Why Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections Are Most Common In Older Women
Urinary tract infections are an aggravation at any age, but theyre most common in older women. For senior women, UTIs can cause serious health problems and may not come with the usual symptoms.
At Alpenglow Gynecology, we help patients of all ages in Littleton, Colorado, treat the uncomfortable symptoms associated with UTIs. Rickie Guida, WHNP-BC and our entire care team are committed to helping older women understand and treat UTIs before they cause lasting damage. We offer a comprehensive line of womens health services to help you feel your best at every age.
Do I Need To See A Doctor
Yes. Painful urination can be a symptom of a more serious problem. You should tell your doctor about your symptoms and how long youve had them. Tell your doctor about any medical conditions you have, such as diabetes mellitus or AIDS, because these could affect your bodys response to infection. Tell your doctor about any known abnormality in your urinary tract, and if you are or might be pregnant. Tell your doctor if youve had any procedures or surgeries on your urinary tract. He or she also need to know if you were recently hospitalized or stayed in a nursing home.
If your doctor thinks your pain may be from vaginal inflammation, he or she may wipe the lining of your vagina with a swab to collect mucus. The mucus will be looked at under a microscope to see if it has yeast or other organisms. If your pain is from an infection in your urethra , your doctor may swab it to test for bacteria. If an infection cant be found, your doctor may suggest other tests.
Recommended Reading: What Medicine Can I Take For Urinary Tract Infection
Here Are A Few Common Risk Factors Of Urinary Infection:
Also Check: Urinary Tract Infection And Sex
Wipe From Front To Back
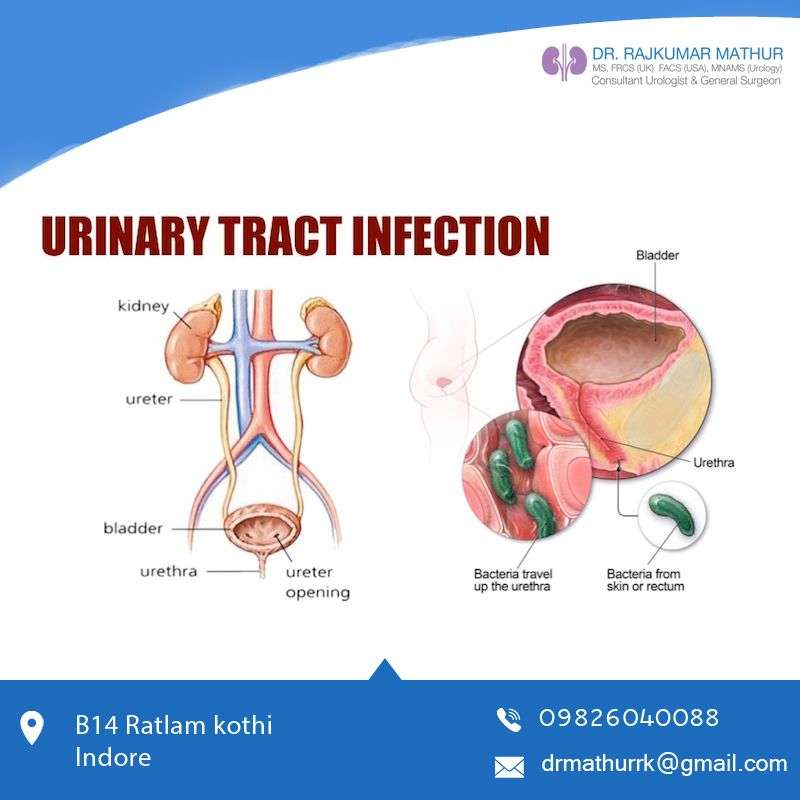
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases , UTIs can develop when bacteria from the rectum or feces gain access to the urethra. This small channel allows urine to flow out of the body.
Once bacteria are in the urethra, they can travel up into other urinary tract organs, where they can lead to infections.
After urinating, wipe in a way that prevents bacteria from coming into contact with the genitals. Use separate pieces of toilet paper to wipe the genitals and anus.
When Urinary Tract Infections Keep Coming Back
|
Image: Thinkstock |
If you are prone to recurrent UTIs, you can head them off before they take hold.
Unless youre in the fortunate minority of women who have never had a urinary tract infection , you know the symptoms well. You might feel a frequent urgency to urinate yet pass little urine when you go. Your urine might be cloudy, blood-tinged, and strong-smelling. For 25% to 30% of women whove had a urinary tract infection, the infection returns within six months.
If you have repeated UTIs, youve experienced the toll they take on your life. However, you may take some comfort in knowing that they arent likely to be the result of anything youve done. Recurrent UTIs arent due to poor hygiene or something else that women have brought on themselves. Some women are just prone to UTIs, says infectious diseases specialist Dr. Kalpana Gupta, a lecturer in medicine at Harvard Medical School.
Recommended Reading: Urinary Tract Infection Home Test Walgreens
E Coli And Urinary Tract Infections
Every year, there have been around more than 7-8 million cases of UTI alone in the United States as per one of the reports of CDC. Urinary tract infections are more commonly seen in women than men. In fact, women are four times more prone to getting a urinary tract infection than men. Over 50 percent of women get urinary tract infections at least once in their lifetime.
One of the main reasons is that women have a short urethra, thereby making it possibly easier for E.coli bacteria as well as any other bacteria to easily enter the urinary bladder. In addition, the opening of the urethra in women is near the anus, where bacteria from the bowels are excreted.
Both men and women may develop urinary tract infections if they have the following factors:
- Kidney stones or any urinary tract obstruction
- An impaired or weak immune system
- An indwelling catheter
- Spinal cord injury or any other form of nerve damage around the bladder, which prevents complete emptying of the bladder and allowing bacteria to grow and multiply
- Diaphragm use in women
- Spermicidal condom use in sexually active women
To view this video please enable JavaScript, and consider upgrading to a web browser thatsupports HTML5 video
Is Cranberry Juice Helpful For Utis
Cranberry juice has long been used as a home remedy for UTIs, but despite this, there is a lot of conflicting information surrounding whether or not it actually works.
Scientists have argued over how effective cranberry juice actually is at preventing and flushing out UTIs due to conflicting conclusions in studies on the topic.
However, drinking it wont do you any harm, so it could be worth a try.
Just ensure you pick unsweetened cranberry juice, as the sugar in sweetened cranberry juices can actually feed a bacterial infection.
Recommended Reading: How To Cure A Urinary Tract Infection In A Woman
Group B Streptococcus **
Group B strep is a common bacterium often carried in the intestines or lower genital tract. It is not sexually transmitted. Also, it is not spread through contaminated food or water.
GBS infections are serious and potentially life-threatening. However, their association with urinary tract infections , such as kidney, bladder or prostate infections, is rather rare.
Risk for serious Group B strep infections increases in adults 65 years and older.
**The epidemiological evidence gathered through our multi-year observations supports the use of herbs contained inUribiotic Formulafor urinary tract infections caused byGroup B streptococcus . This evidence, however, has not been evaluated by the FDA.
Escherichia Coli In Vaginal And Urinary Tract Infections
Escherichia coli is a gram-negative facultative anaerobe that can cause of urinary tract and vulvovaginal infections,such as aerobic vaginitis. E. coli is a common cause of infections in the digestive tract resulting in diarrhoea, and gallbladder and blood infections, as E. coli lives naturally in the digestive tract.
E. coli is easily passed from the anus to the vagina and urinary tract, and may cause food poisoning. E. coli is adapted to live in the urinary tract, where the force of urine makes it cling on harder to your cells. This means you cant wash E. coli away by drinking a lot of water.
E. coli can also swim. E. coli in the vagina is less common than in the urethra, but vaginal infections can also occur, contributing to vaginal odour, inflammation and discharge. Usually a test will reveal E. coli in the vagina or urinary tract.
E. coli creates biofilms, which is the sticky matrix that protects E. coli and friends, and blocks other, friendly microbes from colonising. This is particularly problematic in the urinary tract and vagina, where a seemingly successful treatment leaves you susceptible to infections in future.
People who get UTIs really get them. You can get one or two, but typically you either do or you dont, and this is largely down to whether unhealthy biofilms make it easy for you to develop a UTI again. No unhealthy biofilms means each new infection is truly new.
Also Check: Rabbit Urinary Tract Infection Natural Treatment
How Does E Coli Make You Sick
The most familiar strains of E. coli that make you sick do so by producing a toxin called Shiga. This toxin damages the lining of your small intestine and causes your diarrhea. These strains of E. coli are also called Shiga toxin-producing E. coli . The STEC that is most well-known in North America and most often referred to is E. coli O157:H7, or just E. coli O157
There are other types of STEC that are called non-O157 STEC. These strains cause similar illness to the O157 strain but are less likely to lead to serious complications.
Treating An Uncomplicated Uti Caused By E Coli
Treatment options vary widely for UTIs, however the conventional treatment is antibiotics, in particular fluoroquinolone. Antibiotic resistance is an issue, with multi-drug resistant Enterobacteriaceae, mostly E. coli, being a matter of concern.
E. coli strains are resistant to penicillins and cephalosporins, as well as fluoroquinolones and gentamicin. Non-antibiotic treatments that can be applied at home include herbal medicines, reflexology, and others, but ongoing or severe infection, especially involving the kidneys, requires prompt medical attention.
Recommended Reading: Can Probiotics Help With Urinary Tract Infection
Read Also: Cystex Urinary Pain Relief Directions
How Your Digestion Can Contribute To A Uti Or Aerobic Vaginitis
The urinary tract has its own microbial ecosystem, which in women resembles vaginal flora. This means that a healthy vagina supports a healthy urinary tract.
If you have digestive problems, the gut microbiome can become unhealthy, contributing to poor vaginal health due to proximity of the anus to the vagina.
Poor digestive health typically results in unbalanced gut flora, where pathogens are able to proliferate because of the absence or lack of healthy intestinal flora. E. coli naturally resides in the colon, and can overgrow, resulting in more frequent cross-contamination with the vagina and urinary tract. This highlights the importance of focusing on gut health when dealing with frequent vulvovaginal or urinary tract infections.
Constipation, for example, leaves stool in the colon for long periods of time, providing an ongoing food source for microbes. Having a healthy bowel movement every day at least once ensures that the microbial colonies in the digestive tract are kept in check, since the stool passing through acts like a broom.
Fibre makes stools larger and firmer, creating a sort of boulder that moves through the intestines, picking up anything in its way and pushing it out.
Diarrhoea doesnt have the same effect as constipation, but comes with its own issues think of wet sand in a wet sock. Bits of faeces can remain on the intestine walls, being slow to move through. This too provides a lingering food source for microbes.
When Should I Call My Healthcare Provider
- Fever.
- Back pain.
- Vomiting.
If you have any of these symptoms, or your other symptoms continue after treatment, call your healthcare provider. A UTI can spread throughout your urinary tract and into other parts of your body. However, treatment is very effective and can quickly relieve your symptoms.
Also Check: Myasthenia Gravis And Urinary Incontinence
Phylogenetic Group And Vf Distribution Among Patient Groups And Clinical Syndromes
E. coli is commonly classified into four main phylogenetic groups namely A, B1, B2, and D as defined by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and multilocus sequence typing . Several studies have shown that E. coli pathogenic strains from extraintestinal infections mostly derive from group B2, and to a less extent group D . Most studies quote prevalence rates around 6365% for group B2 in pathogenic strains, and 1015% for group D . Commensal E. coli are mainly associated with phylogenetic groups A or B1, and are mainly devoid of virulence determinants . The overlapping associations of VFs and phylogeny with clinical virulence makes it difficult to understand which directly determines virulence. However, some studies in children showed that pyelonephritis isolates more often belonged to group B2, contained on average higher prevalences of individual VF genes, and consequently had higher VF scores than did cystitis or fecal isolates, suggesting that both VF repertoire and phylogenetic background play important roles in UTI pathogenesis.
You May Like: Kidney Stone In Urinary Tract
The Connection Between E Coli And Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections, or UTIs for short, are the most common type of bacterial infection diagnosed today. And the most common bacteria to cause these infections are Escherichia coli, aka E. coli. In fact, E. coli is responsible for more than 85 percent of all urinary tract infections, according to research published in March 2012 in the journal Emerging Infectious Diseases.
Worldwide, 150 million people are affected by UTIs each year, and about 10.5 million of those individuals are in the United States, according to research published in May 2015 in the journal Nature Reviews Microbiology. Women get urinary tract infections up to 30 times more often than men do, with up to 60 percent of women getting a UTI at least once in their lives.
Also Check: How To Avoid Urinary Tract Infections After Intercourse
The Types And Causes Of Prostate Infections
When the gland is infected, it gets bigger. Usually, the men between the ages of 30 and 50 suffer from infected prostate but this condition is observed in older or younger men too.
There are 4 types of infection in the prostate gland. They have different symptoms and they are caused by different pathogens .
The four types are:
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis
- Prostatodynia
The most common causes of prostate infections are fungi, genital viruses, and streptococcal staphylococcal organisms. There are two ways for these organisms to enter the prostate.
First, by entering the prostate trough the prostate ducts. The other is by leaving the infected urine and again trough the ducts, the organism will end up in the prostate gland.
Survival Rate Of E Coli
Unfortunately, E. coli bacteria return in as many as 30 percent of people apparently cured by antibiotics! These uropathogens are able to survive an antibiotic treatment by reverting to an inactive state.
It is true that within several days of antibiotic treatment, the number of bacteria reproducing can drop to zero. Not all the bacteria are killed, though.
About 3 percent of the E. coli bacteria may be still present in a dormant state after treatment with Cipro . About 7 percent may linger after treatment with Bactrim-Septra .
Even after a month of antibiotic exposure, about 10 million of the original 1 billion bacteria may remain. No wonder uropathogenic E. coli has been called one of the most dangerous antibiotic-resistant bacterium.
Also Check: Royal Canin Urinary Tract Food
Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli **
In most cases, that is in about 80 percent in adults, urinary tract infections are caused by a variety of pathogens, infectious bacteria normally present in the intestines, especially in the colon.
Nearly all infections of the lower urinary tract are caused by a few strains of E. coli bacteria, called uropathogenic Escherichia coli .
As a part of the gastrointestinal system, they do not belong in the urinary tract. These bacteria, however, have multiple little hairs called cilia that function like little feet that allow them to climb from the skin up the urinary tube into the bladder.
If E. coli bacterium gets into the urinary tract, the body has ways of fighting it off. The obvious method is to simply flushing it out with the urine. But this pathogen has evolved ways of anchoring itself to the uroepithelial cells.
It takes advantage of receptors naturally found on the mucosal lining there. These receptors are like molecular “docking bays” for substances which the cells need for their normal growth and development.
E. coli uses “grappling hooks”, called type I pili, to hook on to these receptors, and then to invade the cell. These pathogenic “grappling hooks” are composed of long, fibrous chains of a molecular “glue” called adhesin.
How To Reduce Your Risk
As the studys researchers blame improper food handling for food-borne UTIs, you can minimize your chances of developing an E. coli infection by:
Washing your hands
Clean your hands thoroughly after using the bathroom and before food preparation.
Cooking meats thoroughly
Use a meat thermometer to ensure chicken is cooked to an internal temperature of at least 165°F .
Preventing cross contamination
Be sure to thoroughly wash your hands, counters, cutting boards, and utensils after they come in contact with raw meat.
**The epidemiological evidence gathered through our multi-year observations supports the use of herbs contained inUribiotic Formulafor urinary tract infections caused byE. coli. This evidence, however, has not been evaluated by the FDA.
Don’t Miss: How Does A Person Get Urinary Tract Infection
Can Sex Make A Uti Worse
If you already have a UTI, having sex can make the infection feel worse, exacerbating the symptoms. Using spermicides can increase discomfort because it can cause irritation. Using non-lubricated latex condoms can also increase friction leading to irritation. Using a water-based lubricant or lubricated condoms will help avoid making your UTI feel more irritated. After and before sex, be sure to urinate immediately to flush out the bacteria.
Also Check: Myasthenia Gravis And Urinary Incontinence