Check If It’s A Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms of a urinary tract infection may include:
- pain or a burning sensation when peeing
- needing to pee more often than usual during the night
- pee that looks cloudy, dark or has a strong smell
- needing to pee suddenly or more urgently than usual
- needing to pee more often than usual
- lower tummy pain or pain in your back, just under the ribs
- a high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
The Most Common Symptom Is A Burning Sensation When You Pee
Other symptoms include:
- Nausea and vomiting, especially if you’re dehydrated from not drinking enough liquid . If you have diarrhea, this can make it hard to keep up with urinationyou might need to change positions or wear extra clothes while doing so. Additionally, some people with UTI may experience blood in their urine . This is most common among young girls who haven’t been sexually active yet it’s also linked with eating disorders like anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa. If you notice blood on your underwear or bedding after urinating at night and before getting up in the morningor if there’s any other unusual amount of bright red drainage coming out of your urinary tractit could be a sign that something else is wrong besides just having an ordinary UTI!
Older Adults Dont Need Powerful Antibiotics For Utis
Treatment for UTIs should begin with narrow-spectrum antibiotics, say Dr. Lathia and Dr. Goldman.
These drugs are less likely to lead to antibiotic resistance and problematic side effects than broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Today, amoxicillin is commonly prescribed as first-line treatment for UTIs in older adults.
Other common narrow-spectrum must be used with caution when patients have chronic kidney disease or take blood pressure medication, as many older adults do or because their side effects can be serious in older adults.
Read Also: How To Kill E Coli Bacteria In Urinary Tract
How To Use Spermicide
The insertion method may vary slightly with different forms of spermicide, but they typically come with an applicator, so people can lie down, squat, or put one foot on a chair and insert it. Most spermicides are only effective for 1 hour after insertion. A person should also reinsert spermicide for each act of penetrative sex.
It is also advisable that people use spermicide together with another barrier form of birth control, such as a condom.
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections
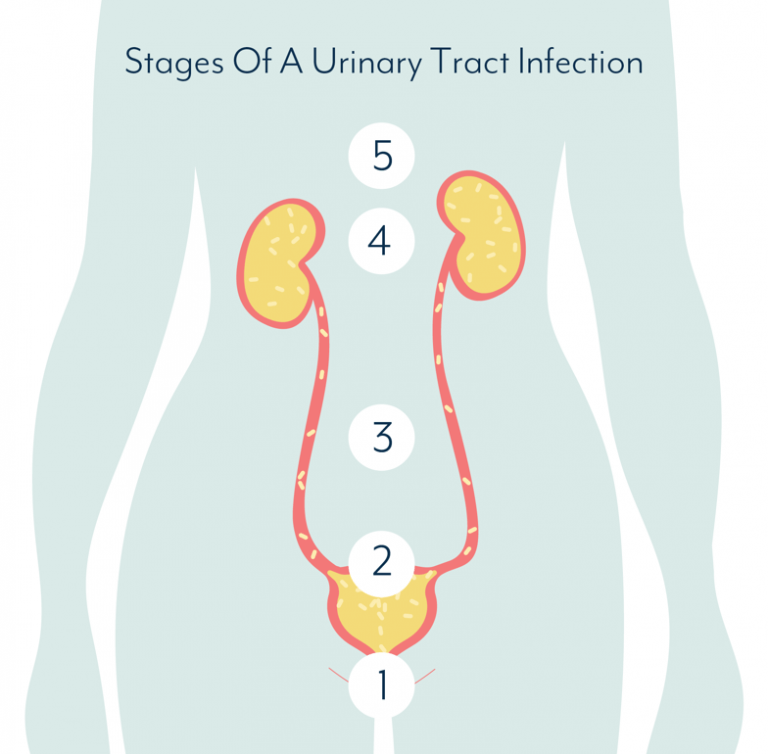
Most women who have had an uncomplicated UTI have occasional recurrences. Many of these women get another infection within a year of the previous one. A much smaller number of women have ongoing, recurrent urinary tract infections, which follow the resolution of a previously treated or untreated episode.
Recurrence is often categorized as either reinfection or relapse:
- Reinfection. Most cases of recurring UTIs are reinfections. A reinfection occurs several weeks after antibiotic treatment has cleared up the initial episode. It can be caused by the same bacterial strain that caused the original episode or a different one. The infecting organism is usually introduced from fecal matter and moves up through the urinary tract.
- Relapse. Relapse is the less common form of recurrent UTI. It is diagnosed when a UTI recurs within 2 weeks of treatment of the first episode and is due to treatment failure. Relapse usually occurs in kidney infection or is associated with obstructions such as kidney stones, structural abnormalities or, in men, chronic prostatitis.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection In Boys
Treatments For Specific Populations
Treating Pregnant Women
Pregnant women should be screened for UTIs, since they are at high risk for UTIs and their complications. Antibiotics used for treating pregnant women with UTIs include amoxicillin, ampicillin, nitrofurantoin, and cephalosporins . Fosfomycin is not as effective as other antibiotics but is sometimes prescribed for pregnant women. In general, there is no consensus on which antibiotic is best for pregnant women although some types of antibiotics, such as fluoroquinolones and tetracyclines, should not be taken as they can cause harm to the fetus.
Pregnant women with asymptomatic bacteriuria have an increased risk for acute pyelonephritis in their second or third trimester. They need screening and treatment for this condition. In such cases, they should be treated with a short course of antibiotics . For an uncomplicated UTI, pregnant women may need longer-term antibiotics .
Treating Children with UTIs
Children with UTIs are generally treated with TMP-SMX, cephalexin and other cephalosporins, or amoxicillin/clavulanic acid . These drugs are usually taken by mouth in either liquid or pill form. Doctors sometimes give them as a shot or IV. Children usually respond to treatment within a few days. Prompt treatment with antibiotics may help prevent renal scarring.
Children with acute kidney infection are treated with various antibiotics including oral cefixime or a short course of an intravenous antibiotic . An oral antibiotic then follows the IV.
Why Do I Need Urinalysis
Healthcare providers order urinalysis tests for several reasons since a urine sample can provide many insights into your health. Your provider may order a urinalysis for you for one or more of the following reasons:
- As part of your routine medical exam to screen for early signs of certain health conditions.
- If youre experiencing and signs and symptoms of certain health conditions, such as diabetes or kidney disease.
- To monitor certain health conditions you’re receiving treatment for, such as diabetes or kidney disease.
- To diagnose a urinary tract infection .
- If youve been admitted to a hospital.
- As a preparatory checkup for surgery.
Recommended Reading: Royal Canin Urinary So Coupons
How Are Urinary Tract Infections Treated
You will need to treat a urinary tract infection. Antibiotics are medicines that kill bacteria and fight an infection. Antibiotics are typically used to treat urinary tract infections. Your healthcare provider will pick a drug that best treats the particular bacteria thats causing your infection. Some commonly used antibiotics can include:
- Nitrofurantoin.
Its very important that you follow your healthcare providers directions for taking the medicine. Dont stop taking the antibiotic because your symptoms go away and you start feeling better. If the infection is not treated completely with the full course of antibiotics, it can return.
If you have a history of frequent urinary tract infections, you may be given a prescription for antibiotics that you would take at the first onset of symptoms. Other patients may be given antibiotics to take every day, every other day, or after sexual intercourse to prevent the infection. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best treatment option for you if you have a history of frequent UTIs.
When Should I Call A Doctor For A Urinary Tract Infection
Sometimes, the bodys natural immune system fights off the infection quickly without medical intervention. Most urinary tract infections, however, will not resolve themselves, and they can become severe quickly. If symptoms persist for more than a few days, its a good idea to speak with a doctor and begin taking antibiotics. There are some over-the-counter test strips that can help identify the presence of bacteria in the urine if you wish to check for an infection before pursuing medical care.
If your primary symptom is frequent urination accompanied by burning, you may wish to try an over-the-counter remedy for a few days. Beware, however, that drugs like AZO can suppress the symptoms of a UTI without treating its cause, which may actually worsen the infection. Always use caution when using any home remedies without antibiotics.
If you develop lower back pain or pelvic pain in conjunction with a fever or nausea, be sure to get medical assistance right away. These are signs of a severe infection that has spread to the kidneys. Left untreated, this infection may cause kidney damage and ultimately lead to kidney failure. It could also release the bacteria into your bloodstream, leading to a life-threatening infection.
Read Also: Stds That Cause Urinary Retention
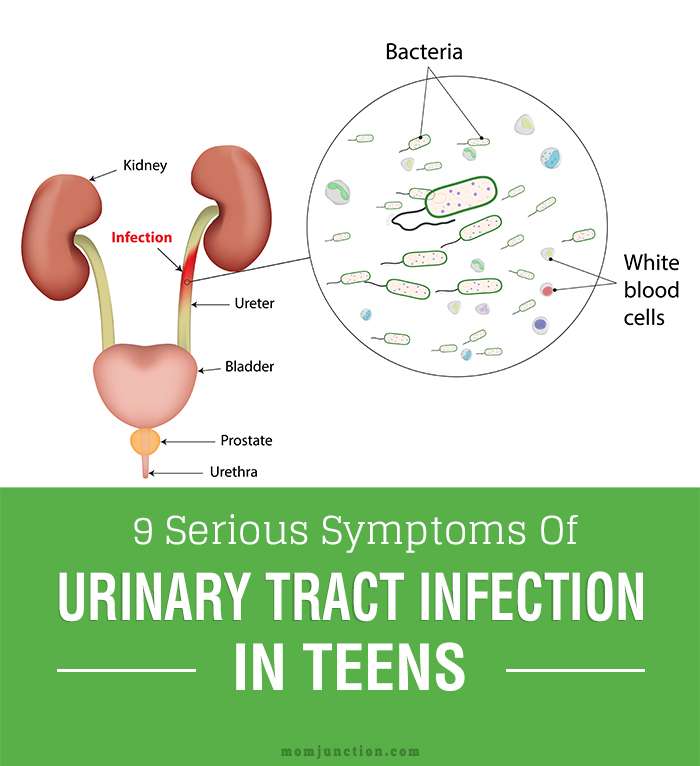
What Is Urinary Tract Infection
UTI is a fungal or bacterial infection in any of the 4 parts of the urinary tract. The urinary tract includes the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, and the kidneys. The urethra and bladder are called the lower urinary tract, and the ureters and kidneys comprise the upper urinary tract. An infection will most commonly begin in the urethra and move up through the rest of the urinary tract. The majority of UTI cases are diagnosed and treated while still in the lower tract. When fungi or bacteria enter the urethra, the bodys own immune system will fight against them, and will usually kill them before an infection takes hold. If, for some reason, the body is not able to fight them off on its own, a UTI results.
Generally, a person who gets UTI will have one or more of the following risk factors:
Bowel incontinence
A recent medical procedure involving the urinary tract
How Can I Prevent Chronic Urinary Tract Infections
- Keep your genital area clean
- Wipe from front to back after a bowel movement
- Drink plenty of fluids, particularly water, to flush bacteria out of your urinary system
- Urinate immediately after intercourse to help eliminate any bacteria
- Use forms of birth control other than a diaphragm and spermicides
- Avoid douches, powder and deodorant sprays
- Wear un-dyed, full cotton underwear
Other prevention measures being studied include drinking cranberry juice and, for women past menopause, the use of estrogen cream or pills.
Don’t Miss: Azo Urinary Tract Defense Vs Urinary Pain Relief
How Long Will The Effects Last
For most UTIs, the symptoms go away within 24 hours after you begin treatment. Take all of the medicine your healthcare provider prescribes, even after the symptoms go away. If you stop taking your medicine before the scheduled end of treatment, the infection may come back.
Without treatment, the infection can last a long time. If it is not treated, the infection can permanently damage the bladder and kidneys, or it may spread to the blood. If the infection spreads to the blood, it can be fatal.
When Should I Be Concerned About Pelvic Pain
Pelvic pain may be serious if your symptoms developed suddenly or if the discomfort is severe. If you have pelvic pain that lasts for more than two weeks, schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Pelvic pain can be concerning and because its a symptom of so many conditions, it can be particularly frustrating. Your healthcare provider can help determine the cause of your pelvic pain so you can receive the treatment you need to feel better.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 06/20/2022.
References
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. . ACOG practice bulletin no. 51. Chronic pelvic pain. Obstetrics & Gynecology, 103, 589605. Accessed 6/20/2022.
- Andrews, J, Yunker, A, Reynolds, WS, et al. . Noncyclic chronic pelvic pain therapies for women: Comparative effectiveness . Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Accessed 6/20/2022.
- Merck Manual. Pelvic Pain. Accessed 6/20/2022.
- Merck Manual. Pelvic Pain During Early Pregnancy. Accessed 6/20/2022.
- Merck Manual. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease . Accessed 6/20/2022.
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services.Policy
Don’t Miss: Women’s Urinary Incontinence Treatment
What Does It Mean When You Have A Burning Sensation In Urine
Urinary tract infections, vaginal yeast infections, and sexually transmitted diseases, such as Chlamydia, gonorrhea or herpes, are common causes. Urinary burning will also occur if you experience damage or injury to any of the structures of the urinary tract, including the kidney, bladder, urethra or ureter.
How can I stop the burning from an urinary tract infection?
To stop the burning associated with urinary tract infections, you must have the infection treated by a doctor. Not treating the infection can put you at risk for kidney damage and a severe infection, which may require hospitalization.
Am I At Risk Of A Uti
While UTIs can happen to anyone, they are more common in females who are sexually active or menopausal, or have health conditions such as diabetes or urinary incontinence. Females who use spermicides or diaphragms as contraception are also at increased risk of UTIs, and may benefit from other contraceptive options if they get recurrent UTIs.
Some people at greater risk of developing urinary tract infections:
- Females nearly 1 in 3 females will have a UTI that needs treatment before the age of 24.
- Males with prostate problems an enlarged prostate gland can cause the bladder to only partially empty, raising the risk of infection.
- Older people some medications and problems with incontinence mean that older people are more likely to get a UTI.
- People with urinary catheters people who are critically ill and people who cant empty their bladder are at a greater risk of infection.
- People with diabetes changes to the immune system make people with diabetes more vulnerable to infection.
- Infants babies in nappies commonly get UTIs, in particular, infants born with physical problems of the urinary system are at greater risk.
Recommended Reading: Signs Of A Urinary Tract Infection In A Man
Do Urinary Tract Infections Always Burn
Urinary tract infections dont always cause signs and symptoms, but when they do they may include: A strong, persistent urge to urinate. A burning sensation when urinating. Passing frequent, small amounts of urine.
How long does it take for the burning to go away with a UTI?
Pain and burning resolved within 1-3 days. After one week, symptoms resolved in about 60% of the patients.
Symptoms Of Utis In Older People
The classic lower UTI symptoms of pain, frequency, or urgency and upper tract symptoms of flank pain, chills, and tenderness may be absent or altered in older people with UTIs.
Symptoms of UTIs that may occur in seniors but not in younger adults include mental changes or confusion, nausea or vomiting, abdominal pain, or cough and shortness of breath. A preexisting health condition may further confuse the picture and make diagnosis difficult.
Also Check: How Does Someone Get A Urinary Tract Infection
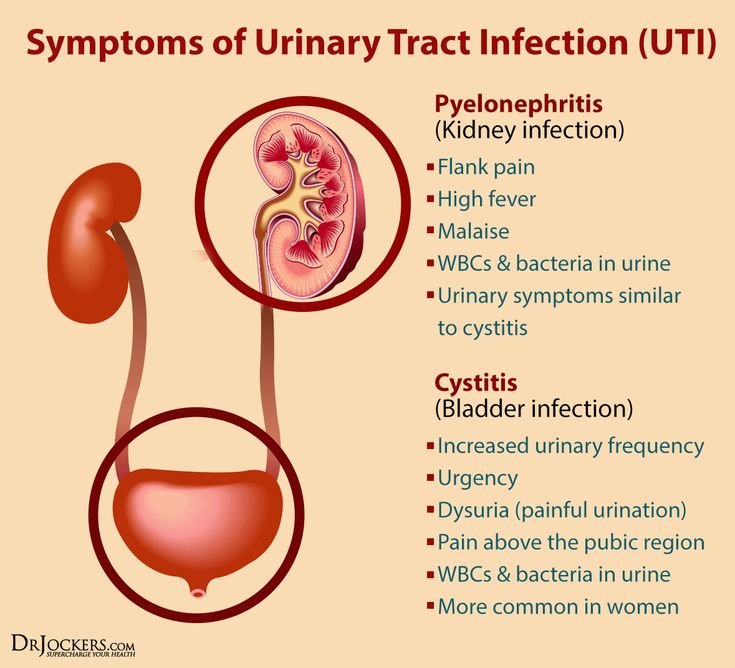
Symptoms Of Urinary Tract Infections
The symptoms of an infection in your upper urinary tract are different from symptoms of infection in your lower urinary tract .
However, in some cases you may notice the symptoms of both, as one can spread to the other.
Symptoms of a UTI are similar to those of many other conditions and don’t necessarily mean you have an infection.
When To See A Doctor About A Uti
As mentioned, antibiotics are typically needed to treat a UTI, so it’s important to seek prompt care if you notice the signs of one.
Especially if:
- Your symptoms are severe or getting worse
- Your symptoms don’t improve after a few days
- You’re getting recurrent UTIs
“Early and effective UTI treatment helps ensure that the infection is dealt with while it’s easiest to treat and before it progresses to the kidneys,” says Dr. Kannady. “Even a mild kidney infection can come with fairly debilitating symptoms, including fever, vomiting and intense pain. These infections also require a longer course of antibiotics.”
And the more serious the kidney infection, the greater the risk of complications. They can range from hospitalization to even permanent kidney damage or a life-threatening bloodstream infection in some cases.
In men, UTIs also can spread to the prostate and cause prostatitis which also often requires a longer course of antibiotics to treat.
“By initiating antibiotics as soon as a UTI is identified, we can greatly reduce the risk of these more complex and serious outcomes,” says Dr. Kannady.
Lastly, if your UTI symptoms don’t improve after taking antibiotics for a few days, be sure to follow up with your doctor.
Recommended Reading: Otc Urinary Tract Infection Medication
How Are Urinary Tract Infections Diagnosed
Your doctor will use the following tests to diagnose a urinary tract infection:
- Urinalysis: This test will examine the urine for red blood cells, white blood cells and bacteria. The number of white and red blood cells found in your urine can actually indicate an infection.
- Urine culture: A urine culture is used to determine the type of bacteria in your urine. This is an important test because it helps determine the appropriate treatment.
If your infection does not respond to treatment or if you keep getting infections over and over again, your doctor may use the following tests to examine your urinary tract for disease or injury:
- Ultrasound: In this test, sound waves create an image of the internal organs. This test is done on top of your skin, is painless and doesnt typically need any preparation.
- Cystoscopy: This test uses a special instrument fitted with a lens and a light source to see inside the bladder from the urethra.
- CT scan: Another imaging test, a CT scan is a type of X-ray that takes cross sections of the body . This test is much more precise than typical X-rays.
Prevention Of Urinary Tract Infections
In order to prevent the development of UTIs, it is important to drink plenty of water, urinate when you feel the urge, rather than holding urine for extended periods, and urinate after intercourse. Certain substances, such as cranberry pills, lactobacillus, and methenamine may be prescribed to those who are frequently afflicted by UTIs.
You May Like: Antibiotic For Women’s Urinary Tract Infection
How Can I Prevent Utis
Its not always possible to prevent UTIs, but theres things you can do to try.
Things to do
Things to avoid
If you or someone you look after needs help washing, going to the toilet or getting dressed, its important to get the help you need. Find out more about arranging care and support.
My 94-year-old father got a UTI and the hospital staff assumed he had dementia, because he wasnt making any sense. I had to make sure they knew this wasnt normal for him.
| Leicester