Treatment For Kidney Infections
People with uncomplicated kidney infections may be treated at home with oral antibiotics. Ciprofloxacin or another fluoroquinolone is typically given but other antibiotics, such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole , may be used. People with moderate-to-severe acute kidney infection and those with severe symptoms or other complications may need to be hospitalized. In such cases, antibiotics are usually given intravenously for several days. Chronic pyelonephritis may require long-term antibiotic treatment.
Can You Treat A Uti Without Antibiotics
Antibiotics are an effective treatment for UTIs. However, the body can often resolve minor, uncomplicated UTIs on its own without the help of antibiotics.
Complicated UTIs will require medical treatment. These UTIs involve one or more of the following factors:
- changes in the urinary tract or organs, such as a swollen prostate or reduced flow of urine
More severe risks of using antibiotics include:
You May Like: Side Effects Of Bv Antibiotics
Treating E Coli Infections That Cause Neonatal Meningitis
While its true that E. coli causes about 20 percent of all neonatal meningitis cases, bacterial meningitis is still considered very rare in developed countries thanks to the success of vaccines.
If neonatal meningitis is suspected, a healthcare professional will draw blood and perform a spinal tap in order to test spinal fluid for the E. coli bacteria. If bacterial meningitis is confirmed, treatment would consist of IV antibiotics and fluids.
With early diagnosis and proper treatment, a child with bacterial meningitis has a reasonable chance of a good recovery.
Additional reporting by Joseph Bennington-Castro.
Also Check: Blood In Urine After Antibiotics
Recommended Reading: How To Clear Up A Urinary Tract Infection
Question : What Is The Role Of Combination Antibiotic Therapy For The Treatment Of Infections Caused By Cre
Recommendation: Combination antibiotic therapy is not routinely recommended for the treatment of infections caused by CRE.
Rationale: Although empiric combination antibiotic therapy to broaden the likelihood of at least one active therapeutic agent for patients at risk for CRE infections is reasonable, data do not indicate that continued combination therapy once the -lactam agent has demonstrated in vitro activity offers any additional benefit . Rather, the continued use of a second agent increases the likelihood of antibiotic-associated adverse events .
Observational data and clinical trials comparing ceftazidime-avibactam, meropenem-vaborbactam, and imipenem-cilastatin-relebactam to combination regimens to treat CRE infections have not shown the latter to have added value . Randomized trial data are not available comparing these agents as monotherapy and as a component of combination therapy . However, based on available outcomes data, clinical experience, and known toxicities associated with aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones, and polymyxins, the expert panel does not recommend combination therapy for CRE infections, when susceptibility to a preferred -lactam agent has been demonstrated.
Can I Become Immune To The Antibiotics Used To Treat A Uti
Your body can actually get used to the antibiotics typically used to treat a urinary tract infection . This happens in people who have very frequent infections. With each UTI and use of antibiotics to treat it, the infection adapts and becomes harder to fight. This is called an antibiotic-resistant infection. Because of this, your healthcare provider may suggest alternative treatments if you have frequent UTIs. These could include:
- Waiting: Your provider may suggest that you watch your symptoms and wait. During this time, you may be encouraged to drink plenty of fluids in an effort to flush out your system.
- Intravenous treatment: In some very complicated cases, where the UTI is resistant to antibiotics or the infection has moved to your kidneys, you may need to be treated in the hospital. The medicine will be given to you directly in your vein . Once youre home, you will be prescribed antibiotics for a period of time to fully get rid of the infection.
You May Like: Royal Canin Urinary Tract Food
You May Like: Can Toilet Paper Cause Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms Of Severe Infection In The Kidney
Symptoms of kidney infections tend to affect the whole body and be more severe than those of cystitis . They may include:
- Symptoms of lower UTIs that persist longer than a week. Sometimes lower UTI symptoms may be the only signs of kidney infection. People at highest risk for such “silent” upper urinary tract infections include people with diabetes, impaired immune systems, or a history of relapsing or recurring UTIs.
- An increased need to urinate at night.
- Chills and persistent fever .
- Pain in the flank .
- Vomiting and nausea.
How Is A Uti Diagnosed In A Child
The healthcare provider will ask about your childs symptoms and health history. The provider will give your child a physical exam. Your child may also have tests, such as:
- Urine testing. This is also known as urinalysis. Your childs urine is sent to a lab to check for red blood cells, white blood cells, bacteria, protein, and signs of infection. The urine will also be sent for a culture and sensitivity. This is done to figure out what type of bacteria is causing the infection and what medicine is best to treat the infection.
- Kidney ultrasound. This is a painless imaging test. It uses sound waves and a computer to make images of blood vessels, tissues, and organs. It can show internal organs as they function and can assess blood flow through vessels. A boy with a UTI or a girl younger than age 5 or 6 may need this test.
- Voiding cystourethrogram . This is a type of X-ray of the urinary tract. A thin, flexible tube is put in the tube that drains urine from the bladder to the outside of the body . The bladder is filled with a liquid dye. X-ray images are taken as the bladder fills and empties. The images will show if there is any reverse flow of urine into the ureters and kidneys.
Recommended Reading: Urinary Infection Treatment Home Remedies
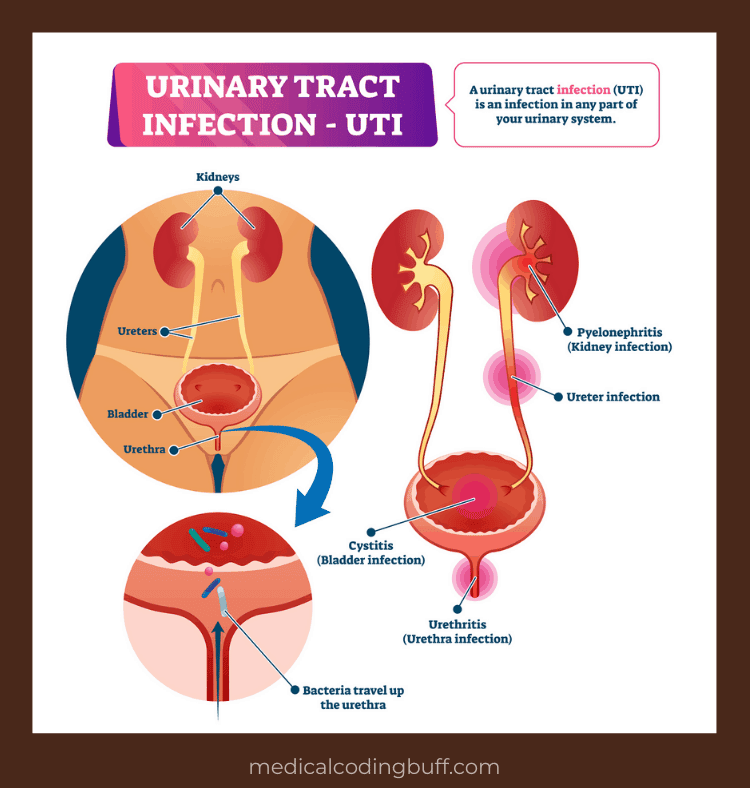
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection is an infection of the urinary system. This type of infection can involve your urethra , kidneys or bladder, .
Your urine typically doesnt contain bacteria . Urine is a byproduct of our filtration systemthe kidneys. When waste products and excess water is removed from your blood by the kidneys, urine is created. Normally, urine moves through your urinary system without any contamination. However, bacteria can get into the urinary system from outside of the body, causing problems like infection and inflammation. This is a urinary tract infection .
Are There Distinct Upec Pathotypes
Individual genes or even clusters of genes encoding a single complete virulence factor are not by themselves sufficient to allow bacteria to cause disease. Rather, complementary sets of virulence factors work together to direct bacteria through a particular interaction with the host that can result in disease. Strains of a given bacterial species that have a particular set of virulence factors in common that direct them through a particular pathogenesis process are called a pathotype. As mentioned earlier, E. coli causing enteric/diarrhoeal disease can be grouped into at least six different pathotypes. What is the evidence that E. coli causing UTIs may also be made up of distinct pathotypes?
After removing pathotype 1 strains from the analysis, cnf1 and hly are still strongly associated with each other , and with sfa as well . Further, hly also appears to be associated with papGAD/IA2, an association that does not exist when all isolates are compared . Therefore, we defined all strains that were cnf1+hly+sfa+, after the removal of pathotype 1 strains, as pathotype 2 strains. The strains containing cnf1 are almost always grouped as either pathotype 1 or pathotype 2. When the pairwise association analysis was performed on the remaining strains after removal of both pathotype 1 and 2 strains, hly was positively associated with papGAD/IA2 at a level that reaches statistical significance in each of the collections .
Don’t Miss: Can A Urinary Tract Infection Go Away Without Antibiotics
Assessment Of Disease Status
We followed the TCVS participants from 2005 to 2014 by linking the baseline data to the National Health Insurance Research Database and the death records at the National Health and Welfare Data Science Center , Ministry of Health and Welfare.
In Taiwan, the National Health Insurance Program is a governmental universal health insurance program covering nearly 100% of the population. Individuals medical claim data including diagnosis from both inpatient and outpatient are available. In order to protect the privacy of individuals as required by local law, personal identification number is masked and all analyses must be performed within the HWDC. Only summarized research results , could be released.
What Is Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
Some people, especially children age five and under, who become infected with a STEC infection develop a condition called hemolytic uremic syndrome . In this condition, toxins in your intestines from STEC cause diarrhea, travel into your bloodstream, destroy red blood cells and damage your kidneys. This potentially life-threatening illness develops in about 5% to 10% of people who are infected with STEC.
Early symptoms of HUS include:
- Sleepiness, confusion, seizures.
- Kidney failure.
If you develop severe diarrhea or if you have bloody diarrhea, go to the hospital for emergency care. HUS, if it develops, occurs an average of 7 days after your first symptoms occur. It is treated with IV fluids, blood transfusions and dialysis .
Also Check: Function Of Kidney In Urinary System
How Many Strains Of E Coli Cause Diarrhea
Six different strains of E. coli are known to cause diarrhea. These strains are:
- Shiga toxin-producing E. coli : This is the bacteria most commonly known for E. coli food contamination. This strain is also called enterohemorrhagic E. coli and verocytotoxin-producing E. coli .
- Enterotoxigenic E. coli : This strain is commonly known as a cause of travelers diarrhea.
- Enteroaggregative E. coli .
- Diffusely adherent E. coli .
Treating An Uncomplicated Uti Caused By E Coli
Treatment options vary widely for UTIs, however the conventional treatment is antibiotics, in particular fluoroquinolone. Antibiotic resistance is an issue, with multi-drug resistant Enterobacteriaceae, mostly E. coli, being a matter of concern.
E. coli strains are resistant to penicillins and cephalosporins, as well as fluoroquinolones and gentamicin. Non-antibiotic treatments that can be applied at home include herbal medicines, reflexology, and others, but ongoing or severe infection, especially involving the kidneys, requires prompt medical attention.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Best Medicine For Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms Of Urinary Tract Infections
A UTI can cause the following symptoms:
What Should I Eat If I Have E Coli
Drink clear fluids for several days. Make sure that some of these fluids are packed with electrolytes, such as broth or soup. Two or three days after the onset of symptoms, diarrhea may ease off. Re-introduce solid foods back into the diet gradually. Bland foods such as rice, toast, and eggs are best. Avoid high-fiber foods, dairy, spicy foods, and fatty foods.
Also Check: How To Stop Urinary Tract Infection Pain
Ok Got It But Then What Is A Kidney Infection
A kidney infection is, in essence, a UTI that has spread into the kidneys. While this type of infection is rare, its also very dangerous and if youre experiencing any of the following signs of a kidney infection, you should see a doctor immediately:
-
Upper back or side pain
-
Fever, shaking or chills
-
Feeling nauseous
While most kidney infections can be treated simply with an antibiotic, if left untreated, a kidney infection can cause damage to your kidneys, leading to chronic kidney disease. The bacteria could even spread to your bloodstream creating a life-threatening situation.
When Can I Return To Work Or School If Ive Been Infected With E Coli
Check with your healthcare provider. If your infection was part of a local outbreak, your local state health department may have specific instructions about when its safe to be around groups of people.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
The best and easiest way to avoid getting an E. coli infection is to frequently wash your hands with soap and water. Wash your hands before and after handling foods , after using the bathroom, after touching animals , after changing diapers and after shaking hands or being touched by others . Washing your hands can not only prevent contracting E. coli, but also many other infectious disease that are spread from person to person. Make frequent hand washing a new habit.
Keep in mind that most strains of E. coli are harmless. Even if you do come down with the STEC O157 strain, your symptoms will resolve on their own within five to seven days. Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated and get plenty of rest.
Do call your healthcare provider if you have diarrhea for more than three days, have trouble keeping fluids down and have continuous bouts of vomiting and have a fever. These symptoms could mean you are developing serious complications that could lead to kidney failure.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 09/21/2020.
References
Also Check: Urinary Incontinence Without Sensory Awareness
Urinary Tract Infections In Women
UTIs are common, particularly with increasing age. Women are more likely to get a UTI than men. Nearly 1 in 3 women will have a UTI needing treatment before the age of 24.
In women, the urethra is short and straight, making it easier for germs to travel into the bladder. For some women, UTIs relate to changes in their hormonal levels. Some are more likely to get an infection during certain times in their menstrual cycle, such as just before a period or during pregnancy.
In older women, the tissues of the urethra and bladder become thinner and drier with age as well as after menopause or a hysterectomy. This can be linked to increased UTIs.
During pregnancy, the drainage system from the kidney to the bladder widens so urine does not drain as quickly. This makes it easier to get a UTI. Sometimes germs can move from the bladder to the kidney causing a kidney infection. UTIs during pregnancy can result in increased blood pressure, so it is very important to have them treated as soon as possible.
Women are more at risk of repeated UTIs if they:
- use spermicide jelly or diaphragm for contraception
- have had a new sexual partner in the last year
- had their first UTI at or before 15 years of age
- have a family history of repeated UTIs, particularly their mother
- suffer from constipation
E Coli Uti Pathogenesis
UTI pathogenesis is a complex process that is influenced by various host biological and behavioral factors, and by properties of the infecting pathogen, including VFs. This presents a challenge in epidemiological studies regarding the role of specific VFs in UTI pathogenesis because of the confounding effect of host factors.
In most noncompromised individuals, the urinary tract is normally sterile, and the entry of exogenous microorganisms is prevented by urine flow, secreted and tissue-associated antibacterial factors, and the bactericidal activities of effector immune cells. In most cases, the host fecal flora is the source of the infecting E. coli strain, and spreads via the perineal, vaginal, and periurethral areas to the lower urinary tract where they may establish colonization . Two hypotheses have been proposed to explain the movement of the organism from the fecal flora to the urinary tract. The prevalence hypothesis holds that the numerically most prevalent E. coli clones in the feces will be involved, whilst the pathogenicity theory holds that E. coli strains with enhanced virulence potential will be selected . These two mechanisms may not be mutually exclusive, but instead may jointly contribute to UTI pathogenesis .
Don’t Miss: Foods That Cause Urinary Incontinence
Specific Risk Factors In Men
Men become more susceptible to UTIs after the age of 50, when they begin to develop prostate problems. Benign prostatic hyperplasia , enlargement of the prostate gland, can produce obstruction in the urinary tract and increase the risk for infection. In men, recurrent UTIs are also associated with prostatitis, an infection of the prostate gland. Although UTIs are less common in men, they can cause more serious problems in men than in women. Men with UTIs are more likely to require hospitalization than women.
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Urinary Tract Infections In Children
BRETT WHITE, MD, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, Oregon
Am Fam Physician. 2011 Feb 15 83:409-415.
Acute urinary tract infections are relatively common in children, with 8 percent of girls and 2 percent of boys having at least one episode by seven years of age. The most common pathogen is Escherichia coli, accounting for approximately 85 percent of urinary tract infections in children. Renal parenchymal defects are present in 3 to 15 percent of children within one to two years of their first diagnosed urinary tract infection. Clinical signs and symptoms of a urinary tract infection depend on the age of the child, but all febrile children two to 24 months of age with no obvious cause of infection should be evaluated for urinary tract infection . Evaluation of older children may depend on the clinical presentation and symptoms that point toward a urinary source . Increased rates of E. coli resistance have made amoxicillin a less acceptable choice for treatment, and studies have found higher cure rates with trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole. Other treatment options include amoxicillin/clavulanate and cephalosporins. Prophylactic antibiotics do not reduce the risk of subsequent urinary tract infections, even in children with mild to moderate vesicoureteral reflux. Constipation should be avoided to help prevent urinary tract infections. Ultrasonography, cystography, and a renal cortical scan should be considered in children with urinary tract infections.
Recommended Reading: How To Ease Urinary Tract Infection Pain