Why Some People Regain Bladder Function Relatively Quickly
For some, loss of bladder control can be temporary. After a spinal cord injury, you may experience the temporary and complete loss of reflexes below your level of injury called spinal shock.
This is primarily caused by reduced blood supply and inflammation. Blood is rich in oxygen and nutrients that are essential for cellular activity. Excessive swelling in the spinal cord can decrease blood flow by up to 80%, causing major bodily functions to dysfunction.
Fortunately, spinal shock is a temporary condition that can last anywhere from a few days to several months. Once inflammation of the spinal cord starts to die down, functions below the level of injury may gradually start to return.
But is it possible to regain bladder control after spinal shock subsides?
Possible Mechanisms Underlying Recovery
Reorganization of the micturition reflex following spinal cord injury is dependent in part on the plasticity of bladder afferent pathways and the unmasking of reflexes triggered by unmyelinated, capsaicin-sensitive, C-fiber bladder afferent neurons. Plasticity of bladder afferent neurons is associated with morphologic, chemical, and electrical changes, which appears to be mediated in part by neurotrophic factors released at the level of spinal cord and the peripheral target organs . Upregulation of anti-inflammatory mediators and neuroprotective molecules is likely to play an important role in the plasticity of bladder afferent pathways as well as reorganization of synaptic connections in the spinal cord . In rats, poor voiding efficiency at 4 and 8 weeks after spinal cord injury was coincident with upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines , chemokines and downregulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IL-13, whereas spontaneous recovery of voiding function at 12 weeks was associated with maximum expression of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-1018, neurotrophin BDNF and CXCL-5 as well as the neuroprotective leptin19 in bladder .
Nearly Half Of All Patients Undergoing Elective Cervical Spine Surgery Had Moderate
Numbers:
- The prevalence of moderate lower urinary tract symptoms in the patient sample was 40%
- The prevalence of severe lower urinary tract symptoms in the patient sample was 8%
- Clinically relevant urinary bother was reported in 18% of patients
- The odds of moderate-to-severe lower urinary tract symptoms among patients with myelopathy was greater than that observed in patients without myelopathy
- The prevalence of clinically relevant urinary bother was higher in patients with myelopathy compared with those with no myelopathy .
Nearly half of all patients undergoing elective cervical spine surgery had moderate-to-severe lower urinary tract symptoms. This is more than double the prevalence that has been reported in a community-dwelling adult population. These symptoms can impair quality of life, lead to surgical complications , and may be mistaken for cauda equina , prompting potentially unnecessary imaging and studies.
Dr. Albert also suggested:
Recommended Reading: Why Do I Have A Urinary Tract Infection
When Nerve Damage Causes Bladder Problems: Neurogenic Bladder
Until a few short years ago, Rob, who is in his 80s, had been relatively free of health problems. He was an active guy, skiing and hiking in his beloved Washington State mountains. Husband, father and grandfather, he was living a happy retirement from Boeing Aircraft. Then what he thought was a small nagging problem was diagnosed as a complex medical problem.
When ongoing heartburn was keeping him awake at night, he went to a GI doctor for help. A scan showed Robs bladder was so enlarged it was pushing against his stomach, causing the heartburn. One doctor visit after another revealed more than one medical issue. Rob began a series of tests and surgeries to treat bladder cancer, prostate cancer and an aortic aneurysm.
His cancers were removed, but nerve damage from his surgery left Rob unable to fully empty his bladder. Today, he relies on using a straw-like tube, called a catheter, to help empty his bladder completely. Rob has neurogenic bladderand he isnt alone. Millions of Americans have this health issue. Neurogenic bladder is when a person lacks bladder control due to damage to the nerves carrying messages between the bladder and the brain. This damage may be the result of a spinal cord injury, an infection of the brain or spinal cord, heavy metal poisoning or diseases affecting the nerves, such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, Parkinsons disease or diabetes. People born with problems of the spinal cord, such as spina bifida, are also at risk for neurogenic bladder.
Help For Bladder And Bowel Incontinence
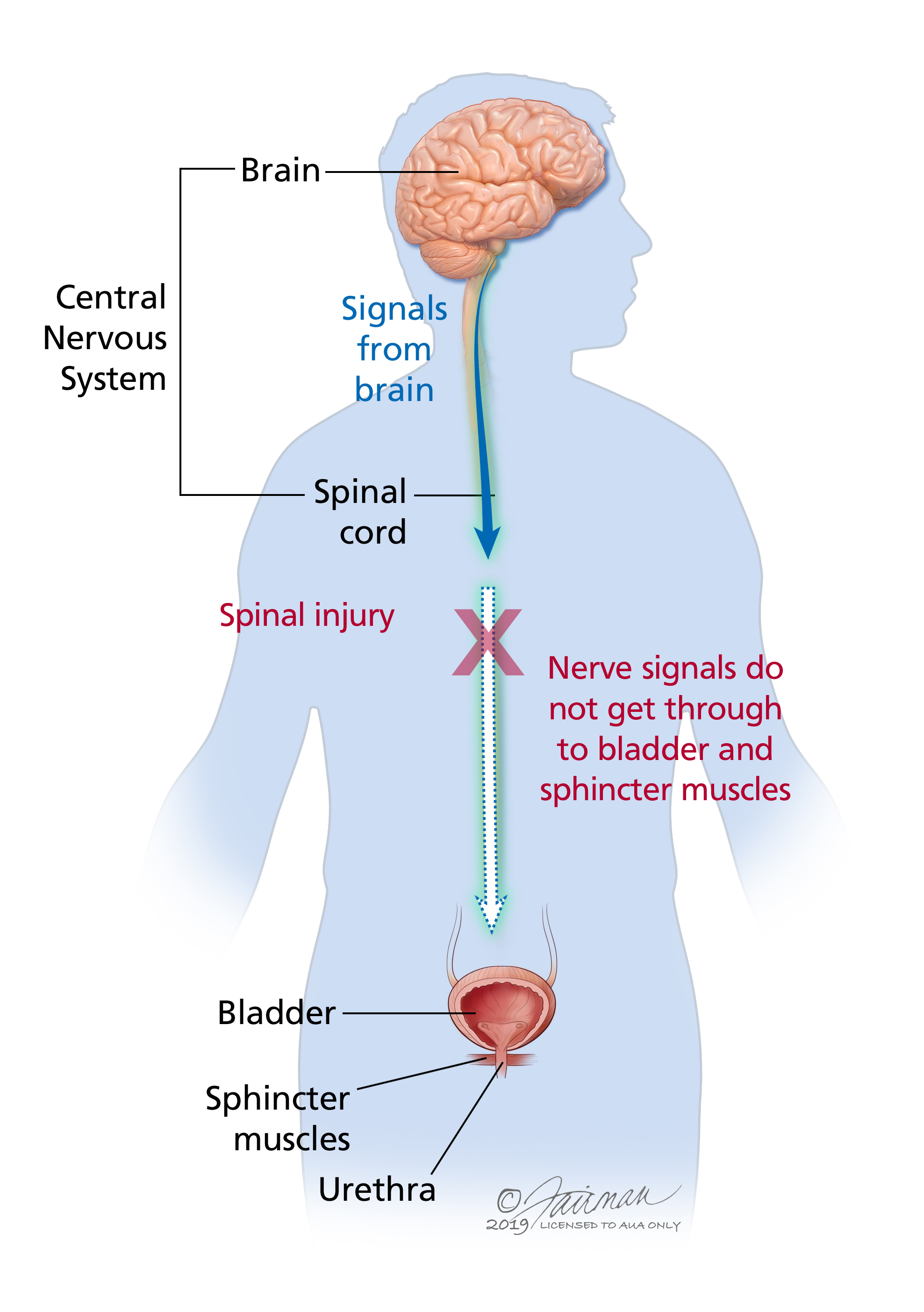
Even though these more serious conditions may occur because of spinal cord injury, the most common condition affecting continence is neurogenic bladder/bowel. If this is what you are experiencing there are many things available to help you carry on with your life.
There are absorbent products like incontinence pads, adult pull-up diapers and adult diapers with tabs that keep you dry and are discreet. There is also a wide variety of catheters available that are designed, using the latest technology, to be discreet and effective. Your doctor may prescribe medicine that can help and in some instances, surgery may be an option. If the neurogenic bowel is affecting you, there are different ways to regularly empty the bowel, when you choose, so you can gain control back in this area of your life.
You May Like: How Do You Say Urinary Tract Infection In Spanish
Regaining Bladder Control After Spinal Cord Injury: Key Points
Loss of bladder control is one of the most common outcomes of spinal cord injury. While it might be possible to improve bladder control, the outcomes of every SCI are different.
Learning to manage bladder problems is essential to avoid accidents and prevent further complications from developing.
Hopefully, this article helped you better understand how spinal cord injury can affect bladder functions and how to manage complications to improve your quality of life. Good luck!
Circumventing The Problem: Urinary Diversion
Conduit urinary diversion might be a good option for management of neurogenic bladder with decreased compliance and upper tract deterioration or severe urinary incontinence. The ileal conduit was introduced by Bricker and has stood the test of time due to its relatively shorter construction time and the familiarity of urologists with this procedure. The reported outcomes were good to fair in only 50% of patients, with a 25% mortality rate, resulting mainly from urinary tract complications that occurred several years after the procedure and were attributable to recurrent UTIs.126128 However, contemporary studies have reported better results, with rates of preservation of renal function reaching 100%.129,130 However, major long-term complications have been encountered with ileal conduit diversion, including pyocystitis, stomal bleeding and irritation, metabolic acidosis, and urolithiasis. A prospective study in patients with neurogenic bladder dysfunction secondary to SCI or multiple sclerosis reported that cystectomy and ileal conduit urinary diversion improved urinary quality of life by decreasing the limitations and constraints induced by urinary disorders but had no effect on general quality of life.131
Recommended Reading: Fruits Good For Urinary Tract
How The Study Was Conducted
The researchers worked with five men who had spinal cord injuries. The men underwent 15 minutes of magnetic stimulation every week from a device thats approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration but is experimental when used in bladder rehabilitation.
After four sessions, the men saw a noticeable improvement in their bladder function. All five were able to urinate on their own. One participant was able to stop using his catheter completely and urinate by himself 13 years after his injury.
These improvements lasted for up to four weeks after the magnetic stimulation.
The other four men still had to use the catheter at least once daily, but that was an improvement from their previous frequency of six or more times a day.
The participants bladder capacity also increased, as did the volume of urine they were able to produce voluntarily without a catheter.
Lu says the results are promising and gave the study participants hope.
They were highly encouraged and could not wait until this strategy is available for clinical treatment, he said.
Whats Different About Females
Because women have no penis, collecting urine is more difficult. There is no good external collection device, like a condom catheter, for women. Women doing ICP have more problems with incontinence than men because the female urethra is short and more likely to leak urine.
Women get different complications from having an indwelling Foley catheter for a long time. The urethra can become dilated , which results in more leakage. Switching to a larger catheter just dilates the urethra more, causing more incontinence. For this reason, a suprapubic tube is a good option for a woman who otherwise would be using a Foley catheter.
You May Like: Urinary Tract Test At Home
Kidney And Bladder Stones
Stones are common in people with SCI. They can develop early on because large quantities of calcium leave the bones in the first few months after injury. It is more common to get stones later, and this is due to infections over the long term. Bacteria break down urea into chemicals that form stones, which can cause blockages, kidney damage and serious infections.
What Bladder Problems Can An Sci Cause
An SCI can cause two types of bladder problems. One set of problems occurs immediately after injury, and the other may begin later on after your injury when you are out of spinal shock
Immediately after SCI:
- You might experience spinal shock, when signals from the brain cant get to any or most parts of the body below the spinal cord injury.
- Spinal shock in general usually lasts for up to a few days, but for the bladder it can last several months or longer.
- Your bladder does not squeeze when you are in the period of spinal shock.
After your bladder is out of spinal shock:
Recommended Reading: Azo Urinary Tract Defense Vs Urinary Pain Relief
Increasing Functional Bladder Capacity Botulinum Toxin
Botulinum toxin is a minimally invasive treatment that might achieve the therapeutic goals. This treatment was first used in patients with SCI in 2000 and was subsequently shown to have good efficacy and tolerability both in terms of subjective and objective outcomes.7077 In August 2011, botulinum toxin was finally approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of adults with neurogenic detrusor overactivity who fail treatment with anticholinergic medications.78
Studies that have used 300 units of botulinum-A toxin report increases in mean reflex volumes and maximum cystometric bladder capacities of 216 to 416 mL and 296 to 480 mL, respectively, and decreased maximum detrusor voiding pressures of 66 to 35 cm water.70 The effects of treatment lasted at least 9 months. A particular benefit in patients with tetraplegia was the disappearance of autonomic dysreflexia. Prospective randomized studies have confirmed that treatment with botulinum toxin is associated with a significant reduction in urinary incontinence and improvements in urodynamic parameters and quality of life for patients with SCI.71,73 No differences between doses of 200 units and 300 units were found in terms of tolerability, efficacy, or duration of effect. This treatment may be repeated several times over a period of years. Botulinum toxin has been shown to be equally effective in initial and subsequent repeat treatments for up to 6 years.7477
Cystoplasty
There Is A Connection Between Urinary Problems And Cervical Neck Pain The Vagus Nerve And Blood Pressure
The Vagus Nerve controls the muscle movement of the bladder during urination. If you look at the illustration above you will see where the Vagus nerve is closely related to the C1 C2 C3 vertebrae. While doctors usually discuss the vagus nerve in singular sense, there are two vagus nerves, one on each side of the neck and in combination they are referred to as the vagal nerves. This means that the degenerative damage in your neck can significantly impact the function of one or both vagus nerves.
There has been some degree of controversy as to whether or not the vagus nerves do provide nerve impulses and function to the bladder. It should not be far fetched to think they do. The vagus helps regulate your heartbeat, the vagus helps regulate your breathing, your vagus regulates functions of your digestive tract. Wouldnt it be within the realm of possibility that the vagus could also regulate the bladder? Lets get to the science so we may be able to explain how treating your neck pain can, among other things, help regulate your bladder.
We are going to go back to a 1987 study performed on dogs, that makes a connection to neck area pain, the heart, and urinary bladder problems. If your neck pain includes problems of regulating heartbeat, you may find a long-sought answer to some of your problems.
Here are the highlights:
What did the researchers find?
What does this mean to you?
Urinary problems, heart rate, blood pressure, seemingly all have a common neck component.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms Of A Severe Urinary Tract Infection
Management Of Fecal Incontinence
Guidelines for the management of fecal incontinence in the acute and chronic phases are proposed in Tables 1, 3, along with suggestions to manage the dog’s environment and feeding.
The primary concern expressed by owners of dogs with fecal incontinence is management of the mess produced by inadvertent defecation, with secondary concerns of skin damage due to contamination with fecal material and contamination of the vulva causing urinary tract infections. Careful questioning of the owner is needed to determine when the incontinence is occurring and the nature and volume of the stool. The most practical and effective management technique is to use a low residue diet that reduces stool volume sometimes dramatically, and usually resolves loose stool or diarrhea. All dietary indiscretions should be avoided because the consequences can be challenging.
Pharmacological Interventions For Bladder Management
Pharmacological interventions will vary depending on the localization of the inciting injury and it is imperative to consider carefully the characteristics of the clinical signs when choosing medications. Table 2 present some possible medications for neurogenic bladder management.
Table 2. Possible drugs suggested to act on the lower urinary tract physiology during neurogenic dysfunction.
Terazosin, a long-acting selective -1 adrenoreceptor blocking molecule has been used to treat vesico-sphincter dyssynergia in spinal cord-injured male humans and reduced bladder outlet obstruction but causes side effects such as collapse and has not been reported in clinical papers since 2002. In dogs, terazosin has been used to treat vesico-urethral reflex dyssynergia but not in the context of spinal cord injury and showed side effects in 93% of the cases . Similarly, tamsulosin is also a -1 adrenoreceptor blocking molecule with higher affinity that terazosin but has not been trialed after spinal cord injury in dogs.
When faced with an atonic bladder , the clinician has few options and there is no clear pharmacological method to reduce constant urinary leakage, which is problematic. Bethanechol can be trialed to improve bladder contraction but there is no clinical evidence to back this and the efficacy is poor in the author’s experience.
Read Also: Vinegar For Urinary Tract Infection
Keep It Going: Get 15 Pages Of Rehab Exercises For Sci Recovery In Our Free Ebook
Get instant access to our free exercise ebook for SCI survivors. If you liked this post, youll LOVE our emails and ebook.
Each exercise features pictures of a licensed therapist to help guide you. Youll also receive our popular recovery emails with SCI survivor stories and other useful tips you can opt out anytime.
We will never sell your email address, and we never spam.
What Did The Researchers Do And Find
- Based on data from 1,250 patients with traumatic spinal cord injury included in the European Multicenter Spinal Cord Injury study, we derived two simple and reliable models to predict urinary continence and complete bladder emptying 1 y after traumatic spinal cord injury.
- Our models have been validated in an independent cohort of 111 patients with traumatic spinal cord injury.
Don’t Miss: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Cause Urinary Tract Infections
What Causes Loss Of Bladder Control After Spinal Cord Injury
The spinal cord transmits messages between the brain and body. However, after a spinal cord injury, messages may not be able to get past the site of injury, resulting in paralysis and loss of sensation below your level of injury.
Many people lose control of bladder functions after a spinal cord injury because the bladder muscles are innervated by some of the lowest nerve segments of the spinal cord. Damage to the spinal cord not only affects functions at the injury site but can also affect all functions below.
The reason why some spinal cord injury patients have normal bladder functions is because they have incomplete SCIs, which means some connections were not damaged by the injury. As a result, they may have some preserved motor control and sensation below their level of injury.
Next, well discuss different types of neurogenic bladder dysfunction that can result from spinal cord injury.
Bladder And Bowel Management In Dogs With Spinal Cord Injury
- 1The Royal Veterinary College, University of London, Hertfordshire, United Kingdom
- 2CVS Referrals, Bristol Veterinary Specialists at Highcroft, Bristol, United Kingdom
- 3Department of Clinical Sciences, North Carolina State University College of Veterinary Medicine, Raleigh, NC, United States
- 4Department of Clinical Sciences, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, United States
Recommended Reading: How Does Botox Work For Urinary Incontinence
Treatment Of Urinary Incontinence In Women With Spinal Cord Injury
| The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government. Read our disclaimer for details. |
| First Posted : April 27, 2015Last Update Posted : August 22, 2017 |
- Study Details
| Spinal Cord InjuryUrinary Incontinence | Behavioral: Pelvic floor muscle trainingDrug: vaginal electrical stimulator | Not Applicable |
SCI patients often experience neurogenic bladder dysfunction with neurogenic detrusor overactivity or areflexic bladder. Due to this, 40-50 % of the SCI population suffers from urinary incontinence, which often reduces the patient’s quality of life.
PFMT and NMES of the pelvic muscles are non-invasive and cheap treatments without side effects and several studies have demonstrated the positive effect of intravaginal NMES and/or PFMT on urinary incontinence in able-bodied women as well as women with neurological disorders like multiple sclerosis.
Despite the fact that NMES of weak or paralyzed striated muscles has been used for decades in patients suffering from SCI, to our knowledge, no study has previously investigated the effect of PFMT and intravaginal NMES in women with SCI.