Prevention Of Urinary Tract Infection
There are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of getting a UTI:
- Drink plenty of water and other liquids to help flush out bacteria.
- Urinate frequently, or about every two to three hours.
- For women: Wipe from front to back after urinating or having a bowel movement.
- Urinate before and soon after having sexual intercourse.
- Avoid synthetic underwear, tight pants, and lingering in wet gym clothes or a bathing suit. Though none of this can cause a UTI, these habits can increase the spread of bacteria.
- Avoid vaginal deodorants, douches, powders, and other potentially irritating feminine products.
- Use a method of birth control other than a diaphragm, spermicide, or unlubricated condoms.
Physical Changes Spur Urinary Tract Infections During Menopause
Frequent sexual intercourse is one of the biggest UTI risk factors for younger women. For menopausal women, however, physical changes such as the thinning of vaginal tissue, difficulty fully emptying the bladder, incontinence, and pelvic organ prolapse are the main culprits.
In addition, during menopause, the body produces less estrogen, a hormone that among other functions helps keep the bacteria levels in the lining of the bladder and urethra healthy. Vaginal estrogen creams may restore the normal bacterial balance of the vagina, thus helping to stave off recurrent UTIs.
Things You Can Do Yourself
To help ease pain:
- takeparacetamolup to 4 times a day to reduce pain and a high temperature for people with a UTI, paracetamol is usually recommended over NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or aspirin
- you can give childrenliquid paracetamol
- rest and drink enough fluids so you pass pale urine regularly during the day, especially during hot weather
It’s important to follow the instructions on the packet so you know how much paracetamol you or your child can take, and how often.
It may also help to avoid having sex until you feel better.
You cannot pass a UTI on to your partner, but sex may be uncomfortable.
Taking cystitis sachets or cranberry products has not been shown to help ease symptoms of UTIs.
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of Urinary Tract Infection In Males
Diagnosis Of A Urinary Tract Infection
Diagnosis of a urinary tract infection usually begins with a consultation based on the symptoms and a physical examination. It is usual for a doctor to also ask about sexual history, medical history and any instances of previous UTIs.
A sample of urine might be requested in order to confirm a diagnosis of a urinary tract infection. Dipstick analysis may be done first to indicate the presence of bacteria in the urine. This quick test entails dipping a small chemical strip into a urine sample, then looking for certain color changes on the strip which may indicate abnormal levels of blood, sugar or bacteria in the urine. Looking at the urine sample under a microscope can usually confirm the diagnosis, as well as which bacteria has caused the infection.
If an upper urinary tract infection is suspected, a doctor may also recommend blood tests in order to check the infection hasnââ¬â¢t spread to the bloodstream.
People suffering from recurring or chronic urinary tract infections may be given additional tests to determine if there are any obstructions or abnormalities causing the repeat of the condition. Such tests can include:
- An ultrasound scan of the bladder and kidneys, which uses painless soundwaves to generate an image of the urinary tract
- A CT scan or MRI scan for a more detailed analysis of the urinary tract
- A cystoscopy, in which a small camera is inserted through the urethra to see inside the urethra and bladder
When Should I Call My Healthcare Provider

- Fever.
- Back pain.
- Vomiting.
If you have any of these symptoms, or your other symptoms continue after treatment, call your healthcare provider. A UTI can spread throughout your urinary tract and into other parts of your body. However, treatment is very effective and can quickly relieve your symptoms.
Also Check: Symptoms Of Pinworms In Urinary Tract
Syntomas Of Urinary Tract Infection In The Baby
Identifying the symptoms of urinary tract infection in the baby can be difficult as infants and children are unable to explain what they are feeling. However, in these cases the most common signs are:
- Choro when urinating
- Presence of blood in the diaper
- Irritability constant
Whenever these symptoms arise, it is important to consult with the pediatrician to assess the possibility of the child developing a urinary tract infection. Understand.
You Have No Symptoms At All
Sometimes a UTI may show very minor symptoms or no symptoms at all, Ross says. This is one reason why she advises women to still have regular checkups with their gynecologists even if they’re not in need of a Pap smear.
Regular pelvic exams can help diagnose urinary tract infections before they cause detectable issues, she says. Ideally, you should have one per year.
Don’t Miss: Is Urinary Incontinence A Normal Part Of Aging
Urinary Tract Infection Symptoms
Urinary tract infection symptoms can be frightening and a cause for concern. Some people who have a UTI don’t have any symptoms. Sometimes a doctor may diagnose a UTI based on the description of the patient’s symptoms and ruling out other potential causes. The following slides describe common UTI symptoms in women and men.
Risk Factors That Make You More Likely To Get A Uti
UTIs are much more common in women than men, and they’re especially rare in young and middle-aged men. This is partly due to the female anatomy women have shorter urethras, making it easier for bacteria to enter the bladder.
Having sex more frequently, and with new partners, can increase a person’s risk of developing a UTI. A womans urethra is located next to both the vagina and anus, enabling bacteria to easily travel into the urinary tract during sexual intercourse.
Other factors that can increase the risk of a UTI include:
- Pregnancy
- Wearing thong underwear
Recommended Reading: Sacral Nerve Stimulation For Urinary Incontinence
How To Prevent Urinary Tract Infection
To prevent urinary tract infection is advised:
- Wash the external genital region with water and soap after sexual intercourse
- After urinating and defecating always clean the intimate region from front to back, in order to avoid the arrival of the E. Coli bacteria in the vagina, as this one is present nthe anal and perianal region, being the main cause of urinary tract infection
- Sleak completely the bladder every time it urinates, to avoid the residual urine that increases the chances of urinary tract infection
- Drink more water, ingesting at least 1.5 L of clear liquids per day
- Maintain a fiber-rich feed to decrease the dwell time of the stools within the intestine, which decreases the amount of bacteria within it
- Dont use perfume or cream with perfume in the vagina region because this can irritate the skin and increase the risk of urinary tract infection
- Keeping the vulva region always dry, avoiding wearing very tight clothing and daily absorbent, in order to decrease perspiration in this location.
One should follow these advice on a daily basis, especially during pregnancy, when there is a greater risk of urinary tract infection due to hormonal changes and due to increased weight on the bladder, which favors the proliferation of bacteria.
Risk Factors For Developing Utis
Some people are at greater risk than others of developing UTIs. These include:
- women sexually active women are vulnerable, in part because the urethra is only four centimetres long and bacteria have only this short distance to travel from the outside to the inside of the bladder
- people with urinary catheters such as people who are critically ill, who cant empty their own bladder
- people with diabetes changes to the immune system make a person with diabetes more vulnerable to infection
- men with prostate problems such as an enlarged prostate gland that can cause the bladder to only partially empty
- babies especially those born with physical problems of the urinary system.
Also Check: Hollister Vented Urinary Leg Bag
Uti Tests And Diagnosis
If you suspect that you have a urinary tract infection, go to the doctor. You’ll give a urine sample to test for UTI-causing bacteria.
If you get frequent UTIs and your doctor suspects a problem in your urinary tract, they might take a closer look with an ultrasound, a CT scan, or an MRI scan. They might also use a long, flexible tube called a cystoscope to look inside your urethra and bladder.
Common Symptoms Of Urinary Tract Infections:
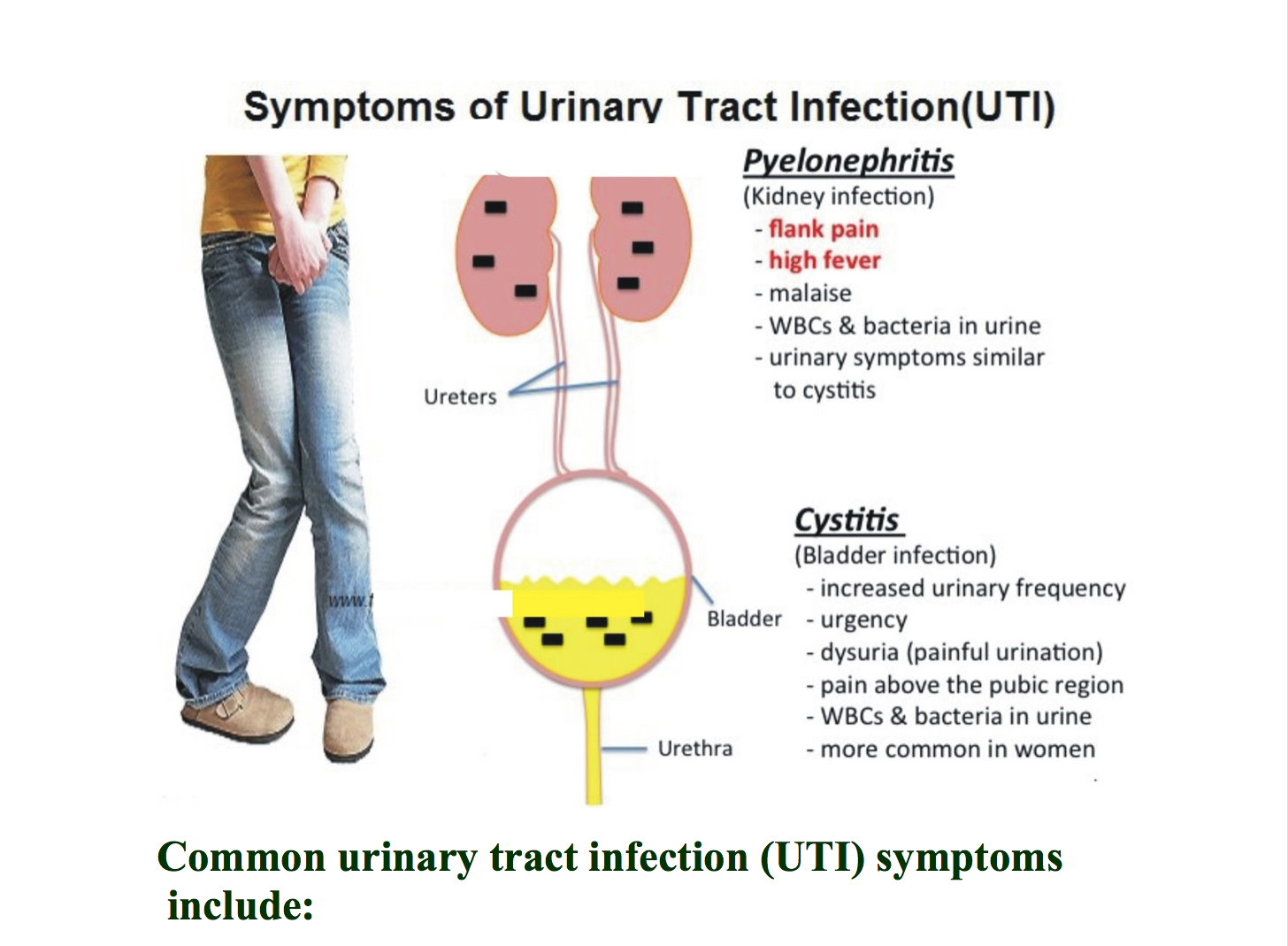
1.) Pain or Burning During Urination
Pain or burning during urination is often the first sign of a UTI. However, this may occur whenever there are bacteria in the urethra or bladder and doesn’t necessarily signify a UTI. If the symptoms only occur briefly and then disappear, it may mean that your body has successfully flushed out the bacteria and avoided infection.
2.) Needing to Urinate Urgently
Sudden and urgent need to urinate, especially if you just went to the bathroom, is another telltale sign of a UTI. This can be caused by bacteria irritating the urethra and the lining of the bladder.
3.) Inability to Fully Empty Bladder
Frequent urination is another sign to look out for. If you have a UTI, it can feel like your bladder is full, though only drops come out when you try to go. If your frequent trips to the bathroom are providing minimal relief, you may have a urinary tract infection.
4.) Urine has Abnormal Consistency or Smell
The color or substance of your urine can be worth monitoring as well. Any discoloration of your urine should be a cause for concern. Cloudy, red, or brown urine are all common signs of a UTI. Additionally, urine that has a strong, pungent smell is a common UTI symptom.
5.) Pressure or pain in the Pelvic Area
For certain women pain or cramping in the pelvis or bladder area may be the most pronounced symptom of a UTI.
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection Natural Cures Garlic
Treatment From A Gp For Utis That Keep Coming Back
If your UTI comes back after treatment, you may have a urine test and be prescribed different antibiotics.
Your doctor or nurse will also offer advice on how to prevent UTIs.
If you keep getting UTIs and regularly need treatment, a GP may give you a repeat prescription for antibiotics.
If you have been through the menopause, you may be offered a vaginal cream containing oestrogen.
Common Uti Symptoms And Signs
The urine of most healthy, properly hydrated people appears light yellow or clear and is nearly free of odor. It also causes zero pain or discomfort to pass.
But for the majority of people who experience a urinary tract infection, thats not the case. Instead, they will likely encounter at least one of the following indicators:
When the kidneys are infected, other noticeable symptoms may include:
- Fever, shaking, and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Upper back, side, or groin pain
While its been long noted that confusion in the elderly is a sign of UTI, a 2019 report in BMC Geriatrics concludes that theres insufficient evidence connecting the symptom to that diagnosis.
RELATED: Causes and Risk Factors of Urinary Tract Infections
Also Check: Purina One For Urinary Tract Health
What Other Conditions Cause Similar Symptoms
Although UTIs are very common, its important to know that other conditions can cause similar symptoms to a UTI.
Some of these more common conditions include:
-
Sexually transmitted infections: Gonorrhea , chlamydia , and mycoplasma are common causes of sexually transmitted infections. They can cause painful urination and are sometimes associated with discharge from the urethra. These infections require specific antibiotics in order to be treated.
-
Vaginitis:Vaginal infections can cause symptoms in the vagina and/or vulva, like burning, itching, or discharge. Although they dont involve the urinary tract, these symptoms can sometimes feel similar to the burning or discomfort associated with a UTI. Common causes of vaginitis include bacteria , yeast , and trichomonas. Skin conditions, like contact dermatitis or lichen planus, can also cause vaginitis. Because the treatment for all of these is different, its important to know what is causing your symptoms.
Some less common conditions that can have similar symptoms to a UTI include:
What Are The Causes Of Dysuria
There are many causes of dysuria. Also know that doctors cant always identify the cause.
WOMEN: Painful urination for women can be the result of:
- Bladder infection .
- Urinary tract infection.
- Endometritis and other causes outside the urinary tract, including diverticulosis and diverticulitis.
- Inflammation of the bladder or urethra . Inflammation is usually caused by an infection.
The inflammation may also be caused by sexual intercourse, douches, soaps, scented toilet paper, contraceptive sponges or spermicides.
Normal female anatomy
MEN: Painful urination for men may be the result of:
- Urinary tract infection and other infections outside the urinary tract, including diverticulosis and diverticulitis.
- Prostate disease.
- Cancer.
Normal male anatomy
Painful urination for men and women may be the result of a sexually transmitted infections or the side effect of medications. Chemotherapy cancer drugs or radiation treatments to the pelvic area may inflame the bladder and cause painful urination.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get A Urinary Tract Infection From Intercourse
Your Pee Looks Like Pink Lemonade Or Tea
Discolored, cloudy urine often accompanies the strong smell of a UTI, Ross says. Normal pee should look clear or light yellow, similar to lemonade. Pee that looks pink or brown might mean there’s bacteria or even a little blood mixed in with your urine. After all, many infections in your urinary tract can cause irritation and bleeding.
3. Your Pee Is Cloudy
You might also notice that your urine looks cloudy, says Sarah Yamaguchi, an LA-based gynecologist at DTLA Gynecology. Overall, experts point out that urine that *just doesnt look right* definitely warrants a trip to the doctor. A urine test will be able to alert your doc to any infections.
How Are Urinary Tract Infections Treated
You will need to treat a urinary tract infection. Antibiotics are medicines that kill bacteria and fight an infection. Antibiotics are typically used to treat urinary tract infections. Your healthcare provider will pick a drug that best treats the particular bacteria thats causing your infection. Some commonly used antibiotics can include:
- Nitrofurantoin.
- Doxycycline.
- Quinolones .
Its very important that you follow your healthcare providers directions for taking the medicine. Dont stop taking the antibiotic because your symptoms go away and you start feeling better. If the infection is not treated completely with the full course of antibiotics, it can return.
If you have a history of frequent urinary tract infections, you may be given a prescription for antibiotics that you would take at the first onset of symptoms. Other patients may be given antibiotics to take every day, every other day, or after sexual intercourse to prevent the infection. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best treatment option for you if you have a history of frequent UTIs.
Recommended Reading: Can Cranberry Juice Cure A Urinary Tract Infection
Treatment For Urinary Tract Infection
The treatment is done with antibiotic use indicated by the doctor, being the most indicated form of treatment. The 7-10-day hard treatment, being important to take the medicine up to date informed by the doctor, even if the symptoms disappear before then. It is also important to drink more water, because the more urine the body produces, the more easily it is eliminated bacteria by the urine. Know the names of.
Check out more tips in our following video:
Medical Treatment Of Urinary Tract Infections
Because urinary tract infections are most often bacterial, they can be treated with antibiotics. As a guideline, antibiotic treatment for UTIs is usually split into two categories:
- Uncomplicated UTI, which is an infection that occurs in an otherwise healthy person with normal kidney function
- Complicated UTI, which usually occurs in people who have a medical or anatomical predisposition to urinary tract infections or treatment failure
The type of antibiotic used and the length of treatment differs, depending on the severity of the infection and medical history of the person with the condition. Symptoms from uncomplicated UTIs usually clear within three days of antibiotic treatment, whereas people with a complicated UTI may require antibiotics for up to two weeks.
Whatever the cause, it is important to complete the entire course of antibiotics prescribed in full, even if symptoms appear to have cleared. This can help to prevent antibiotic resistance developing.
In the rare cases where a urinary tract infection is caused by a virus or fungi, this can be treated with antiviral or antifungal medication respectively.
You May Like: Artificial Urinary Sphincter Surgery Recovery
What Are The Symptoms Of A Uti
One of the most common symptoms of a UTI is a frequent and urgent need to pee. You might feel like you need to pee all the time, even if you just went. Other UTI symptoms include:
-
pain or burning when you pee
-
bad-smelling or cloudy urine
-
blood or pus in your urine
-
soreness, pressure, or cramps in your lower belly, back, or sides
If the infection goes to your kidneys, your UTI symptoms may also include:
-
pain in your mid-back
-
fever
Confusion Or Changes In Mental State
The symptoms of UTIs in older adults are often uncommon and complex. For example, seniors may have bacteria in their urine, which indicates a UTI, but not have any of the typical symptoms.
When seniors have a UTI, they often develop confusion, disorientation, and dizziness. These uncommon symptoms most likely arise due to the infections impact on their immune system.
An untreated UTI will only worsen, leading to more severe symptoms, and giving the infection time to spread to your kidneys. If youre not sure your symptoms are due to a UTI, its best to schedule an appointment so we can determine the cause of your symptoms and begin treatment if needed.
You Might Also Enjoy…
Also Check: Best Probiotic For Women’s Urinary Tract Health