How To Practice Urge Control
Using some of the urge control techniques described above takes practice especially pelvic floor exercises with urgency.
Daily showering is a useful opportunity to practice since getting into the shower can often trigger urgency and urge incontinence.
Practice getting into the shower without emptying your bladder as you contract your pelvic floor muscles.
Managing The Elderly With Urinary Incontinence And Dementia
Si Ching LIM
Senior Consultant, Department of Geriatric Medicine, Changi General Hospital, Singapore
*Corresponding author: Si Ching LIM, Senior Consultant, Department of Geriatric Medicine, Changi General Hospital, Singapore, E-mail:
Received: April 14, 2017 | Accepted: June 03, 2017 | Published: June 05, 2017
Citation: Si Ching LIM Managing the Elderly with Urinary Incontinence and Dementia. Int Arch Urol Complic 3:027. doi.org/10.23937/2469-5742/1510027
Copyright:© 2017 Si Ching LIM. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Medications For Urinary Incontinence
If medications are used, this is usually in combination with other techniques or exercises.
The following medications are prescribed to treat urinary incontinence:
- Anticholinergics calm overactive bladders and may help patients with urge incontinence.
- Topical estrogen may reinforce tissue in the urethra and vaginal areas and lessen some of the symptoms.
- Imipramine is a tricyclic antidepressant.
Don’t Miss: Can Gas Cause Urinary Incontinence
Adherence And The Role Of The Provider
Most behavioral therapies for incontinence are based on self-management models and their success depends on the active participation of a motivated patient. Some patients are self-motivated, but most require assistance from the provider to engage fully in their behavioral program. It can be challenging for women to remember to use their muscles strategically in daily life, as well as to maintain a regular exercise or voiding regimen over time. Self-management is not a concept that every patient understands naturally and they ordinarily need to be empowered to take control of their behavior, including lifestyle and practicing continence skills.
Unlike with some therapies, progress with behavioral treatment is often so gradual as to be imperceptible to the patient. Such gradual change makes it difficult for patients to appreciate even steady improvement over time. According to operant learning principles, positive results reinforce behavior and it is more likely to be repeated. Behaviors that do not produce the desired results tend to be abandoned. Thus, one role of the provider using behavioral interventions is to help the patient sustain her efforts and motivation for long enough to experience a noticeable change in her bladder control.
When Should You See A Doctor
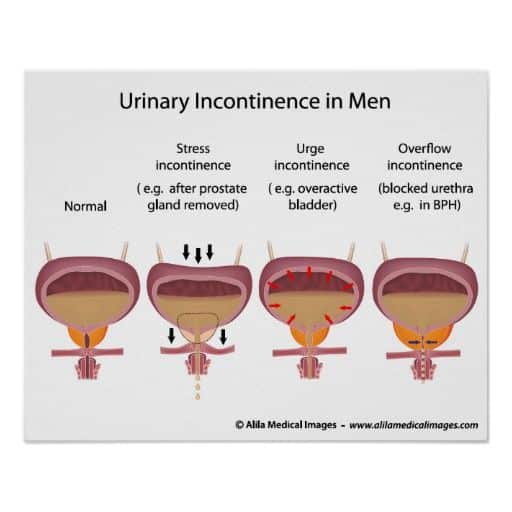
For many people, urge incontinence is merely an inconvenience that doesnt require a doctors visit.
However, if you have a serious case of urge incontinence, you should seek treatment right away. Your symptoms could be signaling:
- bladder infection
- stones in the bladder or kidney
Some symptoms to watch out for alongside your urge incontinence are pain in the pelvic region, burning or pain with urination, or symptoms that continue for several days.
In addition, if urge incontinence impedes your daily activities, you may want to visit your doctor to discuss treatment options or other ways to manage your condition.
To diagnose incontinence and develop a treatment plan, your healthcare provider will ask you about your medical history and history of incontinence. They will likely perform a physical exam, including a pelvic exam, and take a urine sample.
Your healthcare provider may also perform additional tests if necessary, including:
Treatments are varied and depend on your unique symptoms and condition. Each person will have a slightly different treatment plan.
Read Also: Best Pads For Male Urinary Incontinence
Key Points For Avoiding Urge Incontinence
The key to overcoming urge incontinence is to act when you first sense the onset or bladder urgency, otherwise its often too late.
- Contract your pelvic floor muscles strongly
- Walk to the bathroom never run
Use those additional urge control strategies listed above that help you. Everyones different some women find that one or a couple of the techniques listed above can improve bladder control.
If you need more help, speak with your doctor or see a Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist for pelvic floor exercises and bladder control training to overcome urge incontinence.
There Are Two Primary Categories Of Medications Used To Treat Urge Incontinence Including:
- Anticholinergics These medications help relax your bladder, and can be helpful for urge incontinence and overactive bladder. There are a few side effects to be aware of, including dry mouth and eyes, constipation and difficulty completely emptying your bladder.
- Beta 3 agonist This category of medications relaxes the bladder muscle and can increase the amount of urine your bladder can hold. It also may increase the amount you are able to urinate at one time instead of small amounts more frequently. This is a newer category of medications, and your insurance provider may require that you try other conservative or medication options first.
Your health care provider will help you determine which is right for you and your condition.
Recommended Reading: Azo Urinary Tract Defense Vs Azo Urinary Pain Relief
Bladder Training And Other Voiding Schedules
Scheduled voiding regimens have been used for decades to treat urgency incontinence and functional incontinence by modifying voiding habits. These programs include bladder training, timed voiding, habit training, and prompted voiding. All these approaches are based on a regular toileting schedule, but they differ on whether the patient has an active vs. passive role and how the voiding schedule is determined and adjusted.1 Bladder training is self-administered and requires the patient to resist urgency and delay voiding. Timed voiding, habit training, and prompted voiding, are generally used for patients with cognitive impairment and are implemented by caregivers.
Bladder training
Bladder training was developed originally for the treatment of urgency incontinence. Many patients with urgency incontinence also have excessive frequency of micturition. The premise of bladder training is that habitual frequent voiding can reduce bladder capacity and lead to bladder overactivity, which in turn causes more urgency and urgency incontinence.46, 47 The goal of bladder training is to break this cycle using consistent incremental voiding schedules to reduce voiding frequency, increase bladder capacity, and restore normal bladder function.
Other scheduled voiding regimens
Delayed voiding
When To See A Healthcare Provider
Urge incontinence does not need to be severe for you to seek treatment. If it is affecting your quality of life, interfering with sleep, or causing social isolation, speak with a healthcare provider.
Studies show that urinary incontinence can increase your risk of depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. These conditions tend to get worse the longer or more severe your urinary symptoms are.
There are also times in which urge incontinence is a sign of a serious medical condition, such as bladder outlet obstruction . While symptoms alone cannot diagnose BOO, certain signs warrant immediate medical investigation, including:
- Nausea or vomiting
Read Also: Cunningham Clamp For Urinary Incontinence
S Of Managing Urinary Incontinence
Anyone who is experiencing involuntary loss or leaking of urine should consult a physician. Although not in itself a disease, urinary incontinence is never normal and is sometimes a symptom of a serious problem that requires attention. In addition, your doctor will be able to recommend treatments that may eliminate or reduce the severity of your incontinence.
However, even for those whose incontinence will ultimately be cured, there is likely to be a period of time before the cure is attained when management with products is an important interim strategy. For some people, lack of proper management can cause them to hide at home in fear of an embarrassing accident. Some people quit their jobs, give up their volunteer work, shy away from social engagements and even give up necessary routine activities such as grocery shopping. Fortunately, none of these restrictions is necessary. With the proper use of the right products, you can live a full and active life despite urinary incontinence.
Can Pelvic Floor Exercises Treat Urge Incontinence
Yes, pelvic floor exercises can strengthen your muscles that support your urinary system. These exercises can improve symptoms.
Its important to target and use the correct muscles . A physical therapist who specializes in pelvic floor disorders can teach you the proper technique. This healthcare provider may use biofeedback to ensure you get the most benefit from the exercises. It can take four to six weeks to see improvements.
While some people need to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, others have spasm or excess tension in the pelvic floor muscles that can make their overactive bladder worse. In this case, you can work with a pelvic floor physical therapist on relaxing and coordinating these muscles.
You May Like: How To Cure Urinary Incontinence
Oab Or Incontinence Medications Used In Canada
| Once daily |
| The most common adverse events found with anticholinergic medications include : dry mouth, constipation, impaired cognition and blurred vision. Talk to your doctor about limiting these side effects and which medication may be right for you. |
The two most commonly prescribed anticholinergic drugs are oxy- butynin and tolterodine , both of which are available in extended-release formulations.
Recently, medications have been developed that also limit unwanted side effects. These medications include darifenacin , solifenacin , trospium , fesotoredine , Myrbetriq® and oxybutynin chloride gel . Gelnique, is rubbed into the skin, making side effects like dry mouth milder because of constant absorption rates. Myrbetig is a new drug that works by a different mechanism to relax the bladder muscle without blocking the action of acetyl choline and therefore produces lesser side effects. The other drugs are anti-cholinergics but are more specific to the bladder muscle.
Neurotoxins
Re-injection can be considered when the effect diminishes but not within three months of the last injection
Estrogen
Since estrogen helps keep the urethra healthy and strong, the drop in estrogen that occurs in women after menopause especially with aging may contribute to incontinence. Applying estrogen in the form of a vaginal cream , tablet or ring may help ease symptoms of both stress and urge incontinence.
Desmopressin
Bulking agents
Conservative Ways To Treat Urinary Incontinence Include:

- Dietary changes Try to eliminate or cut back on how much caffeine you consume, such as in coffee and tea. In addition, limit the amount of carbonated drinks and acidic foods, such as oranges and pineapples, in your diet. Caffeine prompts your body to get rid of fluids, which causes you to need to urinate. Also, the acids in carbonated drinks and some foods can irritate your bladder and cause you to go more often.
- Manage constipation For some people, urinary incontinence is a symptom of constipation. Your rectum is located near your bladder and shares many of the same nerves. Hard, compacted stool in your rectum can cause these nerves to be overactive and increase urinary frequency.
- Physical therapy A therapist can explain different exercises to do to strengthen the muscles that help control urination. Also known as Kegels, these exercises are especially effective for stress incontinence but also may help urge incontinence.
You May Like: Ulcerative Colitis And Urinary Problems
Botox Injections In The Bladder
An option for women who have failed all other medications. Onabotulinum toxin A is injected into the bladder muscle and causes partial paralysis of the detrusor muscle. Each course last approximately 6-12 months and patients typically will require multiple top-ups for the botox to be effective . This is performed under sedation in hospital as a day case and the botox takes approximately 7-10 days before working.
The botox is injected into the bladder wall as shown in the image, thru a small cystoscope that is introduced via the urethra. Approximately 5% of women will have trouble emptying there bladder following botox and use of a temporary catheter would then be required. The botox is now funded on the PBS in Australia when administered by a Urogynaecologist.
Outlet Factor Stress Incontinence
The most common storage dysfunction related to an outlet factor is stress incontinence. It is due to intra-abdominal pressure exceeding urethral closure pressure, causing involuntary loss of urine. If pelvic floor muscular training fails, the mainstay of treatment is surgery, although lifestyle modifications and controlling comorbidities which put chronic strain on the pelvis may have a supportive role.
Effective surgical options for stress incontinence include the synthetic mid-urethral sling and autologous fascial slings in women, and the transobturator bulbo-urethral sling in men. Implantation of an artificial urinary sphincter can be tried if sling surgery fails.
The role for drug therapy in stress incontinence is very limited. Duloxetine, which is a serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor, has some effects on increasing bladder outlet resistance. It has been effective in controlling mild urinary stress incontinence in women,4 but it is not approved for this indication in Australia.
Read Also: How To Get Rid Of Urinary Tract Infection Pain
Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation
Normal voiding depends not only on the normal function of organs and muscles, but also on nerves that deliver appropriate signals regarding urination. In urge incontinence, the nerves regulating the bladder can become hyper-reactive, sending strong signals to empty before the bladder is full. Nerve stimulation therapies “jam” the pathways that transmit these abnormal messages.
In PTNS, a small acupuncture needle is placed in the ankle along the tibial nerve. A handheld device connects to the needle to deliver mild electrical impulses to the nerve. These travel up the tibial nerve to the sacral nerve plexus, which regulates the bladder. PTNS sessions are painless, last 30 minutes and are repeated weekly for 12 weeks. All sessions take place in a medical office.
Extracorporeal Magnetic Resonance Therapy
Extracorporeal magnetic resonance therapy has been introduced as a therapy for stress incontinence. The NeoControl unit was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for this purpose in 2000. Resonating magnetic flux within a magnetic field induces electrical depolarization of targeted nerves and muscles. No probes are required. The patient simply sits on a chair containing the magnetic device.
A small study achieved an improvement rate of 77% after 8 weeks of therapy, with 56% of patients being completely dry. However, a 3-year follow-up study found that the benefits tend to be temporary: at 6 months, the recurrence rate was 53%.
Don’t Miss: Does Azo Get Rid Of Urinary Tract Infection
Behavioral Treatments For Urge Incontinence
One way of dealing with urge incontinence is to simply change some of your behaviors. For instance, if you can anticipate when your bladder is overactive and may be contracting abnormally, you can take action to avoid any mishaps or urine leakage.
Here are some techniques that may be helpful:
- Biofeedback: Biofeedback is a practice that helps you learn how your body normally behaves. When you do, you will know when it is not functioning properly. In the case of urge incontinence, biofeedback can help you recognize when your bladder is overactive.
Two biofeedback techniques are timed voiding and bladder training. To practice timed voiding, you use a chart to record the times that you urinate and when you leak urine. This will give you an idea of your leakage “patterns.” Then you can avoid leaking in the future by going to the bathroom at those times.
With bladder training, you “stretch out” the intervals at which you go to the bathroom. You do this by waiting a little longer before you go. For instance, to start, you can plan to go to the bathroom once an hour. You follow this pattern for a period of time, and then you change the schedule so that you are going to the bathroom every 90 minutes. Then eventually, you lengthen the interval to every two hours, and so on, until you are up to three or four hours between bathroom visits.
Other behavioral tips for preventing urge incontinence include:
Bladder Has Two Distinct Roles
Don’t Miss: Foods To Help Prevent Urinary Tract Infections
Perform Pelvic Floor Exercises
Your pelvic floor is a sheet of muscles that supports your bladder and bowel. If it weakens, you may experience urine leakage when coughing, laughing, or sneezing, a need to go to the bathroom frequently, or an urgency to get to the bathroom and leaking on the way.
Pelvic floor exercises, which are sometimes known as Kegel exercises, aim to strengthen your muscles to support your organs, improve bladder control, and prevent urine leakage.
The University of Otago in New Zealand led a that compared the exercises with no treatment. They found that people who practiced Kegels were 2.517 times more likely to fully recover from urinary incontinence.
Another study by the Université de Montréal in Canada discovered that adding dance to a pelvic floor muscle program was a recipe for success.
Practicing the combined program on a video game console led to a decrease in daily urine leakage in women over the age of 65 years, compared with the pelvic muscle floor program alone.
The team revealed that the fun dance element motivated women to show up to the physiotherapy program each week, which improved their practice frequency and therefore strengthened their pelvic floor muscles further.
Dancing also allowed the women to apply pelvic floor muscle exercises which are traditionally performed while static to movement.