How Does A Male Get A Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections, bacterial in nature are quite common in men and cause a lot of discomforts. The infection can be anywhere in the urinary tract system which consists of urethra, ureters, bladder, and kidney. UTIs are more common in females as compared to males. But that does not mean males dont need to take precautionary measures or be aware of the causes of urinary tract infections.
How To Prevent Urinary Tract Infections In Men
Younger men cant do too much in terms of preventing a UTI, according to Trost. But older men can take a few steps to lower their risk. One of the best defense mechanisms against UTIs is to completely empty the bladder every time you urinate, says urologist Howard B. Goldman MD, professor and institute vice chairman for quality at the Glickman Urologic and Kidney Institute at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio.
Its also important to drink lots of fluids, especially water, every day. If you already have a UTI, drinking plenty of fluids can help push the bacteria out of the urinary tract and in some very mild UTI cases, that could be enough to treat it. But if you notice any of the signs of a UTI, itâs still very important to head to your doctor for a diagnosis and treatment recommendation.
Without proper UTI treatment, the infection can quickly spread and become a serious and sometimes even fatal threat. So donât brush off symptoms like frequent urination or a burning sensation when you urinate, and donât assume that you canât get a UTI just because youâre a man. Its important that you get these symptoms checked out promptly, too.
Understanding Urinary Tract Infections In Men
Can a man get a urinary tract infection? A surprising number of people assume that only women can get a UTI. While the chance of women getting a UTI is highabout 1 in 2 women will get a urinary tract infection at some point in their livesmen can still contract urinary tract infections.
Urinary tract infections lead to an estimated 8.3 million doctor visits each year. About 20 percent of those cases are from men.
Urinary tract infections are rare in men younger than 50 years old, but the chances of contracting a UTI increase as men get older. Lets take a closer look at urinary tract infections in men, what causes them, symptoms, and how you can treat and prevent them.
Read Also: Urinary Tract Infection In Boy Toddler Symptoms
Other Ways To Prevent Recurring Utis
If you have more than 3 UTIs in 1 year, or 2 UTIs in 6 months, there are other things that may help prevent UTIs.
There is some evidence that women under 65 years old who keep getting UTIs may find it helpful to take:
- a supplement called D-mannose this is not recommended for pregnant women
- cranberry products, such as juice or tablets
Speak to your doctor before taking any of these during pregnancy.
Be aware that D-mannose and cranberry products can contain a lot of sugar.
Page last reviewed: 18 November 2020 Next review due: 18 November 2023
Living With Urinary Tract Infections
If you have 3 or more urinary tract infections each year, your doctor may want you to begin a preventive antibiotic program. A small dose of an antibiotic taken every day helps to reduce the number of infections. If sexual intercourse seems to cause infections for you, your doctor many suggest taking the antibiotic after intercourse.
Read Also: What Is The Most Common Antibiotic For Urinary Tract Infection
Recognizing Uti Symptoms In Men
Some people dont have any symptoms with a urinary tract infection, which usually entails an inflammation of the bladder and can also involve an infection of the lower or upper urinary tract, and in more serious cases the kidneys. In addition, not every man, woman, or child who gets a UTI has typical UTI symptoms, but most do exhibit at least one or more signs of infection. And when men do get UTIs, their symptoms are generally not too different from those that women experience. Common UTI symptoms include:
RELATED: The Link Between UTIs and Sex: Causes and How to Prevent Them
Who Gets Urinary Tract Infections
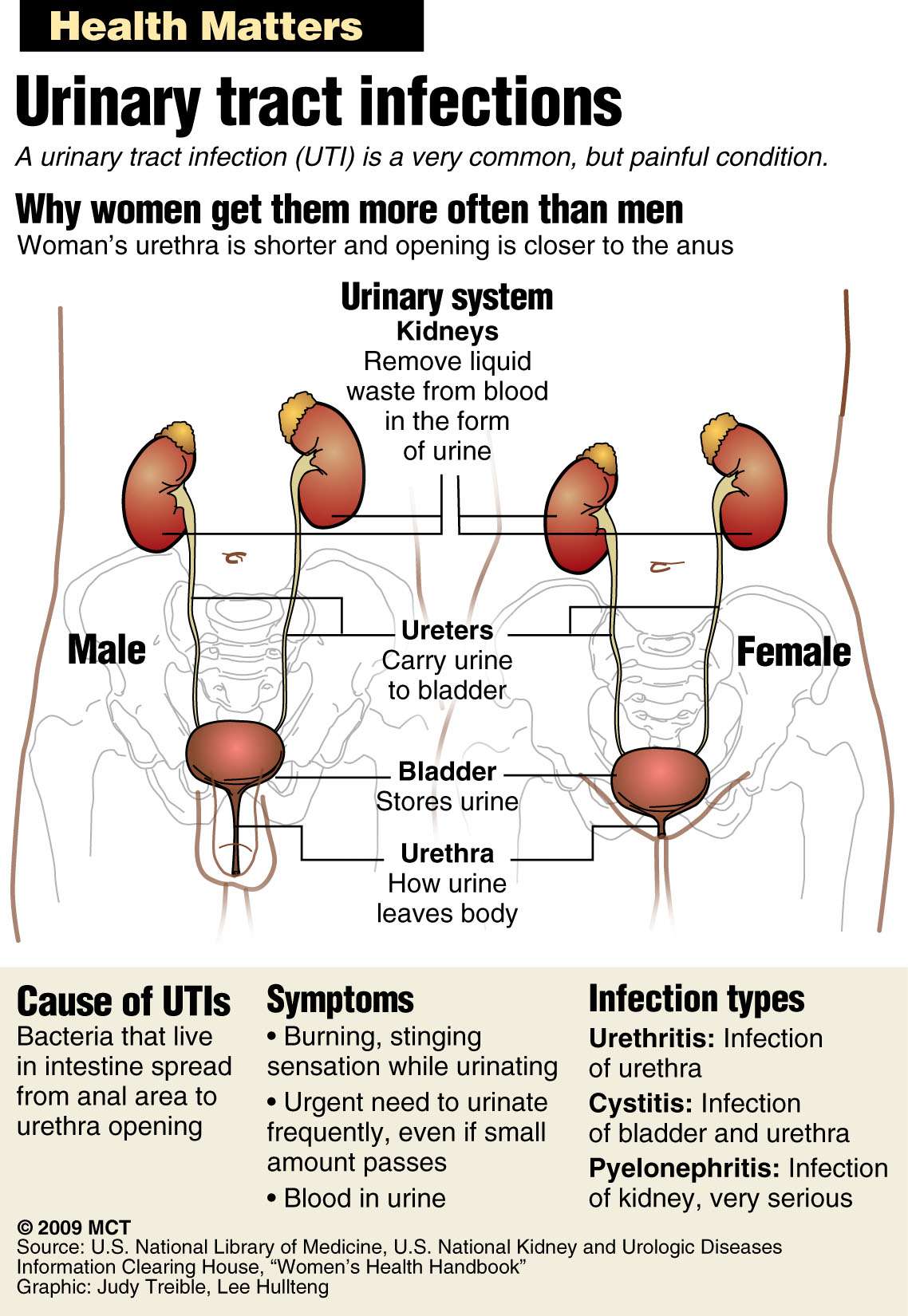
Anyone can get a urinary tract infection, but they are more common in women. This is because the urethra in females is shorter and closer to the anus, where E. coli bacteria are common. Older adults also are at higher risk for developing cystitis. This increased risk may be due to incomplete emptying of the bladder. There are several medical conditions that can be related to this, including an enlarged prostate or a bladder prolapse .
If you get frequent urinary tract infections, your healthcare provider may do tests to check for other health problems such as diabetes or an abnormal urinary systemthat may be contributing to your infections. People with frequent UTIs are occasionally given low-dose antibiotics for a period of time to prevent the infection from coming back. This cautious approach to treating frequent UTIs is because your body can develop a resistance to the antibiotic and you can get other types of infections, such as C. diff colitis. This practice is used very infrequently.
You May Like: Can Urinary Incontinence Be Cured
Myth: Utis Are Nothing To Worry About
Fact: Though painful and uncomfortable, you may think of UTIs as a minor, temporary condition. UTIs can go away on their own or be treated with a course of antibiotics, and though you should never ignore them, most are not cause for alarm. However, UTIs can cause serious complications, including for men.
Men are likelier than women to get UTIs from bacteria that is already present in their body, which poses a risk of the infection spreading. Some complicated UTIs can even cause kidney damage. If you have chronic UTIs, men risk the narrowing of their urethra which can create problems with urinating, in turn increasing your risk of further UTIs.
If you have symptoms of a UTI, including painful urination and cloudy urine, it is important to get checked as soon as possible. So make an appointment with Drs. Herman, Kester, and the Urology Center of Florida today for treatment and relief.
You Might Also Enjoyâ¦
Donât Miss: What Can I Do To Prevent Urinary Tract Infections
Are Any Tests Needed
A urine sample can confirm the diagnosis and identify the germ causing the infection. Further tests are not usually necessary if you are otherwise well and have a one-off infection. However, your doctor may advise tests of your kidney, prostate gland, or bladder if an underlying problem is suspected.
An underlying problem is more likely if the infection does not clear with an antibiotic medicine, or if you have:
- Symptoms that suggest a kidney is infected .
- Recurring urine infections. For example, two or more in a three-month period.
- Had problems with your kidney in the past, such as kidney stones or a damaged kidney.
- Symptoms that suggest an obstruction to the flow of urine.
- Blood-stained urine which persists after treatment with antibiotics.
Tests may include:
- An examination of your prostate gland by examination of your back passage .
- Tests to see how well your bladder is working, called urodynamic tests.
You May Like: Medicine To Take For Urinary Tract Infection
Causes Of Urinary Tract Infections
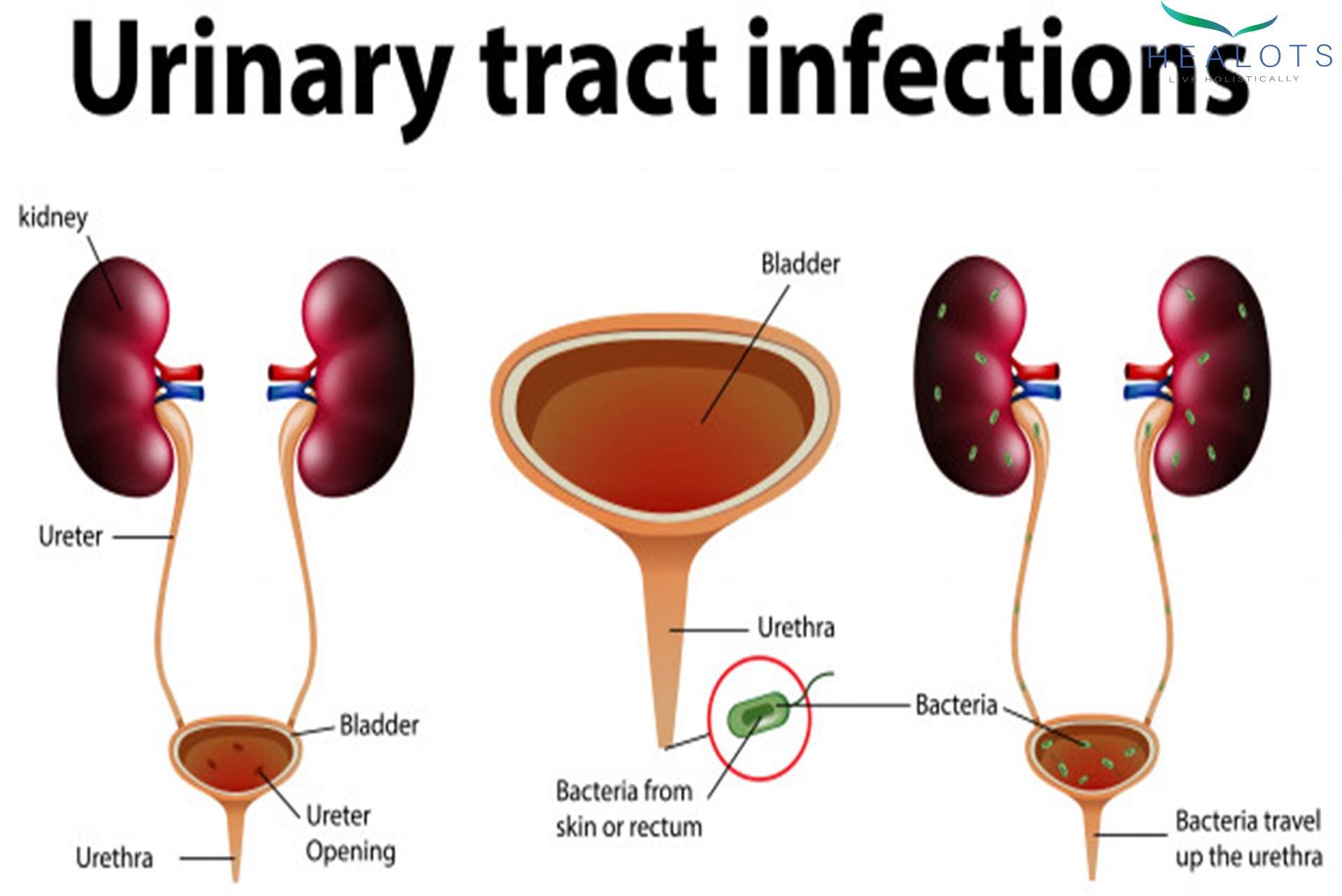
UTIs are usually caused by bacteria from poo entering the urinary tract.
The bacteria enter through the tube that carries pee out of the body .
Women have a shorter urethra than men. This means bacteria are more likely to reach the bladder or kidneys and cause an infection.
Things that increase the risk of bacteria getting into the bladder include:
- having sex
-
do not use scented soap
-
do not hold your pee in if you feel the urge to go
-
do not rush when going for a pee try to fully empty your bladder
-
do not wear tight, synthetic underwear, such as nylon
-
do not drink lots of alcoholic drinks, as they may irritate your bladder
-
do not have lots of sugary food or drinks, as they may encourage bacteria to grow
-
do not use condoms or diaphragms with spermicidal lube on them try non-spermicidal lube or a different type of contraception
How Does It Occur
Normally the urinary tract does not have any bacteria or other organisms in it. Bacteria that cause UTI often spread from the rectum to the urethra and then to the bladder or kidneys. Sometimes bacteria spread from another part of the body through the bloodstream to the urinary tract. Urinary tract infection is less common in men than in women because the male urethra is long, making it difficult for bacteria to spread to the bladder.
Urinary tract infection may be caused by a sexually transmitted disease. Sometimes a stone in the urinary tract blocks the flow of urine and causes an infection. In older men, an enlarged prostate can cause a urinary tract infection by keeping urine from draining out of the bladder completely. Infection might also be caused by the use of a catheter used to drain the bladder or by urethral stricture, which is a narrowing of the urethra by scar tissue from previous infections or surgical procedures.
You may be more likely to have a UTI if you have diabetes or another medical problem that affects the immune system.
Recommended Reading: Purina One Urinary Tract Reviews
Simple Tips For Men To Stay Safe From Urinary Tract Infections
- Have lots of water and healthy fresh juices to flush out the bacteria from the body, especially urinary tract.
- You should never hold the urge to pass the urine for long. It can cause the urinary tract to retain bacteria.
- Try to completely pass the urine, so that the bladder is completely empty.
- Maintain proper hygiene of the penis, especially when you are not circumcised. Clean and wash the intimate area properly so that no harmful bacteria can grow under the foreskin.
- Have foods rich in Vitamin C such as kiwi, orange, cantaloupe, melon, lemon, broccoli, papaya, etc. Vitamin C kills the harmful bacteria causing urinary infections and improves the overall functioning of the urinary system.
- Cranberry juice is a wonderful home remedy for urinary infections. Just make sure that you consume it without any added sugar for the best results.
- Probiotics majorly promote good health of the gut. The good bacteria called lactobacillus, found in probiotic yogurt, kefir, kimchi boost the health of your gut. It also prevents the unusual growth of the bacteria. So, keep the urinary tract free of any kind of infection.
- Use garlic or its extract in your diet. It has amazing anti-microbial properties that prevent UTIs.
How Can I Take Care Of Myself
- Follow your healthcare provider’s treatment. Take all of the antibiotic that your healthcare provider prescribes, even when you feel better. Do not take medicine left over from previous prescriptions.
- Drink more fluids, especially water, to help flush bacteria from your system.
- If you have a fever:
- Take aspirin or acetaminophen to control the fever. Check with your healthcare provider before you give any medicine that contains aspirin or salicylates to a child or teen. This includes medicines like baby aspirin, some cold medicines, and Pepto Bismol. Children and teens who take aspirin are at risk for a serious illness called Reye’s syndrome.
- Keep a daily record of your temperature.
Don’t Miss: Physical Therapy For Urinary Incontinence
How Do You Diagnose And Treat A Uti
To diagnose a UTI, your doctor may ask for a sample of your urine. Theyll use this for a urine culture to determine the levels of germs and bacteria in your urine. In rare cases, your doctor may also do an X-ray or ultrasound to get a more comprehensive look at your urinary tract.
If a UTI is confirmed, depending on the location and severity of the infection, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics.
For an uncomplicated lower tract infection, your doctor will likely prescribe a course of antibiotics to be taken over five to seven days.
If you have an upper tract infection, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics for three weeks or longer.
In the rare case of a severe infection, your doctor may recommend hospital treatment and a course of intravenous antibiotics.
How Men Can Prevent Utis
There are things men can do to reduce the chance of getting a UTI. These include:
- Dont hold urine for too long. Bacteria grow in it.
- Drink water to flush your kidneys.
- Practice good hygiene.
- Urinate after sex to flush bacteria from the urethra.
- If you have diabetes, control your blood sugar. High blood sugar can spill into the urine and bacteria thrive on it.
Recommended Reading: Can I Take Azo Urinary Pain Relief While Pregnant
How Common Are Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are very common, occurring in 1 out of 5 women sometime in their lifetime. Though UTIs are common in women, they can also happen to men, older adults and children. One to 2% of children develop urinary tract infections. Each year, 8 million to 10 million visits to doctors are for urinary tract infections.
Myth: Utis Can Be Treated By Cranberry Juice Or Probiotics
Fact: Its conventional wisdom that cranberry juice can help stop or even prevent a UTI. There is a scientific basis for it, given some of the properties of the drink. Cranberry juice has proanthocyanidin, a chemical that inhibits bacteria from sticking to the bladder. But studies show there is no evidence that it can stop or prevent urinary tract infections, and any evidence of probiotics helping to protect from UTIs are minor at best. If you think you may have a UTI, its important you see your doctor and follow a treatment plan, which may include taking a course of antibiotics.
Also Check: What Can Be Done For Urinary Incontinence
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection In Men
Urinary tract infections involve the parts of the body the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra that produce urine and carry it out of the body. Urinary tract infections often are classified into two types based on their location in the urinary tract:
- Lower tract infections These include cystitis and urethritis . Lower urinary tract infections commonly are caused by intestinal bacteria, which enter and contaminate the urinary tract from below, usually by spreading from the skin to the urethra and then to the bladder. Urethritis also may be caused by microorganisms that are transmitted through sexual contact, including gonorrhea and Chlamydia. Another form of male urinary infection is prostatitis which is an inflammation of the prostate.
- Upper tract infections These involve the ureters and kidneys and include pyelonephritis . Upper tract infections often occur because bacteria have traveled upward in the urinary tract from the bladder to the kidney or because bacteria carried in the bloodstream have collected in the kidney.
Donât Miss:
How Do Men Get Utis
In men the urethral opening is at the end of the penis a longer distance from the bladder than in women. Secretions from the prostate gland can also kill bacteria, so the frequency of a urinary tract infection is not as high.
But in men, kidney stones and enlarged prostates are common. Both of these can cause a urinary tract infection.
When men have an enlarged prostate, residual urine can stay in the bladder and collect bacteria, Dr. Bajic says. The enlarged prostate presses on the urethra and blocks urine flow so the bladder doesnt completely empty. This increases the chances of bacterial growth that can lead to a UTI.
Dr. Bajic says kidney stones can act as a sponge for bacteria. Even if the urinary tract infection clears up, the stones can act as a reservoir for bacteria to come back and create another infection, he adds. Sometimes the stones need to be removed to prevent infections from returning.
Acute bacterial prostatitis a prostate infection is another less common cause. This can be life threatening if not treated right away.
Men at higher risk include those who:
- Struggle with kidney stones.
- Participate in anal intercourse without condoms.
You May Like: Natural Remedies For Urinary Urgency
Acute And Chronic Prostatitis
In the 1800s, prostatitis was thought to be secondary to excessive alcohol consumption or physical or sexual activity. It was often associated with gonorrhea and could be fatal or lead to abscess formation. By the 1920s, most cases were attributed to microorganisms, and antibiotics combined with prostate massage were standard therapy after World War II. Although the role of bacteria was questioned in the 1950s, it was reemphasized in 1968 when Meares and Stamey described their “4-glass test.”
Acute prostatitis is caused by an acute infection of the entire prostate gland, resulting in fever and localized pain. Microscopically, neutrophilic infiltrates, diffuse edema, and microabscesses may be seen, which may coalesce into larger collections.
Chronic prostatitis may be caused by inflammatory or noninflammatory diseases. This condition may arise via dysfunctional voiding, intraprostatic reflux, chronic exposure to microorganisms, autoimmune mechanisms, irritative urinary metabolites, and as a variant of neuropathic pain. Chronic bacterial prostatitis often produces few or no symptoms related to the prostate, but it is probably the most common cause of relapsing UTI in men.
Chronic prostatitis has been subdivided by the National Institutes of Health into the following categories: