How To Deal With Elderly Incontinence: A Practical 5
Lets be honestdiscussing private physical issues can be embarrassing at times. As a society, we often feel squeamish at the prospect of having open discussions about incontinence. So lets talk about how to deal with elderly incontinence.
But weve got to do our best to work through any awkward feelings, and the reason why is clear
Over 50% of people aged 65+ report bladder and/or bowel incontinence.
With this in mind, weve put together a five-step guide on how to deal with elderly incontinence. This will be an ideal read if youre:
a) an older adult who wants advice on managing bladder/bowel issues
b) a family member caring for someone with incontinence
Heres a quick summary of what well be covering
-
What causes elderly incontinence?
-
The 3 types of urinary incontinence
-
The 2 types of bowel incontinence
-
What is incontinence care & management?
-
Where can I find elderly incontinence products?
If youre a visual learner, the top tips graphic below may be a helpful place to start:
What Causes Elderly Incontinence?
A range of factors can lead to bowel and bladder problems, but a common challenge that older adults face is functional incontinence. What exactly does functional mean in this context, you may be wondering?
Cognitive, mobility, and sensory limitations can stop elderly people from accessing a toilet when they need it. This could be due to poor eyesight, arthritis, or other health issues. Environmental factors can also play a role.
This ones for guys only
Who Is At Risk For Urinary Incontinence
In adults, you are at higher risk of developing UI if you:
- Are female, especially after going through pregnancy, childbirth, and/or menopause
- Are older. As you age, your urinary tract muscles weaken, making it harder to hold in urine.
- Are a man with prostate problems
- Have certain health problems, such as diabetes, obesity, or long-lasting constipation
- Have a birth defect that affects the structure of your urinary tract
In children, bedwetting is more common in younger children, boys, and those whose parents wet the bed when they were children.
Catheterisation For Detrusor Under
The main treatment strategy for a poorly contractile bladder is clean intermittent catheterisation. Drugs with parasympathetic activities are not widely used because of poor efficacy and poor side effect profile. New treatment modalities like neuromodulation, neurostimulation or reconstruction with muscle transposition have been explored but data is limited for the elderly .
You May Like: How To Treat Urinary Tract Infection Home Remedies
Caring For Someone With Incontinence
So far, weve covered managing your own incontinence, but what if youre caring for an older adult? Incontinence is a common issue faced by dementia caregivers, and can be one of the most challenging parts of providing care. Research shows that:
- Those with dementia have a 2-3-fold increased chance of urinary incontinence
- The more severe the dementia, the more likely that there will be incontinence
- Urinary incontinence contributes to caregiver burden and increases the risk that someone will be admitted to a nursing home.
Steps to take
Dementia may not be the only cause of incontinence, so the first step is to look for other causes, like those reversible ones mentioned earlier .
If there doesnt seem to be any of those issues going on, then managed continence is the approach that is most likely to help. Rather than using the bladder medications, which can worsen confusion and dampen alertness, managed continence includes the use of continence products and a schedule of timed toileting .
In some cases, environmental adjustments and equipment, like bedside commodes, catheters, and urinals, can make frequent toileting easier and less disruptive, especially overnight.
Prevalence And Type Of Urinary Incontinence
The prevalence of UI according to age is shown in . The overall prevalence of UI was 14.8%, increasing from 12.0% for the men aged 7074 years old to 26.3% among men 8589 years old but reduced to 16.3% for those aged 90 years old .
Urgency incontinence was the most frequent type of urinary incontinence, with 20% of men reporting leaking urine before getting to the toilet . About 10% of men experienced post-micturition dribbling and 5% of men reported leaking urine for no obvious reason. Three percent of men reported using pads or other incontinence aids.
Analysis of the data from the ICIQ showed that the frequency of urine leakage was strongly correlated with the quantity of urine leaked . Both frequency and quantity of urine leakage were strongly correlated with the self-perceived impact on daily life rating in the ICIQ. Among those defined with UI, 12.6% reported a score over 5 on the self-perceived impact on life scale . The overall ICIQ summed score in all men in CHAMP ranged from 0 to 18 , with a median score of zero, the first quantile was zero and the third quantile was three.
Recommended Reading:
Also Check: How To Clean My Urinary Tract
Tips For Managing Enuresis
-
Remember, your child cant control the problem without help. Make sure not to scold or blame. Make sure your child is not teased by family or friends.
-
Keep in mind that many children outgrow enuresis.
-
Protect your childs mattress bed with a fitted plastic sheet.
-
Have a change of clothes on hand while out and about.
Dont Miss: What Juice Helps Urinary Tract Infections
Measurement Of Potential Confounders
Men were asked whether a doctor or other health care provider had ever told them they had any of a list of 20 medical conditions the number of conditions was summed to give a co-morbidity score. Men were categorised as having an enlarged prostate or prostate cancer based on self-reported diagnosis by a doctor or other health care provider.
Also Check: Purina Pro Plan Focus Urinary Tract Health Formula
Are You At Risk For A Uti
UTIs are more frequent in older adults. If the following applies to you, you are at a higher risk of having UTIS:
- Urinary retention or neurogenic bladder
- Disposable incontinence products that arent changed regularly
- Alzheimers disease
- A history of UTIs
- Use of a catheter
- Regular incontinence
- Bladder prolapse
Older females who are postmenopausal are at a higher risk of UTIs, because they experience an estrogen deficiency after menopause . In older males, bladder stones, kidney stones, prostate issues, and a history of prostate infections increase the risk of UTIs.
Different Types Of Incontinence
There are four basic types of incontinence: stress, urge, overflow and functional. They may occur alone, or in combination, especially in seniors.
Stress incontinence is the involuntary leakage of small amounts of urine in response to increased pressure on the bladder . It is present in about 35 per cent of incontinent seniors. It is more common in women, often because childbirth caused the pelvic muscles to relax. It also occurs, usually temporarily, in men who have had prostate surgery.
Urge incontinence is the leakage of large amounts of urine when someone is unable to reach the toilet after getting the urge to urinate. It accounts for 60-70 per cent of incontinence problems in seniors.
Overflow incontinence accounts for 10-15 per cent of urinary incontinence. It occurs when there is an obstruction in the bladder, which causes the bladder to overfill. Often, there is no sensation that the bladder is full. Then, when the bladder contracts, urine is released.
Functional incontinence accounts for 25 per cent of the incontinence seen in institutions. It often happens because a person has difficulty moving from one place to another. Poor vision, hearing or speech may interfere with reaching the toilet or telling caregivers of the need to use the toilet. This type of incontinence can also occur in the home.
You May Like: Do Urinary Tract Infections Go Away On Their Own
Incontinence In Older Adults: The Role Of The Geriatric Multidisciplinary Team
Urinary and fecal incontinence are very common in the geriatric population, yet many patients and health care practitioners wrongly consider incontinence a normal part of aging.
Older adults require an incontinence assessment that includes a review of physical, psychological, and social health. Functional status, quality of life, and goals of care must also be considered. Quality of life for older patients can be improved with the help of a nurse continence advisor , a pelvic floor physiotherapist, a geriatrician, and other health professionals skilled in the assessment, diagnosis, and management of urinary and fecal incontinence.
The nurse continence advisorThe nurse continence advisor is a registered nurse who has recognized education, training, and certification in continence management. The NCA focuses on conservative and holistic strategies for managing incontinence and related symptoms, including urinary urgency, frequency, and nocturia, and fecal incontinence and constipation. This nursing specialty was developed in Great Britain in the 1970s in response to long wait lists to see urological specialists, and was introduced in Canada in 1995 by the Ontario Ministry of Health.
This article has been peer reviewed.
Behavioral And Lifestyle Changes
Changing your lifestyle may help with bladder problems. Losing weight, quitting smoking, saying no to alcohol, choosing water instead of other drinks, and limiting drinks before bedtime can help with some bladder problems. Preventing constipation and avoiding lifting heavy objects may also help with incontinence. Even after treatment, some people still leak urine from time to time. There are bladder control products and other solutions, including disposable briefs or underwear, furniture pads, and urine deodorizing pills that may help.
Visit the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases for more information on urinary incontinence in men and urinary incontinence in women.
You May Like: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Feline Multifunction Urinary Hydrolyzed Protein
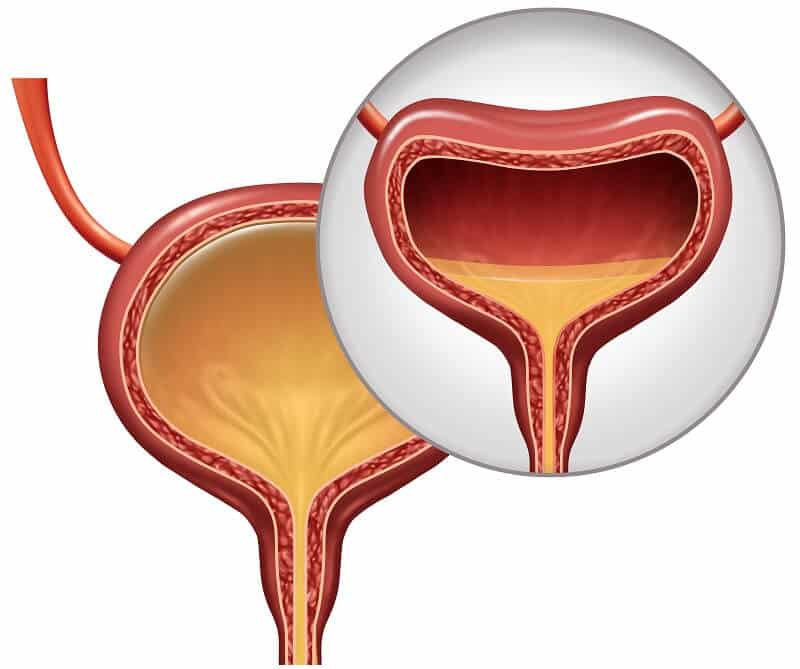
Bladder Anatomy And Physiology
The anatomy and physiology of the bladder are complex, but a basic understanding of these topics is essential in order to appreciate the various types of UI and their management., illustrates the basic anatomic structures and nervous system wiring involved in bladder function, including the detrusor muscle, the internal and external sphincters , and their neurological components.
Bladder anatomy and physiology.
Reduced activation of the sympathetic nervous system results in relaxation of the detrusor muscle, closure of the sphincter, and bladder filling. When the volume of urine in the bladder reaches 200 to 400 mL, the sensation of urge to void is relayed via the spinal cord to the brain centers. Voluntary voiding involves the parasympathetic nervous system and the voluntary somatic nervous system. Influences from these systems cause contractions of the detrusor muscle and corresponding somatic nervous activity, leading to sphincter relaxation.
Etiology And Risk Factors
Multiple factors, including age-related physiological changes, may result in or contribute to the various syndromes of UI. Both genitourinary and non-genitourinary factors may contribute to incontinence in aging patients. Age-related functional changes in the urinary tract may contribute to UI. In women, risk factors for these genitourinary changes include multiple or complex vaginal deliveries, high infant birth weight, a history of hysterectomy, and physiological changes related to the transition to postmenopause. Smoking, a high body mass index, and constipation are also associated with an increased risk of UI.
Pathophysiological causes of UI include lesions in higher micturition centers, in the sacral spinal cord, and in other neurological areas as well. UI may also be associated with numerous comorbidities, such as Parkinsons disease, Alzheimers disease, cerebrovascular disease, diabetes, hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea, and normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Functional factors, including mobility and dexterity, along with reaction time and lack of access to a bathroom facility, may also contribute to UI.
Don’t Miss: Azo Urinary Tract Defense Antibacterial Plus Urinary Pain Relief Tablets
Urinary Incontinence In Older Adults
Urinary incontinence means a person leaks urine by accident. While it can happen to anyone, urinary incontinence, also known as overactive bladder, is more common in older people, especially women. Bladder control issues can be embarrassing and cause people to avoid their normal activities. But incontinence can often be stopped or controlled.
What happens in the body to cause bladder control problems? Located in the lower abdomen, the bladder is a hollow organ that is part of the urinary system, which also includes the kidneys, ureters, and urethra. During urination, muscles in the bladder tighten to move urine into the tube-shaped urethra. At the same time, the muscles around the urethra relax and let the urine pass out of the body. When the muscles in and around the bladder dont work the way they should, urine can leak, resulting in urinary incontinence.
Incontinence can happen for many reasons, including urinary tract infections, vaginal infection or irritation, or constipation. Some medications can cause bladder control problems that last a short time. When incontinence lasts longer, it may be due to:
- Weak bladder or pelvic floor muscles
- Overactive bladder muscles
- Damage to nerves that control the bladder from diseases such as multiple sclerosis, diabetes, or Parkinsons disease
- Diseases such as arthritis that may make it difficult to get to the bathroom in time
Most incontinence in men is related to the prostate gland. Male incontinence may be caused by:
Urinary Incontinence In Men: Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Written byDr. Victor MarchionePublished onAugust 8, 2016
Urinary incontinence or loss of bladder control in men is not uncommon, but it can be treated once the cause is determined.
Uncontrollable urine in men or urinary incontinence occurs in eleven to 34 percent of older men, but it is not just an issue that impacts the aging. Younger men can also experience UI due to health problems. Urinary incontinence also happens to women, but the biggest issue with UI in men is that they are less likely to speak with their doctors about it. This means that the statistics could actually be much higher in men that the current numbers indicate. Discussing the problem is the first step to addressing the symptoms and finding a treatment.
Urinary incontinence often results in the accidental leakage of urine from the body, so it can be uncomfortable and inconvenient. A man can feel a strong, sudden need to urinate just before losing a large amount of urine. Doctors refer to this as urgency incontinence. For some people, this condition keeps them from enjoying certain activities, including sports and exercise. It can also cause a lot of emotional distress.
There are different types of urinary incontinence, so it is important to get a proper assessment from a doctor to determine what type you might have and how to go address it. The types of UI men experience include urgency incontinence, stress incontinence, functional incontinence, overflow UI, and transient UI.
Don’t Miss: Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease
Resignation And Minimization Of Symptoms
I get caught out many a time. Yes. But I don’t have an active enough life not to keep it under control.
I haven’t ever been to the doctor about it at all. I belong to the school where you think you can’t keep worrying the doctor for every small thing.
It’s like anything, I’ll have to put up with it, won’t I? It’s a hindrance sometimes I suppose, but a lot of people is a lot worse off.
Causes Of Urge Incontinence
The urgent and frequent need to pass urine can be caused by a problem with the detrusor muscles in the walls of your bladder.
The detrusor muscles relax to allow the bladder to fill with urine, then contract when you go to the toilet to let the urine out.
Sometimes the detrusor muscles contract too often, creating an urgent need to go to the toilet. This is known as having an overactive bladder.
The reason your detrusor muscles contract too often may not be clear, but possible causes include:
- drinking too much alcohol or caffeine
- not drinking enough fluids this can cause strong, concentrated urine to collect in your bladder, which can irritate the bladder and cause symptoms of overactivity
Overflow incontinence may also be caused by your detrusor muscles not fully contracting, which means your bladder does not completely empty when you urinate. As a result, the bladder becomes stretched.
Your detrusor muscles may not fully contract if:
- there’s damage to your nerves for example, as a result of surgery to part of your bowel or a spinal cord injury
- you’re taking certain medicines
Don’t Miss: What Is A Urinary Tract Infection Caused By
Incontinence In Alzheimer’s Disease
People in the later stages of Alzheimers disease often have problems with urinary incontinence. This can be a result of not realizing they need to urinate, forgetting to go to the bathroom, or not being able to find the toilet. These tips may help:
- Avoid drinks like caffeinated coffee, tea, and sodas, which may increase urination. But dont limit water.
- Keep hallways clear and the bathroom clutter-free, with a light on at all times.
- Provide regular bathroom breaks.
- Use underwear that is easy to get on and off, and absorbent briefs or underwear for trips away from home.
Visit Alzheimers Disease: Common Medical Problems for more tips.
Related Conditions And Causes Of Urinary Incontinence
Fecal incontinence is light to moderate bowel leakage due to diarrhea, constipation, or muscle or nerve damage.
As described in the section above on causes of urinary incontinence, common conditions may contribute to chronic urinary incontinence, including: urinary tract infection , constipation, interstitial cystitis or other bladder conditions, nerve damage that affects bladder control, side effects from a prior surgery, and neurological disorders.
Recommended Reading: Does Cvs Minute Clinic Do Urinary Tract Infections
How Is Urinary Incontinence Treated
You and your doctor or nurse will work together to create a treatment plan. You may start with steps you can take at home. If these steps do not improve your symptoms, your doctor or nurse may recommend other treatments depending on whether you have stress incontinence or urge incontinence or both.
Be patient as you work with your doctor or nurse on a treatment plan. It may take a month or longer for different treatments to begin working.
Read Also: Azo Urinary Tract Defense Vs Urinary Pain Relief