When May My Child Need To Be Hospitalized For A Uti
Your child may need to be hospitalized for the following reasons:
- If theyre a young infant or child.
- If they have a high fever.
- If they have back pain.
- If theyre dehydrated .
- If he or she is unable to tolerate oral antibiotics.
- When there is a concern that the infection has spread to their bloodstream.
How Are Utis Diagnosed In Children
A urine sample is needed to check if your child has a UTI. Your childs doctor or nurse will guide you on how to do this.
Once collected, your childs urine sample is usually first tested by dipping a special paper strip into the urine to check for a colour change that can indicate an infection. The doctor may also send the urine sample to a laboratory to check which bacteria are causing the infection and which antibiotic will be most effective against your childs UTI. These results may take up to 48 hours to return. Sometimes your child will need an ultrasound to check for any problems with the bladder or kidneys.
Urinary Tract Infection Toddlers Treatment
Antibiotics are prescribed to treat a urinary tract infection. Parents can also take some precautionary measures at home to help recovery.
- Hydration – Keep your toddler well hydrated. Drinking fluids prevents constipation and other urinary system disorders.
- Training – Discard soiled diapers immediately. In the case of toilet trained kids, teach them to wipe from front to back. This keeps the bacteria away from the urethra, limiting the chance of infection.
- Hygiene – Maintain strict hygiene. Watch your toddler wash their hands thoroughly after a visit to the bathroom.
Recommended Reading: Z Pack Urinary Tract Infection
Treatment If The Condition Gets Worse Or Recurs
If your child’s urinary tract infection does not improve after treatment with antibiotics, your child needs further evaluation and may need more antibiotics. Your child may have a structural problem that is making the infection hard to treat. Or the cause of the infection may be different from the types of bacteria that usually cause UTIs.
If the infection spreads and affects kidney function or causes widespread infection , your child may be hospitalized. These complications are rare, but they can be very serious. Children with impaired immune systems, untreated urinary tract obstructions, and other conditions that affect the kidneys or bladder are at higher risk for complications.
If tests show a structural problem in the urinary tract that increases your child’s risk for recurrent UTIs, the doctor may consider preventive antibiotics.
What Causes A Uti In Children
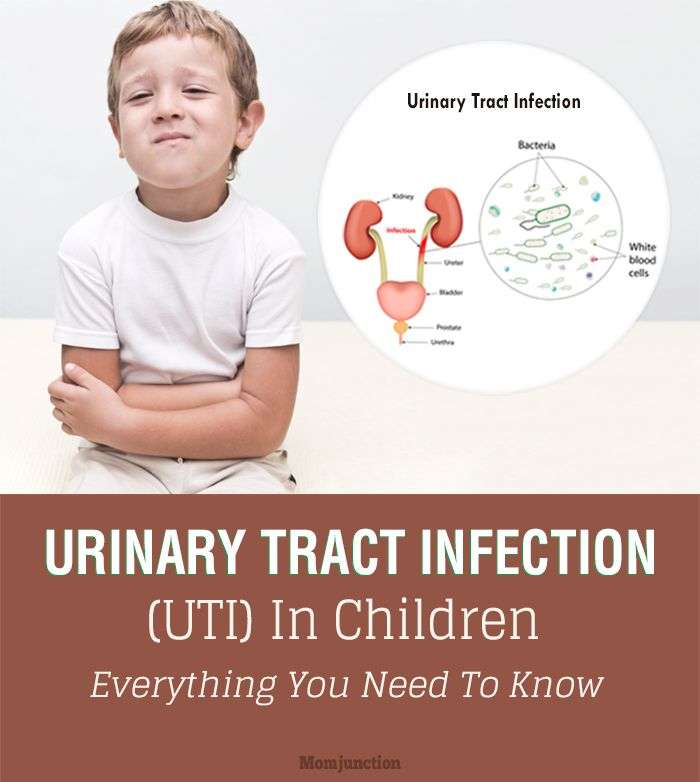
Bacteria, often the intestinal bacteria E. coli, can easily enter the urinary tract from the skin around the anus. UTIs are more common in girls, especially during potty training, because a girl’s urethra is shorter and closer to the anus. Uncircumcised baby boys also have a slightly elevated risk. Some risk factors for UTI are not preventable, including:
- A structural or functional abnormality in the urinary tract .
- An abnormal backward flow of urine from the bladder up the ureters and toward the kidneys, known as vesicoureteral reflux, which is very common in kids with UTIs.
In some cases, additional tests such as ultrasound or bladder x-rays may be recommended to look for these conditions and to determine the most effective treatment.
Don’t Miss: Physical Therapy For Urinary Incontinence
Types Of Utis In Children
Common types of UTIs include:
- Cystitis: this bladder infection is the most common type of UTI. Cystitis occurs when bacteria move up the urethra and into the bladder
- Urethritis: when bacteria infect the urethra
- Pyelonephritis: a kidney infection caused by infected urine flowing backward from the bladder into the kidneys or an infection in the bloodstream reaching the kidneys
What Is The Treatment
UTIs are treated with antibiotics. Usually the antibiotics needed are a liquid or tablets that can be taken at home.
If your child is less than three months of age or very unwell, it is likely they will be admitted to hospital to have antibiotics through a drip .
The earlier the treatment is started the better. If the doctor suspects your child has a UTI they will start him or her on antibiotics once a sample has been collected for testing at a laboratory. The type of antibiotics may be changed when the test results are available from the laboratory.
Antibiotics usually need to be taken for three to five days. It may take a day or two until your childs symptoms start to improve.
You May Like: Does Cranberry Juice Clean Urinary Tract
Key Points About A Uti In Children
- A urinary tract infection is inflammation of part of the system that takes urine out of the body.
- Most infections are caused by bacteria from the digestive tract. The most common is Escherichia coli bacteria. These normally live in the colon.
- A UTI is not common in children younger than age 5. A UTI is much more common in girls because they have a shorter urethra.
- A UTI is unlikely in boys of any age, unless part of the urinary tract is blocked. Uncircumcised boys are more at risk for a UTI than circumcised boys.
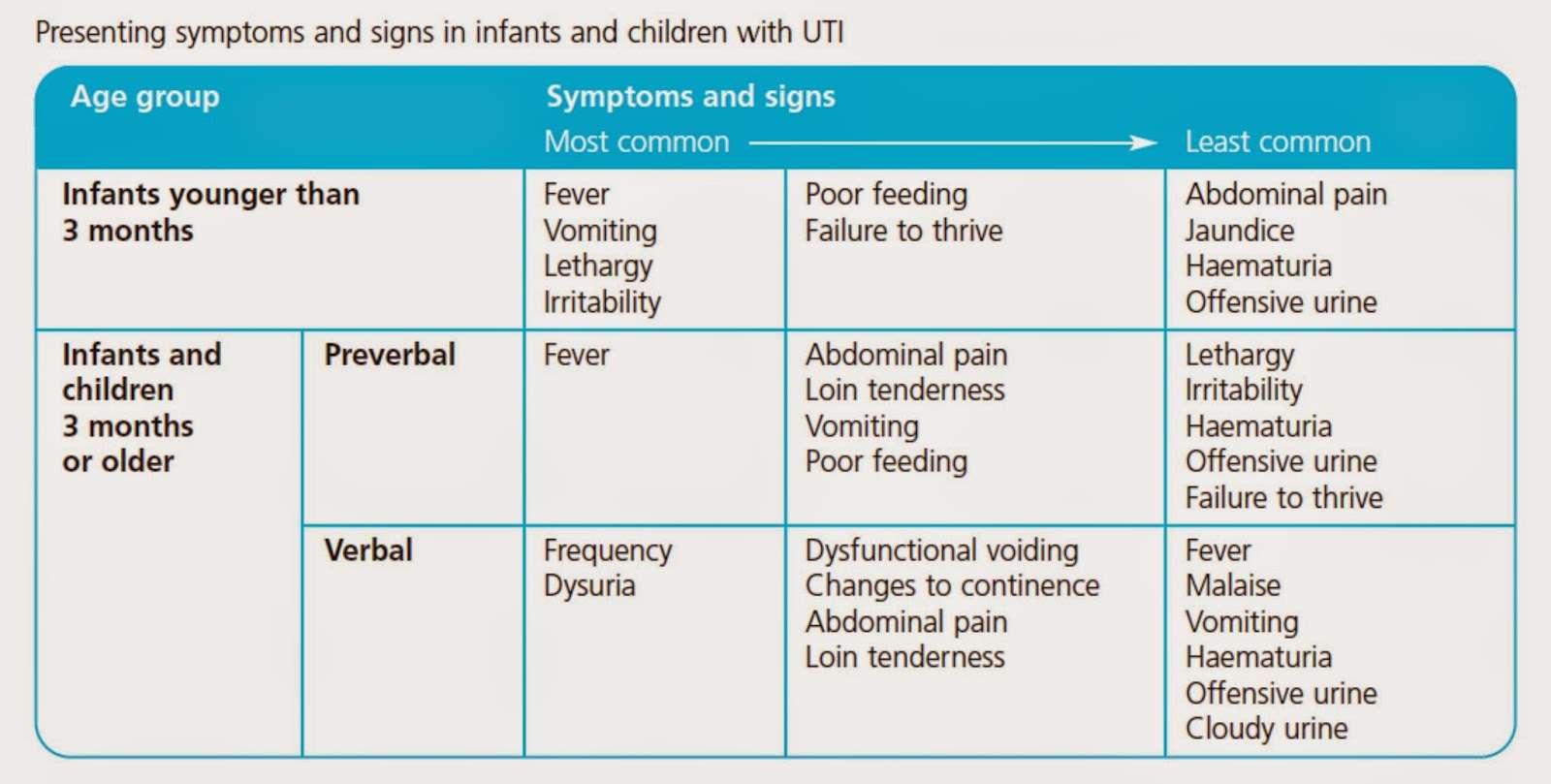
- Symptoms vary by age, and can include fever, need to urinate often, pain, and crying.
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Urinary Tract Infections In Children
BRETT WHITE, MD, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, Oregon
Am Fam Physician. 2011 Feb 15 83:409-415.
Acute urinary tract infections are relatively common in children, with 8 percent of girls and 2 percent of boys having at least one episode by seven years of age. The most common pathogen is Escherichia coli, accounting for approximately 85 percent of urinary tract infections in children. Renal parenchymal defects are present in 3 to 15 percent of children within one to two years of their first diagnosed urinary tract infection. Clinical signs and symptoms of a urinary tract infection depend on the age of the child, but all febrile children two to 24 months of age with no obvious cause of infection should be evaluated for urinary tract infection . Evaluation of older children may depend on the clinical presentation and symptoms that point toward a urinary source . Increased rates of E. coli resistance have made amoxicillin a less acceptable choice for treatment, and studies have found higher cure rates with trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole. Other treatment options include amoxicillin/clavulanate and cephalosporins. Prophylactic antibiotics do not reduce the risk of subsequent urinary tract infections, even in children with mild to moderate vesicoureteral reflux. Constipation should be avoided to help prevent urinary tract infections. Ultrasonography, cystography, and a renal cortical scan should be considered in children with urinary tract infections.
You May Like: What Can I Do To Prevent Urinary Tract Infections
Preventing Urinary Tract Infections In Boys
Many UTIs can be prevented by changing infants diapers frequently, encouraging kids to practice good hygiene, and instructing kids not to hold it when they have to pee because urine that remains in the bladder gives bacteria a good place to grow. Here are some tips on how to prevent UTIs in boys:
What Causes A Urinary Tract Infection In Toddlers
Normal urine is sterile and contains fluids, salts and waste products. An infection occurs when microorganisms cling to the opening of the urethra and begin to multiply. Most infections arise from Escherichia coli bacteria that normally live in the digestive tract.
Different bacteria can cause a urinary tract infection. The seven most common bacteria include the following:
- Escherichia coli , found in about 85% of UTIs in children.
- Klebsiella.
- Pain in the back or side .
- Fatigue.
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of A Severe Urinary Tract Infection
Avoiding Things That May Irritate Your Child’s Bottom
Try to avoid anything that may cause irritation to your child’s bottom:
- avoid giving your child bubble baths, especially if they have sensitive skin
- wash your child’s hair in the shower rather than in the bath so they don’t sit in soapy water
- check for threadworms, which are very common in children, and consider treating your child every 6 months
- encourage girls to wear cotton underwear
What Are The Symptoms

Babies and young children may not have the most common symptoms, such as pain or burning when they urinate. Also, they can’t tell you what they feel. In a baby or a young child, look for:
- A fever not caused by the flu or another known illness.
- Urine that has a strange smell.
- Vomiting.
- The child not being hungry.
- The child acting fussy.
Older children are more likely to have common symptoms, such as:
- Pain or burning when they urinate.
- Needing to urinate often.
- Loss of bladder control.
- Red, pink, cloudy, or foul-smelling urine.
- Pain in the flank, which is felt just below the rib cage and above the waist on one or both sides of the back.
- Lower belly pain.
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection In Pregnancy
How Can You Prevent Utis In The Future
Change your baby’s diapers often to prevent bacteria from growing. As your child gets older, teach them good bathroom habits to prevent UTIs. Instruct girls to wipe from front to back. This helps to prevent bacteria in poop from getting into the vagina and urinary tract. Encourage your kids to go to the bathroom as soon as they feel the urge — not to hold it in.
Girls should avoid bubble baths and should not use perfumed soaps. And, they should wear cotton underwear — not nylon — to improve airflow and prevent bacteria from growing.
Have your kids drink lots of water, which helps flush bacteria out of the urinary tract. Extra water also prevents constipation, which can create blockages in the urinary tract that allow bacteria to grow.
Causes Of Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infection develops when bacteria reach the bladder. In this situation, the bacteria start multiplying and infecting the area. Normally there are two types of urinary tract infections- one is a kidney infection, and the second one is a bladder infection. A kidney infection is more harmful than a bladder infection. When children suffer from a urinary infection, two types of abnormalities are mainly found to be associated : Vesicoureteral reflux and Urinary Obstruction.
Recommended Reading: Sacral Nerve Stimulation For Urinary Incontinence
Eating Diet & Nutrition
Food choices do not help prevent or treat bladder infections in children, but drinking plenty of liquids may help. Talk with a health care professional about how much liquid your child should drink, depending on his or her age, size, and other health conditions.
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and other components of the National Institutes of Health conduct and support research into many diseases and conditions.
What Are Risk Factors For Utis In Children
Risk factors predisposing for childhood UTIs include the following:
- urinary frequency ,
- urinary urgency , and
- loss of previously established urinary control .
Nonspecific but common symptoms include fever and abdominal pain. For some children less than 2 years of age, these more subtle problems may be the only indicator of a UTI. Associated symptoms of concern include flank pain, fever, and vomiting. Obvious blood in the urine as well as a positive family history for childhood urinary tract infections are also red flags and should raise the level of concern. Interestingly, the odor and color of the urine are not predictors of a UTI.
Read Also: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Help With Urinary Tract Infections
Check If It’s A Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms of a UTI may include:
- pain or a burning sensation when peeing
- needing to pee more often than usual during the night
- pee that looks cloudy
- needing to pee suddenly or more urgently than usual
- needing to pee more often than usual
- lower tummy pain or pain in your back, just under the ribs
- a high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
Symptoms Of Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms of urinary tract infection depend on the level of infection in the child. The normal symptoms are fever, low appetite, diarrhea, vomiting, irritation, and overall weakness. In case of bladder infection, the kids may also have foul-smelling urine, blood in the urine, frequent urination, cloudy urine, pain during urination, etc.
You May Like: Is Urinary Incontinence A Normal Part Of Aging
Therapy Of Uti Eradication
Table 1
Empiric oral antibiotics usually recommended are detailed in Table 2. The initial choice of antibacterial therapy is preferably based on the knowledge of the predominant uropathogens in the patients age group, antibacterial sensitivity patterns in the practice area, the clinical status of the patient, and the opportunity for close follow-up.101101 Schlager TA. Urinary tract infections in infants and children. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2003 17:353-65, ix.
Table 2
There is one systematic review with meta-analysis of six randomized controlled trials including 523 children with microbiologically proven UTI and acute clinical pyelonephritis. These RCTs made comparisons of different classes of antibiotics. Reported outcomes were persistence of bacteriuria at 48-72 h, resolution of clinical symptoms, symptomatic recurrence, and adverse effects. Three RCTs compared third generation cephalosporins with other antibiotics, including amoxicillin-clavulanate and TMP-SMX. There was no difference in the reduction of persistent bacteriuria at 48 h , recurrent or persistent UTI five to ten days after the end of therapy , or the incidence of gastrointestinal adverse effects .110110 Hodson EM, Willis NS, Craig JC. Antibiotics for acute pyelonephritis in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 :CD003772.,117117 Masson P, Matheson S, Webster AC, Craig JC. Meta-analyses in prevention and treatment of urinary tract infections. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2009 23:355-85.
Key Points To Remember About Urinary Tract Infections
- a urinary tract infection is an infection in the urine
- UTIs are common in children
- UTIs can cause children to have high temperatures and become unwell
- sometimes UTIs can make children seriously ill, especially babies and young children – see your doctor or after-hours medical centre urgently if that happens
- babies under 12 months need investigation after a UTI to see if there is anything wrong with their urinary tract
Also Check: Urinary Tract Infection Foods To Avoid
Toddler Urinary Tract Infection Symptoms
Symptoms of urinary tract infection in toddlers include a burning sensation during urination , abdominal pain, vomiting, fever, low levels of energy, crankiness, poor appetite, discolored and smelly urine. In some cases the toddler may also have bloody urine. In the case of potty trained children, signs of a UTI infection include frequent and painful visits to the bathroom.
How Is A Uti In Children Treated
A UTI in children is commonly treated using antibiotics. The doctor will send your child’s urine sample to the lab, but analysis may take a couple of days. In the meantime, he or she will prescribe your child an antibiotic that treats the most common bacteria that cause UTIs. If your child’s urine culture identifies bacteria that may be causing symptoms, but is not treated by that antibiotic, the doctor may prescribe a new antibiotic.
Be sure to give your child the antibiotic in the prescribed dosage at the prescribed times each day. Your child must finish the full antibiotic course to ensure the infection doesn’t return. You should also encourage your child to drink plenty of water.
With proper treatment of a UTI in children, they should feel better in two to three days. Your doctor may need to perform further tests if your child has repeated infections. It is important to treat your child’s UTI promptly because untreated infections can cause kidney damage or, in rare cases, a bacterial infection of the bloodstream known as .
Read Also: Hill’s Science Diet Urinary Hairball Control Wet
What Are The Symptoms Of A Uti In A Child
Symptoms can occur a bit differently in each child.
Symptoms in babies can include:
- Fever
Symptoms in children can include:
- Sudden need to urinate
- Loss of control of urine
- Pain while urinating
- Pain above the pubic bone
- Blood in the urine
- Pain in the back or side below the ribs
- Tiredness
The symptoms of a UTI can seem like other health conditions. Make sure your child sees his or her healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
What Is The Urinary Tract And How Does It Normally Work
The urinary tract is the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
The kidneys filter and remove waste and water from the blood to produce urine. The urine travels from the kidneys down 2 narrow tubes called the ureters. The urine is then stored in the bladder.
When your child does a wee, urine flows out of the body through the urethra, a tube at the bottom of the bladder. The opening of the urethra is at the end of the penis in boys and in front of the vagina in girls.
Front view of the urinary tract
Side view of the female urinary tract
Side view of the male urinary tract
Read Also: Best Probiotic For Urinary Tract Infection
When To Contact A Medical Professional
Things you can do to prevent UTIs include:
- Avoid giving your child bubble baths.
- Have your child wear loose-fitting underpants and clothing.
- Increase your child’s intake of fluids.
- Keep your child’s genital area clean to prevent bacteria from entering through the urethra.
- Teach your child to go the bathroom several times every day.
- Teach your child to wipe the genital area from front to back to reduce the spread of bacteria.
To prevent recurrent UTIs, the provider may recommend low-dose antibiotics after the first symptoms have gone away.