Other Disorders Of Urinary System
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
- Acute lower urinary tract infection
- Acute upper urinary tract infection
- Acute urinary tract infection
- Chronic lower urinary tract infection
- Chronic urinary tract infection
- Escherichia coli urinary tract infection
- Infection, urinary tract , upper
- Klebsiella urinary tract infection
- Lower urinary tract infection, acute
- Lower urinary tract infection, chronic
- Lower urinary tract infectious disease
- Persistent urinary tract infection
- Recurrent urinary tract infection
- Upper urinary tract infection
- Upper urinary tract infection, acute
- Urinary tract infection
- Urinary tract infection with fever
- Urinary tract infection due to enterococcus
- Urinary tract infection due to klebsiella
- Urinary tract infection due to pseudomonas
- Urinary tract infection due to urinary catheter
- Urinary tract infection, acute
- Uti after procedure
- 689 Kidney and urinary tract infections with mcc
- 690 Kidney and urinary tract infections without mcc
- 791 Prematurity with major problems
- 793 Full term neonate with major problems
Appendix B Diagnosis And Procedure Codes Used To Identify Cutis
To identify a cUTI, patients were required to have 1 inpatient or outpatient claim with a diagnosis code in any position from Group A or 1 inpatient or outpatient claim with a diagnosis code in any position from Group B and 1 inpatient or outpatient claim with a diagnosis or procedure code in any position from Group C within 7 days of each other.
| ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code . |
|---|
Read Also: What Causes Urinary Urgency And Frequency
What Is The Most Common Bacterial Infection In Women
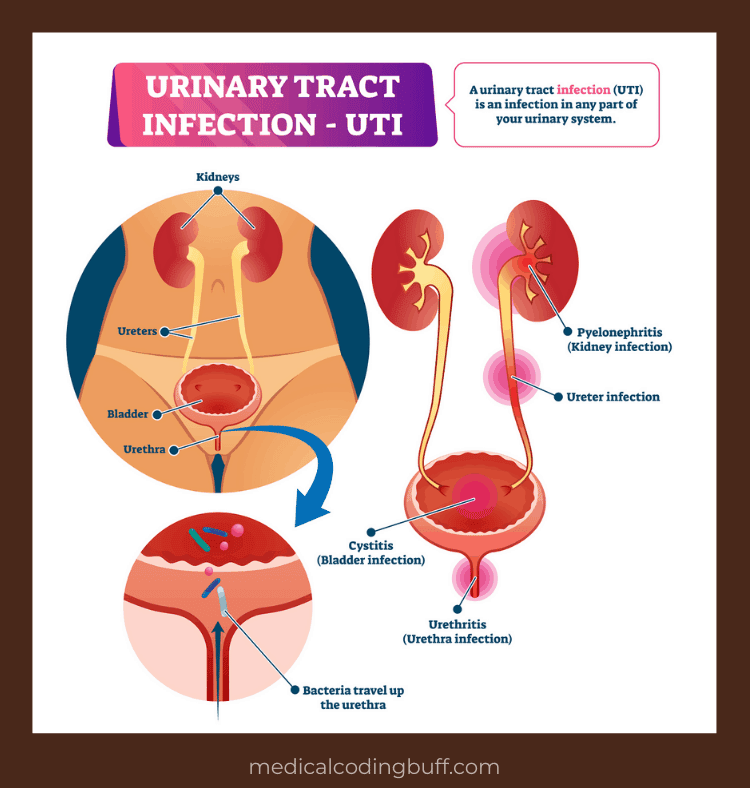
Urinary tract infections are one of the most common, recurrent bacterial infections in individuals, mostly women. Bacteria, such as Escherichia coli , enters the urethra and infects one or several parts of the urinary tract, including the urethra, bladder, ureters, or kidneys. UTIs can be mild to serious and even result in death.
Also Check: How Do You Treat A Urinary Tract Infection At Home
You May Like: What Is Urinary Bladder Cancer
How Is Urinary Incontinence After Prostate Surgery Treated
If you find youre having issues with mild to moderate leakage after surgery, your healthcare provider might suggest starting with noninvasive therapies like medications or physical therapy exercises for the pelvic floor muscles. These treatments may also cut down on the number of times that you have to get up each night to pee.
These methods can sometimes help men who have mild to moderate leakage. Men who have persistent leakage or a more severe problem may need surgery if they do not want to continue to use pads.
Study Design And Population
A retrospective observational cohort study of adult patients with cUTIs in IBM MarketScan Databases between July 1, 2016, and June 30, 2020, was performed . Two IBM MarketScan Research Databases were used in the study: the MarketScan Commercial Claims and Encounters Database and the MarketScan Medicare Supplemental Database . Patients were included if they had 1 IP or OP nondiagnostic claim meeting the diagnosis for a cUTI between January 1, 2017, and June 30, 2019 , were 18 years old as of index date, had 6 months of continuous enrollment with medical and pharmacy benefits before the index date, had 12 months of CE following the index date or evidence of IP death, and had no evidence of a prior cUTI during the 6-month baseline period.
You May Like: Severe Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
List Of Icd 10 Codes For Urinary Tract Infection
The ICD 10 codes for Urinary Tract Infection can be found in chapter 14 of the ICD 10 manual.
ICD 10 Code N30.00: Acute cystitis without hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.01: Acute cystitis with hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.10: Interstitial cystitis without hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.11: Interstitial cystitis with hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.20: Other chronic cystitis without hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.21: Other chronic cystitis with hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.30: Trigonitis without hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.31: Trigonitis with hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.40: Irradiation cystitis without hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.41: Irradiation cystitis with hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.80: Other cystitis without hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.81: Other cystitis with hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.90: Cystitis, unspecified without hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.91: Cystitis, unspecified with hematuria.ICD 10 Code N34.0: Urethral abscess.ICD 10 Code N34.1: Nonspecific urethritis.ICD 10 Code N34.2: Other urethritis.ICD 10 Code N34.3: Urethral syndrome, unspecified.ICD 10 Code N39.0: Urinary tract infection, site not specified.ICD 10 Code N39.9: Disorder of urinary system, unspecific.
When To Treat Uti Guidelines
This guideline is on the use of antibiotics for community-acquired UTIs affecting patients aged 18 years or older. The guideline targets asymptomatic bacteriuria, acute uncomplicated cystitis, acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis, complicated pyelonephritis related to urinary tract obstruction, and acute bacterial prostatitis.
Don’t Miss: Bladder Infection Same As Urinary Tract Infection
What Is The Icd 10 Code For A Recurrent Uti
When do I need a urinary tract infection code?
Therefore, when the documentation states the type of urinary tract infection and the infectious organism, a code from B95-B97 must also be assigned. Urosepsis is a general term, and there is no code for it. If the documentation indicates urosepsis, query the physician for more information.
Can a recurrent urinary tract infection be a reinfection?
Reinfection is recurrent infection with different bacteria from outside the urinary tract. Each infection is a new agent the urine must show no growth after the preceding infection. Relapse is frequently used interchangeably. 6 Of those having recurrent UTI, up to 99% will have reinfections as opposed to bacterial persistence. 2
Determining The Correct Urinary Incontinence Icd 10 Code
Your patient just presented with urinary incontinence. Its been a while since youve had to recall the different types of urinary incontinence, not to mention the treatment options, device reimbursement qualifications, and urinary incontinence ICD 10 coding. Heres a quick refresher of the most common types of incontinence:
- Stress urinary incontinence is an involuntary loss of urine with a sudden increase in abdominal pressure. These patients leak when they sneeze, laugh, cough, or exercise. It is the most common type of incontinence. It affects women more frequently than men, often starting after the trauma of childbirth.
- Urge urinary incontinence occurs when patients have a sudden urge to urinate and subsequent loss of bladder control. It is associated with detrusor muscle hyperactivity. Urge incontinence occurs in both men and women, with a higher incidence among the elderly.
- Mixed urinary incontinence presents with symptoms of both stress and urge incontinence. It is more common to have mixed incontinence than to have solely urge incontinence.
- Overactive bladder is basically urge incontinence without the leaks. These patients are quick enough and mobile enough to get to the toilet before having an accident.
Other types of incontinence include overflow incontinence, functional incontinence, and variations of fecal incontinence. Each type has its own urinary incontinence ICD 10 code.
You May Like: Can Intercourse Cause A Urinary Tract Infection
Disorder Of Urinary System Unspecified
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- N39.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N39.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N39.9 other international versions of ICD-10 N39.9 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
How Is Urinary Incontinence Diagnosed
Your health care provider may use many tools to make a diagnosis:
- A medical history, which includes asking about your symptoms. Your provider may ask you to keep a bladder diary for a few days before your appointment. The bladder diary includes how much and when you drink liquids, when and how much you urinate, and whether you leak urine.
- A physical exam, which can include a rectal exam. Women may also get a pelvic exam.
- Urine and/or blood tests
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Urinary Tract Infection Without Antibiotics
The 4 Types Of Urinary Incontinence And How They Are Diagnosed
If youve ever leaked urine or had trouble getting to the bathroom quickly enough, youre not alone. Almost half of all women leak urine at some point in their lives a condition known as urinary incontinence.
Urinary incontinence can be frustrating and embarrassing. Fortunately, treatment can make a difference. At Virtuosa GYN in San Antonio, Texas, Dr. Susan Crockett offers patients with urinary incontinence a full range of treatment options, from lifestyle changes and exercise to medication and surgery.
To give you a better understanding of your condition, Dr. Crockett offers the following information about the main types of urinary incontinence, along with details about what causes them and how they are diagnosed and treated.
Urinary Tract Infection Site Not Specified

- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific Code
- N39.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2023 edition of ICD-10-CM N39.0 became effective on October 1, 2022.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N39.0 – other international versions of ICD-10 N39.0 may differ.
“use additional code”
You May Like: Pessary Ring For Urinary Incontinence
Did I Prescribe The Right Treatment
When youve diagnosed the patient and figured out the correct urinary incontinence ICD 10 code, its time to recommend an appropriate treatment. Primary care physicians and gynecologists may not be familiar with all the at-home options to treat their stress urinary incontinence patients. Typical suggestions include Kegel exercises and limiting fluid intake, and currently, there are no medications approved to treat stress urinary incontinence. Invasive treatments include surgery, internal tissue manipulation, and intravaginal monitoring and stimulation, plus these treatments typically require a specialists care.
For patients with mild to moderate incontinence symptoms, it may be preferential for the primary care physician or gynecologist to provide conservative care directly. This approach results in more immediate care for the patient, continuity of care to monitor progress, and minimized costs.
- Have trouble performing Kegel exercises correctly .
- Prefer the convenience and privacy of in-home treatment.
- Need care after their 6-week postpartum checkup.
Urinary Tract Infection Site Not Specifiedn390
Chapter 14 – Diseases of the genitourinary system » Other diseases of the urinary system » Urinary tract infection, site not specified
Related MeSH Terms
1 indication for 200 drugs
Diseases » Infections » Urinary Tract Infections
Diseases » Urogenital Diseases » Urologic Diseases » Urinary Tract Infections
Inflammatory responses of the epithelium of the URINARY TRACT to microbial invasions. They are often bacterial infections with associated BACTERIURIA and PYURIA. MeSH
Hierarchy Tree View
YOU AGREE THAT THE INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE IS PROVIDED AS IS, WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT OF ANY THIRD-PARTY PATENT, COPYRIGHT, OR ANY OTHER THIRD-PARTY RIGHT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE CREATORS OF THE WEBSITE OR WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF OR IN ANY WAY CONNECTED WITH THE WEBSITE, THE USE OF THE WEBSITE, OR THIS AGREEMENT, WHETHER IN BREACH OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, EVEN IF SUCH PARTY IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Also Check: Ams 800 Urinary Control System
What Is An Acute Bladder Infection
Acute cystitis is a sudden inflammation of the urinary bladder. Most of the time, a bacterial infection causes it. This infection is commonly referred to as a urinary tract infection . Irritating hygiene products, a complication of certain diseases, or a reaction to certain drugs can also cause acute cystitis.
Read Also: Spinal Stenosis And Urinary Retention
Personal History Of Diseases Of Urinary System
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
- History of chronic urinary tract infection
- History of febrile urinary tract infection
- History of febrile uti
- History of of recurrent uti
- History of recurrent urinary tract infection
- History of recurrent uti
- History of urinary tract infection
- History of urinary tract infection
- Z87.440 is considered exempt from POA reporting.
- 951 Other factors influencing health status
You May Like: Mrx Rc Feline Multi Urinary Calm
Predictors Of Antibiotic Duration
Having 3 or more visits with urology increased therapy days by 28% , but this was not the case for primary care patients with 3 or more visits or urology patients with 2 visits . We found no evidence to support our hypothesis that a shorter interval between visits was associated with longer duration of therapy.
Table 5. Factors Associated With Antibiotica Duration in Days Using Generalized Estimating Equations Poisson Regression
Note. RR, relative risk CI, confidence interval aOR, adjusted relative risk DM, diabetes mellitus.
Bold text indicates a significant finding, or a finding with a P-value < 0.05.
a Includes -lactams, fluoroquinolones, nitrofurantoin, and TMP-SMX, while excluding ceftriaxone . When visits contained duplicate entries for same antibiotic , only 1 instance was used for the analysis.
b Includes patients seeking care at family medicine or internal medicine practice.
c Different sample size compared to the overall sample size , as no interval available for first visit.
d Defined as having a urine culture on the previous visit with resistance to either nitrofurantoin or TMP-SMX.
e Different sample size compared to overall sample size not each visit had a prior visit with susceptibility data.
What Is The Diagnosis Code For Uti
Diagnosis Coding for UTIs Coding for urinary tract infections in ICD-10 requires a knowledge of the ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting and the chapter-specific guidelines in Chapter 14, Diseases of the Genitourinary System . The codes for UTIs are located in different blocks within Chapter 14 based on anatomical site.
Don’t Miss: How To Dissolve Urinary Crystals In Cats
Treatment For Uti Icd 10
It is highly important to understand the symptoms and causes of a urinary tract infection in order to treat the infection effectively and minimize the risk of getting infected.
The patient needs to stay hydrated, urinate when the need arises, wipe from front to back after using the toilet a good sexual hygiene is needed. Doctors usually treat Urinary Tract Infection with antibiotics.
Analysis Of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection Management In Women Seen In Outpatient Settings Reveals Opportunities For Antibiotic Stewardship Interventions

Published online by Cambridge University Press: 17 January 2022
- Department of Family and Community Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas
- Barbara W. Trautner
- Affiliation:Section of Health Services Research, Department of Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TexasDepartment of Surgery, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TexasCenter for Innovations in Quality, Effectiveness and Safety , Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Houston, Texas
- Roger J. Zoorob
- Department of Family and Community Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas
- George Germanos
- Affiliation:Department of Family and Community Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TexasDepartment of Internal Medicine, Baylor Scott and White Health, Round Rock, Texas
- Michael Hansen
- Department of Family and Community Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas
- Jason L. Salemi
- College of Public Health, University of South Florida, Tampa, Florida
- Kalpana Gupta
- VA Boston Healthcare System, Boston, MassachusettsBoston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts
- Larissa Grigoryan
- Department of Family and Community Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas
- *
Also Check: Can Cranberry Pills Cure A Urinary Tract Infection
What Are The Treatments For Urinary Incontinence
Treatment depends on the type and cause of your UI. You may need a combination of treatments. Your provider may first suggest self-care treatments, including
- Lifestyle changes to reduce leaks:
- Drinking the right amount of liquid at the right time
- Being physically active
- Staying at a healthy weigh
- Avoiding constipation
If these treatments do not work, your provider may suggest other options such as
- Medicines, which can be used to
- Relax the bladder muscles, to help prevent bladder spasms
- Block nerve signals that cause urinary frequency and urgency
- In men, shrink the prostate and improve urine flow
Read Also: Can Allergies Cause Urinary Problems
How Is Uti Icd 10 Diagnosed
There are two types of UCTs that lead to UTIs urine infections and urethritis . Urinary tract infections happen when the bacteria in the urinary tract get into the urine or small amounts of urine.
If a doctor suspects that the UTI is caused by bacteria, they may use a simple urine test to diagnose the infection. A negative result is sufficient to diagnose a UTI, which is quite easy to diagnose.
If a person has a culture test, the lab technicians will take the urine and culture it to see if there are bacteria in the urine. If the test is positive, it means that the bacteria got into the urine. The test takes at least 2 days, but usually takes 8 days to be fully positive.
Also Check: Is Urinary Tract Infection A Sexually Transmitted Disease
The Icd Code N390 Is Used To Code Pyuria
In medicine, pyuria /pajri/ is the condition of urine containing white blood cells or pus. Defined as the presence of 6-10 or more neutrophils per high power field of unspun, voided mid-stream urine. It can be a sign of a bacterial urinary tract infection. Pyuria may be present in the septic patient, or in an older patient with pneumonia.