What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Utis
UTIs can cause such signs as:
- pain, burning, or a stinging sensation when peeing
- an increased urge or more frequent need to pee
- fever
- waking up at night a lot to go to the bathroom
- belly pain in the area of the bladder
- foul-smelling pee that may look cloudy or contain blood
If you have any symptoms of a UTI, youll need to go to a doctor right away. The sooner you begin treatment, the less uncomfortable youll be. Call your doctors office or clinic. If you cant reach your doctor, you can visit an urgent care center or hospital emergency room. The most important thing is to take action as soon as possible.
Can I Prevent A Urinary Tract Infection
You can usually prevent a urinary tract infection with lifestyle changes. These tips can include:
In some post-menopausal women, a healthcare provider may suggest an estrogen-containing vaginal cream. This may reduce the risk of developing a UTI by changing the pH of the vagina. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have recurrent UTIs and have already gone through menopause.
Over-the-counter supplements are also available for UTIs. These are sometimes recommended for people who have frequent UTIs as another way to prevent them. Talk to your healthcare provider before starting any supplements and ask if these could be a good choice for you.
How Common Are Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are very common, occurring in 1 out of 5 women sometime in their lifetime. Though UTIs are common in women, they can also happen to men, older adults and children. One to 2% of children develop urinary tract infections. Each year, 8 million to 10 million visits to doctors are for urinary tract infections.
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection Pills Cvs
What Symptoms Are Associated With A Uti
Urinary tract infections dont always have symptoms, and the symptoms can depend on where the infection is.
Some common symptoms associated with a lower tract UTI include:
-
Pain or burning during urination
-
Frequent and urgent urination
When the upper tract is involved, symptoms can include:
-
Pain in your back or side
-
Fevers and chills
What Are The Types Of Urinary Tract Infections
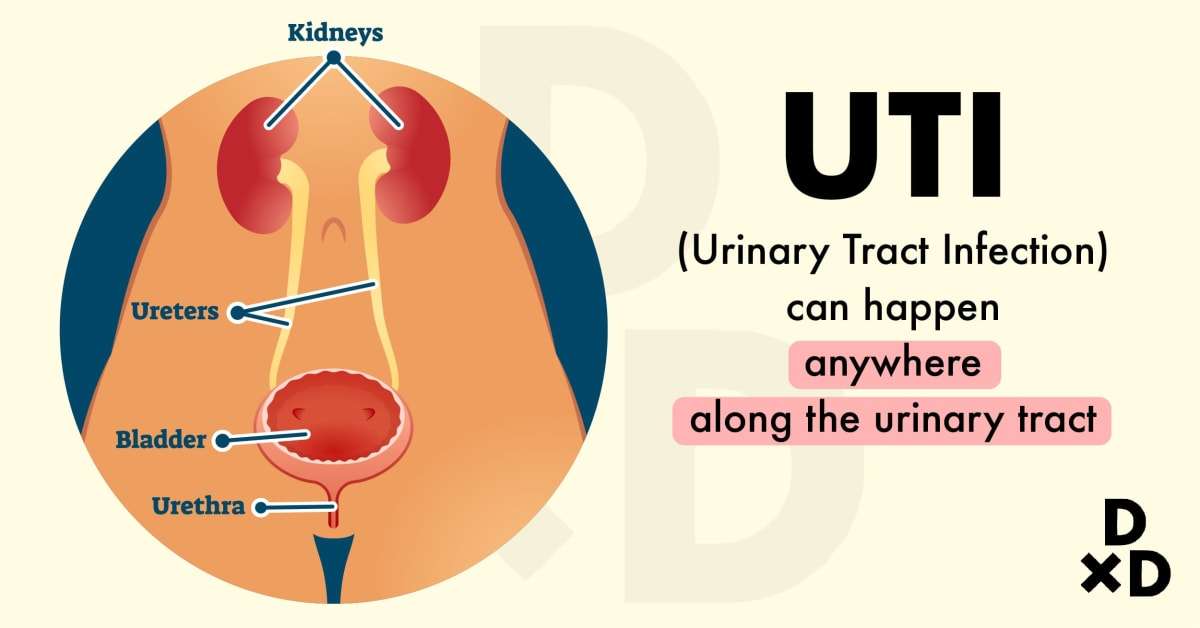
Urinary tract infections are common in females, and cystitis represents the majority of these infections. Related terms include pyelonephritis, which refers to upper urinary tract infection bacteriuria, which describes bacteria in the urine and candiduria, which describes yeast in the urine. Very ill patients may be referred to as having urosepsis.
Read Also: How To Treat E Coli Urinary Tract Infection
What Microorganisms Are Involved
The microorganisms that cause these infections usually come from the intestinal tract. Specifically, most are bacteria the most common one isEscherichia Coli, regardless of the persons condition.
Other microorganisms are Klebsiella and Proteus bacteria. But, if the person has more complicated infections or has a catheter, doctors should consider the possibility of multi-resistant microorganisms. They can also be due to multiple bacteria.
What Are The 4 Types Of Infections
Infection occurs when germs enter your body and multiply, resulting in disease. There are four main types of infections:
In response to an infection, the immune system goes into overdrive, activating white blood cells and antibodies to fight the foreign invader. This can cause symptoms such as fever, headache, and rash.
1. Viral infection
Viruses can cause a wide range of infectious diseases. Viruses cause illness by killing cells or interfering with cell function.
The virus infiltrates a host’s body and attaches itself to a cell, where it releases its genetic material. The virus multiplies as the cell replicates. When a cell dies, more viruses are released, infecting new cells. Some viruses alter the function of cells rather than killing them.
Bodies frequently respond by inducing fever , secreting a chemical called interferon or mobilizing the immune system’s antibodies and other cells to target the invader.
Most viral diseases are self-limiting, and the immune system may be able to fight them off. In rare cases, doctors may prescribe antiviral medications. Vaccinations can also help fight viral diseases.
2. Bacterial infection
Bacteria cause a wide range of infectious diseases, including strep throat and urinary tract infections, meningitis, and tuberculosis. Bacteria are also to blame for many skin rashes.
Antibiotics are the first-line defense against bacterial infections.
3. Fungal infection
Recommended Reading: What Remedies For Urinary Tract Infection
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection in any part of your urinary system, which includes your kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra.
If you’re a woman, your chance of getting a urinary tract infection is high. Some experts rank your lifetime risk of getting one as high as 1 in 2, with many women having repeat infections, sometimes for years. About 1 in 10 men will get a UTI in their lifetime.
Here’s how to handle UTIs and how to make it less likely you’ll get one in the first place.
Medication For Urinary Tract Infection In Dogs
The aforementioned medications are used to treat a bacterial urinary infection in dogs. Non-bacterial infections are treated with other medications, such as fungicides and anti-parasitics. When there are blockages caused by stones or prostatitis, these problems should be treated at the same time as the infection. In addition, the veterinarian will recommend a diet that allows the normal pH of the urine to be restored, as it becomes alkaline during infection.
The prognosis depends on the complication of the infection, as well as the causative agents. Simple infections caused by bacteria usually have an excellent prognosis. In contrast, yeast infections are more difficult to treat. The most complicated urinary infections have a variable prognosis, depending on each case. Treatment is the same for male or female dogs, i.e. dependent on the udnerlying cause.
Read Also: Urinary Tract Infection Does It Go Away On Its Own
How Do You Diagnose And Treat A Uti
To diagnose a UTI, your doctor may ask for a sample of your urine. Theyll use this for a urine culture to determine the levels of germs and bacteria in your urine. In rare cases, your doctor may also do an X-ray or ultrasound to get a more comprehensive look at your urinary tract.
If a UTI is confirmed, depending on the location and severity of the infection, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics.
For an uncomplicated lower tract infection, your doctor will likely prescribe a course of antibiotics to be taken over five to seven days.
If you have an upper tract infection, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics for three weeks or longer.
In the rare case of a severe infection, your doctor may recommend hospital treatment and a course of intravenous antibiotics.
You May Like: Z Pack Urinary Tract Infection
Home Remedies For Urinary Tract Infection Symptoms
In addition to antibiotics, many people seek natural, at-home remedies to help UTIs. A heating pad can relieve pressure and pain, and wearing loose cotton clothing is recommended. For those with recurrent UTIs, modifying certain habits may help: Choose fragrance-free personal care products to reduce the risk of irritation, and cut back on foods that can irritate the bladder caffeine, alcohol, spicy food, raw onions, citrus fruits, carbonated drinks, and artificial sweeteners.
You May Like: What Can Be Done For Urinary Incontinence
Who Is At Risk For A Bladder Infection
Anyone can get bladder infections, but women are more prone to getting them than men. This is because women have shorter urethras, making the path to the bladder easier for bacteria to reach.
Females urethras are also located closer to the rectum than mens urethras. This means there is a shorter distance for bacteria to travel.
As men age, the prostate can enlarge. This can cause blockages to the flow of urine and increase the likelihood of a man developing a UTI. UTIs tend to increase in men as they age.
Other factors can increase the risk of bladder infections for both men and women. These include:
- advanced age
- nitrites
- bacteria
Your doctor may also perform a urine culture, which is a test to determine the type of bacteria in the urine causing the infection. Once the type of bacteria is known, it will be tested for antibiotic sensitivity to determine which antibiotic will best treat the infection.
You can connect with a primary care doctor or an urologist in your area using the Healthline FindCare tool.
Bladder infections are treated with prescription medications to kill the bacteria, usually antibiotics, and medications that relieve pain and burning.
What Is The Treatment For Urinary Tract Infections
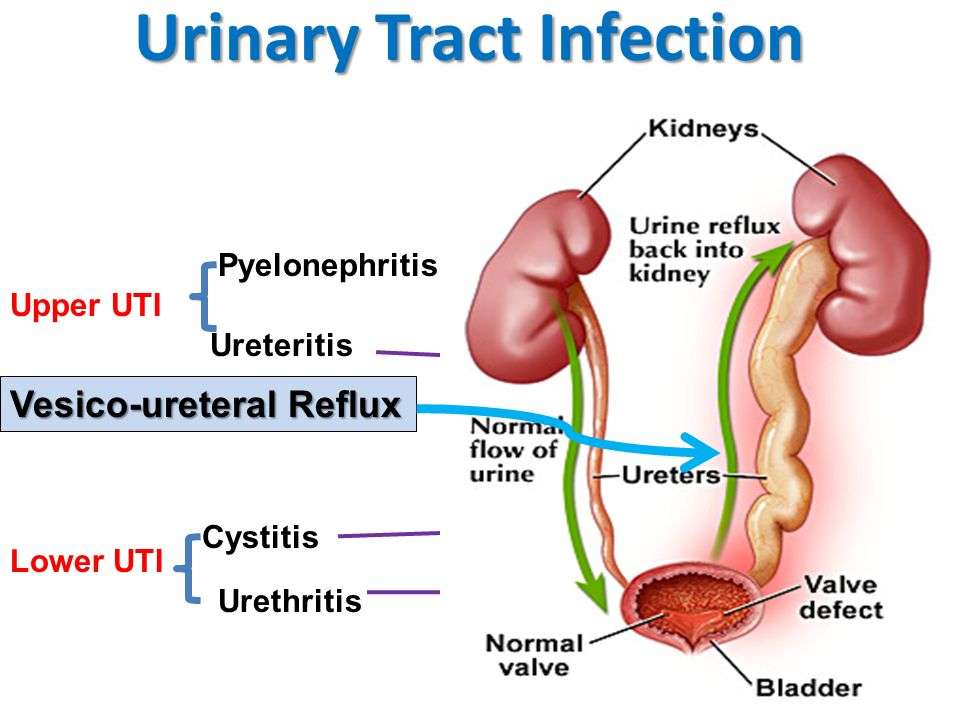
Specific treatment for UTIs will be determined by your physician based on:
- Your age, overall health, and medical history
- Extent of the infection
- Your tolerance for specific medications, procedures, or therapies
- Expectations for the course of the disease
- Your opinion or preference
Most commonly UTI’s are treated with antibiotics. The type of antibiotic and length of treatment is determined by the specific bacteria and type of infection. Many women can be treated with a short course of antibiotics. Sometimes bladder analgesics such as phenazopyridine can be given to relieve the symptoms of the UTI. While these will not kill the bacteria they can significantly reduce symptoms. Drinking plenty of water to help cleanse the urinary tract of bacteria can be helpful. In cases of asymptomatic bacteriuria, often no treatment necessary or recommended.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection In Boy Toddler Symptoms
Bacteriuria High Bacteria In The Urine But No Symptoms
In elderly women, bacteriuria, or high levels of bacteria in the urine, is often present but with no symptoms. More than 50% of women over the age of 80 may have bacteriuria and therefore may test positive for a UTI in a urine culture. However, this is often asymptomatic, and if the individual is not experiencing symptoms, expert physicians recommend not treating with antibiotics. In this instance, bacterial populations are living in the bladder at all times, and while this is not an infection, it does leave the individual vulnerable to infection because changes in the makeup of this urinary microbiome could lead to a rise in pathogenic or bad bacteria and to an infection. Bacteriuria in the elderly should be monitored because if an infection does develop and is untreated it may lead to a kidney infection and sepsis, which can lead to death. UTI symptoms in the elderly can be difficult to decipher as they are different from those experienced by younger women and include additional symptoms like imbalance, forgetfulness, and dementia-like symptoms. You can read more on UTIs in the elderly half-way down the page here.
Duration Of Urinary Tract Infections
Once treatment has started, symptoms of simple bladder infections usually go away within one to two days, though you’ll need to continue taking any course of antibiotics as prescribed. If the infection is complicated and has spread to the kidney, it may take a week or longer before symptoms disappear.
Recommended Reading: What Tests Are Done For Urinary Incontinence
What To Expect At Home
UTIs can lead to infection. Most often the infection occurs in the bladder itself. At times, the infection can spread to the kidneys.
Common symptoms include:
- Pain or burning when you urinate
- Needing to urinate more often
- Hard to empty your bladder all the way
- Strong need to empty your bladder
These symptoms should improve soon after you begin taking antibiotics.
If you are feeling ill, have a low-grade fever, or some pain in your lower back, these symptoms will take 1 to 2 days to improve, and up to 1 week to go away completely.
Urinary Tract Infections In The Elderly
Because the elderly often do not experience or report obvious symptoms that younger people have, urinary tract infections can be easily overlooked. Confusion, feelings of general discomfort, disorientation, fatigue, weakness, behavior changes, falling, or a new, acute incontinence are reported as common complaints. Because these symptoms are so general, this often results in a delaying treatment, inviting the complication of sepsis to occur.
UTIs can cause a change in behavior in older people and people with dementia. Masquerading as confusion, agitation, or withdrawal, UTI may actually be the cause of behavioral shifts. The person may not be able to communicate how they feel, therefore it is very important to be familiar with the symptoms of UTI and seek medical help to enable appropriate treatment.
It is also important to be aware that any infection could speed up the progression of dementia and so all infections should be quickly identified and treated.
You May Like: How To Manage Urinary Incontinence
Research And Statistics: Who Gets Urinary Tract Infections
In the United States, UTIs result in about 10 million doctor’s office visits annually. People of any age can get a UTI, though most commonly it affects women. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 40 to 60 percent of women develop a UTI during their lives.
Twelve percent of men will have symptoms of at least one UTI during their lives, per the American Urological Association. While UTIs are uncommon in young men, the risk of infection increases with age, especially in men over 50.
Women are at greater risk of urinary tract infections for anatomical reasons: Women have a shorter urethra than men and their urethra is closer to the anus, which means the bacteria that live there dont have to travel far to infect the bladder.
In children, UTIs are common and also occur more frequently in girls than boys. About 3 percent of girls and 1 percent of boys will have a UTI by the time they’re 11 years old.
How Do Cats Get Urinary Tract Infections
Cats get urinary tract infections when bacteria winds up in their bladder, and a common source of bacteria is an unclean litter box.
Cats normally get UTIs from a dirty litter box, Dr. Bonk said. Bacteria on feces can travel up the urethra when a cat squats to urinate.
While both male and female cats can get UTIs, females are more prone to infection.
UTIs are more common in females than males due to the size of the urethra, Dr. Bonk said.
Certain chronic illnesses can make your cat more susceptible, too.
Cats with diabetes and those prone to urinary crystals and stones are more likely to develop UTIs, Dr. Bonk said.
Don’t Miss: How Does Cranberry Juice Help Urinary Tract Infections
Related Conditions And Causes Of Uti
There are a number of health conditions that share some symptoms with urinary tract infections, including:
The following conditions may make you more susceptible to developing a UTI and increase the severity of symptoms:
Type 2 diabetes
And having a UTI can increase a man’s risk for benign prostatic hyperplasia .
A Pharmacist Can Help With Utis
You can ask a pharmacist about treatments for a UTI. A pharmacist can:
- offer advice on things that can help you get better
- suggest the best painkiller to take
- tell you if you need to see a GP about your symptoms
Some pharmacies offer a UTI management service and can prescribe antibiotics if they’re needed.
Read Also: Symptoms Of Pinworms In Urinary Tract
Are There Home Remedies For A Urinary Tract Infection
There are a variety of self-care measures and other treatments available for urinary tract infections.
- Use a hot-water bottle to ease the pain.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Avoid coffee, alcohol, and spicy foods, all of which irritate the bladder.
- There are some indications that cranberry juice can help fight a urinary tract infection.
Because the symptoms of a urinary tract infection mimic those of other conditions, someone should see a health care professional if a urinary tract infection is suspected. A urine test is needed to confirm an infection. Self-care is not recommended.
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection In Cats
A urinary tract infection in cats is a type of bladder infection.
A urinary tract infection in cats is when bacteria get into the normally sterile urinary bladder, Dr. Bonk told The Dodo.
UTIs in cats can quickly become dangerous if they arent taken care of right away.
If left untreated, urinary tract infections can move into the kidneys, where they can cause serious complications, Dr. Bonk said. UTIs may also lead to the formation of bladder stones, which can block the urethra and lead to rupture of the urinary bladder.
You May Like: How Dangerous Is A Urinary Tract Infection
What About Antibiotic Resistance
Resistance rates for antibiotics are always variable based on local patterns in the community and specific risk factors for patients, such as recent antibiotic use, hospital stay or travel. If you have taken an antibiotic in the last 3 months or traveled internationally, be sure to tell your doctor.
High rates of antibiotic resistance are being seen with both ampicillin and amoxicillin for cystitis , although amoxicillin/clavulanate may still be an option. Other oral treatments with reported increasing rates of resistance include sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim and the fluoroquinolones. Resistance rates for the oral cephalosporins and amoxicillin/clavulanate are still usually less than 10 percent.
Always finish taking your entire course of antibiotic unless your doctor tells you to stop. Keep taking your antibiotic even if you feel better and you think you don’t need your antibiotic anymore.
If you stop your treatment early, your infection may return quickly and you can develop resistance to the antibiotic you were using previously. Your antibiotic may not work as well the next time you use it.
Southern Cross Medical Library
The purpose of the Southern Cross Medical Library is to provide information of a general nature to help you better understand certain medical conditions. Always seek specific medical advice for treatment appropriate to you. This information is not intended to relate specifically to insurance or healthcare services provided by Southern Cross. For more articles go to the Medical Library index page.
Donât Miss: How To Get Rid Of Recurring Yeast Infections
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Urinary Incontinence