumentation or catheterization.
Gonococcal urethritis is more common in ethnic minorities, lower socioeconomic groups, and persons living in urban centers. The risk to a male having intercourse with an infected female is 17%. Some of these associations may be limited by confounding. The peak age for urethritis is 20-24 years.
Mumps orchitis occurs in 18% of postpubertal boys infected with the mumps virus.
John L Brusch, MD, FACP Corresponding Faculty Member, Harvard Medical SchoolJohn L Brusch, MD, FACP is a member of the following medical societies: American College of Physicians, Infectious Diseases Society of AmericaDisclosure: Nothing to disclose.
Cultures And The Laboratory Diagnosis Of Utis
Routine bacterial urine cultures. Urine culture may not be necessary as part of the evaluation of outpatients with uncomplicated UTIs . However, urine cultures are necessary for outpatients who have recurrent UTIs, experience treatment failures, or have complicated UTIs. Urine cultures are also necessary for inpatients who develop UTIs. The bacterial culture remains an important test in the diagnosis of UTI, not only because it helps to document infection, but also because it is necessary for determination of the identity of the infecting microorganism and for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. This is particularly true because of the increased incidence of antimicrobial resistance.
Catheterized patients and many patients with infections of the lower urinary tract have colony counts much lower than 105 cfu/mL if the specimens are obtained via suprapubic aspirate or catheterization . Accordingly, the most appropriate diagnostic criterion for urine culture specimens obtained via suprapubic aspirate or catheterization is a bacterial concentration of 102 cfu/mL .
Interpreting culture results for urine specimens yielding common urinary tract pathogens.
Also Check: How Do I Get Rid Of Urinary Retention
Drinking Plenty Of Fluids
While youre being treated for a UTI, drink lots of fluids. This will make you pee more often, which flushes bacteria out of your body. The best choice is water.
To avoid worsening your symptoms, limit beverages that irritate the urinary tract. These drinks include:
- carbonated drinks, like soda
- artificially-sweetened beverages
Many people think cranberry juice can help, but the research is lacking. A 2012 review of studies determined that cranberry juice cant prevent or resolve UTIs.
Context Of Previous Studies
The findings of this systematic review are consistent with a previous systematic review which concluded that no sign or symptom on its own is powerful enough to rule in or rule out the diagnosis of UTI . However, the relative diagnostic importance of individual symptoms and signs varies between this review and the previous systematic review . The previous systematic review found that presence of dysuria, frequency, hematuria, back pain and costovertebral angle tenderness increase the probability of UTI using a diagnostic threshold ranging from between 102 CFU/ml and 105 CFU/ml, also history of vaginal discharge, history of vaginal irritation and vaginal discharge on examination decrease the probability of a UTI. In this systematic review we found that dysuria and frequency increase the probability of UTI across different reference standard thresholds 102 CFU/ml, 103 CFU/ml and 105 CFU/ml. Hematuria is also significant in the present study using a diagnostic threshold of 102 CFU/ml and 103 CFU/ml. However, in contrast to the previous systematic review back pain is not significantly associated with UTI across the different reference standard thresholds. Vaginal discharge is identified as an important symptom for decreasing the probability of UTI in the present study.
Read Also: Botox For Urinary Incontinence Cost
Reasons Why There May Be Blood In Your Urine
Hematuria is the medical term for blood in urine. Its fairly common and affects up to 30% of the adult population. The volume of blood in urine ranges from microscopic, meaning
Blood can appear in the urine in microscopic amounts which would only be seen by medical instruments, or it may appear to cause a pinkish discoloration in the urine . So it is possible to get hematuria and not even know it, and it can happen for a variety of reasons.
To get both a proper diagnosis and treatment for a condition like hematuria you will want a skilled and capable medical team. Drs. Craig Herman, Steven Kester and the staff at the Urology Center of Florida have been serving the Fort Lauderdale, Pompano Beach, and Greater South Florida areas for decades and have the expertise and experience to give quality treatment for hematuria and other urological needs.
Ways To Prevent Acute Cystitis
Acute cystitis is usually brought on by bacteria entering the bladder through your urethra. Minimize your risk of developing a UTI and bladder infection by taking necessary precautions. Drink plenty of water, both to prevent dehydration and encourage frequent urination, which flushes bacteria out of your bladder regularly.
If youre sexually active, remember to pee as soon as possible following intercourse. Avoid using birth control that could irritate the area around your urethras opening or introduce bacteria into your bladder. Many types of spermicidal jellies, cervical sponges, and diaphragms foster increased or altered bacterial growth.
Also Check: How Can A Woman Get A Urinary Tract Infection
How Can Pyelonephritis/complicated Uti Be Prevented
Single dose antimicrobial prophylaxis is recommended for prevention of urosepsis in patients undergoing invasive GU procedures, such as transrectal prostate biopsy and bladder biopsy. The regimen of choice has been ciprofloxacin however, increased resistance to ciprofloxacin has led to breakthrough episodes of sepsis and bacteremia. Optimal prophylaxis regimens other than the fluoroquinolones are currently being evaluated but can be guided by local resistance data or by rectal cultures.
Antimicrobial prophylaxis with TMP-SMX is used in patients undergoing renal transplantation.
Patients with recurrent episodes of complicated UTI due to a nidus of infection, such as stone, stent, or other foreign body, may be managed with antimicrobial prophylaxis while definitive management of the underlying disease process is planned. This strategy is not effective long-term because of issues of antibiotic resistance and adverse effects.
Reducing the use of urinary catheters is the primary method for preventing catheter-associated UTI.
Symptoms Of Acute Cystitis With Hematuria
While the most obvious symptom of acute cystitis with hematuria is blood in your urine, a bladder infection presents several other symptoms. You might feel a strong, overwhelming urge to pee and a burning sensation when you do go.
Additionally, some experience bladder leakage throughout the day or need to urinate many times in small amounts. Keep in mind that urine that gives off a strong smell, and appears cloudy instead of clear, is usually an indication of bacterial infection.
Other signs of acute cystitis include soreness or discomfort in your lower pelvis, similar to dull menstrual cramps. Also, be on the lookout for a feeling of pressure on your lower abdomen around the bladder area, as well as a low-grade fever. Note that women with a history of UTIs tend to be more susceptible to recurring infections.
Children are equally vulnerable to UTIs particularly younger girls who may not wipe properly after using the bathroom. If you notice your little one wetting their pants in the daytime, after theyve passed the stage where this is considered normal, consult your pediatrician.
Children are equally vulnerable to UTIs particularly younger girls who may not wipe properly after using the bathroom.
Furthermore, if acute cystitis symptoms return, the medication for your initial infection might not be working. In this case, youll need to consult your doctor for a different prescription or treatment.
Read Also: Urinary Tract Infection Mayo Clinic
Strengths And Limitations Of This Study
The systematic search, the conservative inclusion criteria, the inclusion of additional data from authors, and the quality assessment of the included studies can be seen as strengths of this study. In addition, given the lack of consensus regarding reference standard thresholds for UTI, the current study is the first study to determine the diagnostic accuracy of symptoms and signs across the three thresholds 102 CFU/ml, 103 CFU/ml and 105 CFU/ml. Lastly, this study highlights the additional importance of using dipstick test, particularly tests for nitrites, as an additional diagnostic tool when ruling in a UTI diagnosis based on particular symptomatology.
Which Individuals Are At Greater Risk Of Developing Pyelonephritis/complicated Urinary Tract Infection
-
Complicated UTI risk is greatest in patients with abnormal voiding and may be suggested by a history of urinary retention, recurrent UTI, or urinary procedures, including stent or catheter placement. Any condition or foreign body resulting in obstruction of normal urinary flow predisposes to complicated UTI. Diabetes increases the risk of perirenal abscess and emphysematous pyelonephritis.
-
Specific factors include:
Beware: there are other diseases that can mimic pyelonephritis/complicated urinary tract infection:
-
Urethritis due to sexually transmitted pathogens can mimic cystitis.
-
Nephrolithiasis mimics pyelonephritis.
-
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome in males mimics prostatitis.
-
Systemic conditions and non-GU infections can result in fever, tachycardia, mental status change, and/or hypotension and may be misdiagnosed as UTI because of the presence of pyuria or asymptomatic bacteriuria. When making a diagnosis of complicated UTI on the basis of systemic symptoms alone, other diagnoses need to be excluded.
You May Like: Azo Urinary Tract Health Side Effects