What Should You Tell The Family About The Patients Prognosis
-
Diabetes is associated with xanthogranulomatous, papillary necrosis, and emphysematous pyelonephritis, severe conditions requiring a combined surgical and medical approach.
-
Obstruction that cannot be relieved or presence of a stone or stricture increase the likelihood of infection and make treatment of infection more difficult.
-
The overall 28-day and 1-year all-cause mortality rates following a UTI associated with gram-negative bacteremia was found to be 4.9% and 15.6% , respectively, in a population-based retrospective study. Mortality rates were higher with advancing age and in patients with health-care acquired infections.
-
Catheter associated UTI was the third leading cause of hospital associated infection-related death in US hospitals in 2002.
Add what-if scenarios here:
If the urine culture reveals yeast, assess for symptoms of urinary tract infection because funguria most often represents asymptomatic colonization of the urinary tract . If symptoms of urinary tract infection are present, assess for fungal balls within the urinary tract , control hyperglycemia , and institute anti-fungal therapy. Urology consultation may be needed for removal of fungal balls or irrigation of the urinary system with an antifungal agent .
How Did The Patient Develop Pyelonephritis/complicated Urinary Tract Infection What Was The Primary Source From Which The Infection Spread
-
Pyelonephritis and complicated UTI most commonly occur by migration of enteric bacteria from the intestinal tract into the urethra and ascension into the urinary system.
Basic epidemiology
-
The term complicated, as opposed to uncomplicated, suggests there is a predisposing reason for the infection, including the presence of abnormal voiding or a foreign body . Known or suspected multi-drug resistance is also a complicating factor.
-
Complicated UTI can occur in any gender and at any age but is most common in men after the fifth decade when benign prostatic hypertrophy is present and in both men and women who have voiding abnormalities related to other conditions.
-
Most UTIs in young premenopausal nonpregnant women and in young adult men are not complicated.
-
UTIs in patients with diabetes or in postmenopausal women should be considered complicated if there is abnormal voiding associated with those conditions.
-
Additional factors that suggest complicated UTI include conditions that make treatment more difficult, such as pregnancy, multidrug resistance, and immunosuppression.
Dont Miss: Discomfort In Urinary Tract Male
Interstitial Cystitis/painful Bladder Syndrome
Interstitial Cystitis or also known as Painful Bladder Syndrome creates a chronic pain related to the lower urinary tract, more specifically, the bladder. Individuals with this experience a pain or pressure sensation symptom for greater than 6 weeks but no infection can be identified. While the cause of interstitial cystitis is not known, an autoimmune response triggers inflammation that increase the sensitivity of neurons in the mucosa of the bladder, making it more vulnerable to bacteria colonization. The inflammation and hardening of the wall of the bladder can also create hemorrhagic ulcers and a decrease in bladder capacity. The epithelial cells of the bladder also secrete antiproliferative factor which block cell growth of the inner wall of the bladder and causes an increased bladder sensation
Also Check: How Do I Know If I Have Urinary Tract Infection
What Is The Urinary Tract
The urinary tract is the bodys drainage system for removing wastes and extra fluid. The urinary tract includes
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs, each about the size of a fist. They are located just below the rib cage, one on each side of the spine. Every day, the kidneys filter about 120 to 150 quarts of blood to produce about 1 to 2 quarts of urine, composed of wastes and extra fluid. Children produce less urine than adults. The urine flows from the kidneys to the bladder through tubes called ureters. The bladder stores urine until releasing it through urination. When the bladder empties, urine flows out of the body through a tube called the urethra at the bottom of the bladder.
Am I At Risk Of A Uti

While UTIs can happen to anyone, they are more common in females who are sexually active or menopausal, or have health conditions such as diabetes or urinary incontinence. Females who use spermicides or diaphragms as contraception are also at increased risk of UTIs, and may benefit from other contraceptive options if they get recurrent UTIs.
Some people at greater risk of developing urinary tract infections:
- Females nearly 1 in 3 females will have a UTI that needs treatment before the age of 24.
- Males with prostate problems an enlarged prostate gland can cause the bladder to only partially empty, raising the risk of infection.
- Older people some medications and problems with incontinence mean that older people are more likely to get a UTI.
- People with urinary catheters people who are critically ill and people who cant empty their bladder are at a greater risk of infection.
- People with diabetes changes to the immune system make people with diabetes more vulnerable to infection.
- Infants babies in nappies commonly get UTIs, in particular, infants born with physical problems of the urinary system are at greater risk.
Recommended Reading: Urinary Tract Infection Or Bladder Infection
Complicated Urinary Tract Infection
Complicated UTI is infection involving a functional or anatomically abnormal urinary tract or infection in the presence of comorbidities that place the patient at risk for more serious adverse outcomes.11 Risk factors for complicated UTI, including UTI in males, are listed in Table 91-1.9 The diagnostic criterion is the isolation of 105 CFU/mL of urine culture. Unfortunately, patients with complicated UTIs are a very heterogeneous group, and few clinical trials have been conducted to guide management. In general, patients in this group are more likely to be infected with resistant organisms.11 Although older literature categorized pyelonephritis as a complicated UTI, current guidelines do not.10,11,12Uncomplicated pyelonephritis refers to the clinical syndrome of fever and flank pain or tenderness with or without vomiting in a patient with an anatomically normal urinary tract without comorbidities. However, the recommended management of patients with uncomplicated pyelonephritis is similar to recommendations for patients with complicated UTI and differs from the management of patients with uncomplicated cystitis .
Uti Signs And Symptoms In Childrenare Different
UTIs are the second most common type of infection in children, behind ear infections. Unfortunately, early symptoms of UTI in young children are not always apparent. And sometimes there are no UTI symptoms at all, or your child is simply unable to articulate the UTI symptoms he or she is experiencing. When it comes to babies under 2 years old, parents need to tune in to these signs of a urinary tract infection:
- Fever A fever of 104°F or higher may be the sole symptom in babies. Its also the most common symptom of UTI during babys first two years.
- Jaundice Up to 18 percent of babies with prolonged or worsening jaundice also have UTIs. When jaundice occurs one full year after birth, its a strong indicator of UTI.
- Poor feeding or failure to thrive
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Crying while urinating
Meanwhile, older children generally have similar symptoms to adults, including urgency, cloudy urine, and pain during urination. For children whove already been toilet trained, bed-wetting is also a sign of a UTI.
Read Also: Acv For Urinary Tract Infection
Signs And Symptoms Of Cystitis
The main symptoms of cystitis include:
- pain, burning or stinging when you pee
- needing to pee more often and urgently than normal
- urine that’s dark, cloudy or strong smelling
- pain low down in your tummy
- feeling generally unwell, achy, sick and tired
Possible symptoms in young children include a high temperature of 38C or above, weakness, irritability, reduced appetite and vomiting.
Read more about treating cystitis
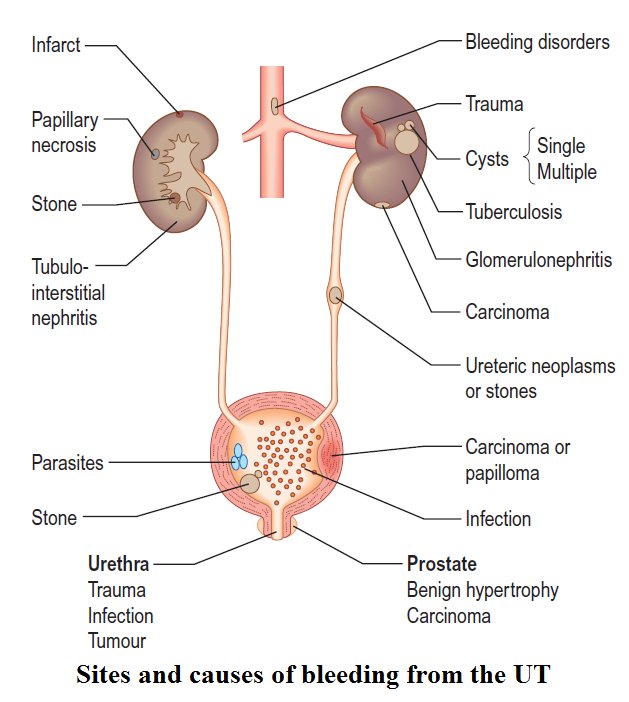
How Do I Stop Blood In My Urine
Depending on the condition causing your hematuria, treatment might involve taking antibiotics to clear a urinary tract infection, trying a prescription medication to shrink an enlarged prostate or having shock wave therapy to break up bladder or kidney stones. In some cases, no treatment is necessary.
Also Check: Foods For Urinary Tract Health
Acute And Chronic Prostatitis
In the 1800s, prostatitis was thought to be secondary to excessive alcohol consumption or physical or sexual activity. It was often associated with gonorrhea and could be fatal or lead to abscess formation. By the 1920s, most cases were attributed to microorganisms, and antibiotics combined with prostate massage were standard therapy after World War II. Although the role of bacteria was questioned in the 1950s, it was reemphasized in 1968 when Meares and Stamey described their 4-glass test.
Acute prostatitis is caused by an acute infection of the entire prostate gland, resulting in fever and localized pain. Microscopically, neutrophilic infiltrates, diffuse edema, and microabscesses may be seen, which may coalesce into larger collections.
Chronic prostatitis may be caused by inflammatory or noninflammatory diseases. This condition may arise via dysfunctional voiding, intraprostatic reflux, chronic exposure to microorganisms, autoimmune mechanisms, irritative urinary metabolites, and as a variant of neuropathic pain. Chronic bacterial prostatitis often produces few or no symptoms related to the prostate, but it is probably the most common cause of relapsing UTI in men.
Chronic prostatitis has been subdivided by the National Institutes of Health into the following categories:
Try Taking A Probiotic
Introducing a probiotic to your system may help to replenish the naturally occurring, healthy bacteria that live in the gut. It is thought that probiotics may prevent harmful bacteria from attaching to the urinary tract cells, and may also lower the urine Ph, making it less hospitable to harmful bacteria. And, if you have taken an antibiotic to treat a UTI, taking a probiotic is a great way to build up the healthy bacteria that may have been killed during your course of treatment. Probiotics are found in supplement form , or they occur naturally in some types of food, including certain yogurts, kombucha, or kefir.
Recommended Reading: Can A Urinary Tract Infection Heal On Its Own
Avoid Bladder Irritating Foods When You Have A Uti
Certain foods are known bladder irritants citrus or very acidic foods, artificial sweeteners, caffeine, alcohol these can all irritate the bladder, leading to bladder leaks. And, if you currently have a UTI, they may affect you even more. Try to watch out for these common bladder irritants to prevent further irritation to your bladder and UTI.
What Consult Service Or Services Would Be Helpful For Making The Diagnosis And Assisting With Treatment

If you decide the patient has pyelonephritis/complicated UTI, what therapies should you initiate immediately?
Establish urine flow this may require consultation with urology if a catheter is difficult to place or an obstructing stone needs to be removed. Consultation with interventional radiology may be helpful if an upper tract obstruction requires a percutaneous nephrostomy tube.
Antibiotics should be given consultation with Infectious Diseases may be required for optimal antimicrobial selection if there is known or suspected multidrug resistance.
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis requires surgical consultation for possible nephrectomy renal abscess and emphysematous pyelonephritis require urology consultation for percutaneous drainage.
Key principles of therapy
In patients who require hospitalization, broad spectrum intravenous therapy is indicated empirically while waiting for culture data. In patients who are clinically stable and who do not require IV fluids or other supportive care, outpatient oral antibiotics can be considered. In these patients, an initial one time IV dose of a broad spectrum antimicrobial may be helpful, especially if susceptibility of the infecting uropathogen is not known.
1. Anti-infective agents
If I am not sure what pathogen is causing the infection, what anti-infective should I order?
The empiric therapy should include coverage for Proteus sp. and other urease-producing organisms in patients who have staghorn calculi.
Oral Agents
You May Like: What Are Urinary Tract Symptoms
What Is Acute Cystitis With Hematuria
So exactly what is acute cystitis with hematuria? The term cystitis refers to an inflammation of the bladder. Its traceable to any number of problems, the most typical one being a bacterial infection. Acute cystitis brought on by bacteria is also known as a urinary tract infection . It causes bleeding in the bladder, which then appears in your urine.
Though not uncommon among women, if a UTI is left untreated, it results in serious health consequences. The bacteria moves to your kidneys, which can lead to a major infection or renal failure. Certain drugs, radiation therapy, or even the use of spermicidal jellies, feminine douches, and hygiene sprays may trigger a bladder infection. The insertion of a catheter also increases your risk of developing acute cystitis.
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage
In addition to BPH, individuals with overactive bladder, chronic pelvic pain , inflammation of the prostate or urinary tract infections typically experience lower urinary tract symptoms associated with urine storage, irritation or inflammation. These symptoms can include:
- Urinary frequency
- Nocturia using the restroom several times during the night
Don’t Miss: What Treat Urinary Tract Infections
Classifications Of Urinary Tract Infections:
Uncomplicated UTI: mild UTI, without complications, occur in normal urinary tracts
Complicated : abnormality in urinary system or individual has a health problem that compromises hosts defenses
Recurrent UTI: three or more UTIs in 12 months or 2 or more occurrences within 6 month
-Relapse: a second UTI caused by the same pathogen within 2 weeks of first treatment
-Reinfection: a UTI that occurs greater than 2 weeks after completing treatment for same or a different pathogen
Cultures And The Laboratory Diagnosis Of Utis
Routine bacterial urine cultures. Urine culture may not be necessary as part of the evaluation of outpatients with uncomplicated UTIs . However, urine cultures are necessary for outpatients who have recurrent UTIs, experience treatment failures, or have complicated UTIs. Urine cultures are also necessary for inpatients who develop UTIs. The bacterial culture remains an important test in the diagnosis of UTI, not only because it helps to document infection, but also because it is necessary for determination of the identity of the infecting microorganism and for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. This is particularly true because of the increased incidence of antimicrobial resistance.
Catheterized patients and many patients with infections of the lower urinary tract have colony counts much lower than 105 cfu/mL if the specimens are obtained via suprapubic aspirate or catheterization . Accordingly, the most appropriate diagnostic criterion for urine culture specimens obtained via suprapubic aspirate or catheterization is a bacterial concentration of 102 cfu/mL .
Interpreting culture results for urine specimens yielding common urinary tract pathogens.
You May Like: How Can You Treat A Urinary Tract Infection At Home
Urinary Tract Infection Site Not Specified
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- N39.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N39.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N39.0 – other international versions of ICD-10 N39.0 may differ.
“use additional code”
Quality And Interpretation Of Urine Specimen Collection
Obtaining an adequate quality urine sample is frequently the first major barrier to appropriately diagnosing UTI in older adults. Guidelines specific to long-term care residents recommend collecting a mid-stream clean catch urine specimen for urine studies . In reality, such a collection is an often laborious process requiring the patient to possess not only urinary continence but a degree of cognition, coordination, and mobility that many older adultsâparticularly those who are institutionalizedâmay lack. For patients who cannot provide such a specimen, recommendations are to place an external condom catheter in men or perform in/out urinary catheterization in women, which can cause significant discomfort. Staff collecting urine specimens may use approaches that are not recommended by guidelines, such as obtaining the urine from a chronic urinary catheter or urine collection bag, both of which become contaminated with bacteria within hours of urinary catheter placement . Finally, the person who interprets the results of urine studies may or may not be the same person who ordered the tests and is most certainly not the person who collected the sample.
Recommended Reading: Young Living Essential Oils For Urinary Tract Infection
Are You Sure Your Patient Has Pyelonephritis/complicated Urinary Tract Infection What Should You Expect To Find
-
Urinary tract infections can be separated into distinct syndromes depending on host characteristics and the presence of symptoms. The syndromes of pyelonephritis, infection of the renal parenchyma, and complicated UTI, infections of the urinary tract in patients with functional or anatomical abnormalities, are covered here. The presence of bacteria in the urine without localizing urinary tract or systemic symptoms of infection is considered asymptomatic bacteriuria, a common condition that increases with advancing age and most often does not require treatment. In a patient with bacteriuria and systemic symptoms of infection without localizing genitourinary symptoms, UTI should be considered as a potential diagnosis however, other causes of the systemic symptoms should also be evaluated, because the urine culture may simply be reflecting asymptomatic bacteriuria.
-
Pyelonephritis denotes infection of the renal parenchyma. Symptoms of pyelonephritis include:
local pain
Continue Reading
systemic signs of infection
These symptoms may or may not be associated with symptoms of cystitis .
Role Of The Pharmacist
It is imperative that pharmacists urge patients who present with UTI symptoms to consult with their healthcare provider as soon as possible to receive appropriate care. Pharmacists should counsel patients on nonpharmacologic treatments and present the option of nonprescription products and UTI home test kits. Patients who decide to use UTI home test kits should be advised on how to avoid inaccurate results and to discuss their results with their healthcare provider. Patients who decide to use OTC urinary tract analgesics should be counseled on the recommended maximum dosage and duration and on common AEs. It is imperative to remind patients that these products are intended only to provide relief of pain and other related symptoms until the healthcare provider is seen. These products do not eradicate bacteria or replace the use of antibiotic treatment, and they should not be used as monotherapy.
Also Check: Why Am I Prone To Urinary Tract Infections