Important Tips To Help Keep Your Bladder Healthy
To help prevent bladder outlet obstruction, there are a number of things you can do to help keep your bladder healthy.
Below are some natural tips to prevent this and other related bladder problems.
Double-void urination: To help with urinary symptoms, double-void at night. This means you urinate twice before bed. Go to the bathroom, brush your teeth and finish your bedtime routine, and urinate once more before going to bed.
Schedule bathroom trips: To help retrain the bladder, keep a daily diary of trips to the bathroom and urinary urges. When you figure out how many times you go to the bathroom daily, you can schedule your trips to help improve bladder control.
Watch water intake: Although it is important to drink enough water, too many liquids before bed will increase the need to urinate at night. Try not to drink liquids after 5:00 p.m. or 6:00 p.m. if you suffer from bladder problems.Avoid dietary triggers: Foods that contribute to bladder problems include caffeinated beverages, alcohol, artificial sweeteners, milk and dairy products, spicy foods, soda and other carbonated beverages, citrus juices and fruits, and sugar and high-sugar foods.
Quit smoking: Smoking irritates the bladder and increases bladder cancer risk.
Referral For Specialist Assessment
Refer men for specialist assessment if they have:
- Bothersome lower urinary tract symptoms that have not responded to conservative management or drug treatment.
- LUTS complicated by recurrent or persistent UTIs.
- Urinary retention.
- Renal impairment thought to be due to lower urinary tract dysfunction.
- Suspected urological cancer.
- Stress urinary incontinence.
Other indications for referral include immediate referral for acute retention of urine and acute kidney injury and urgent referral for visible haematuria and culture-negative dysuria.
- Polyuria .
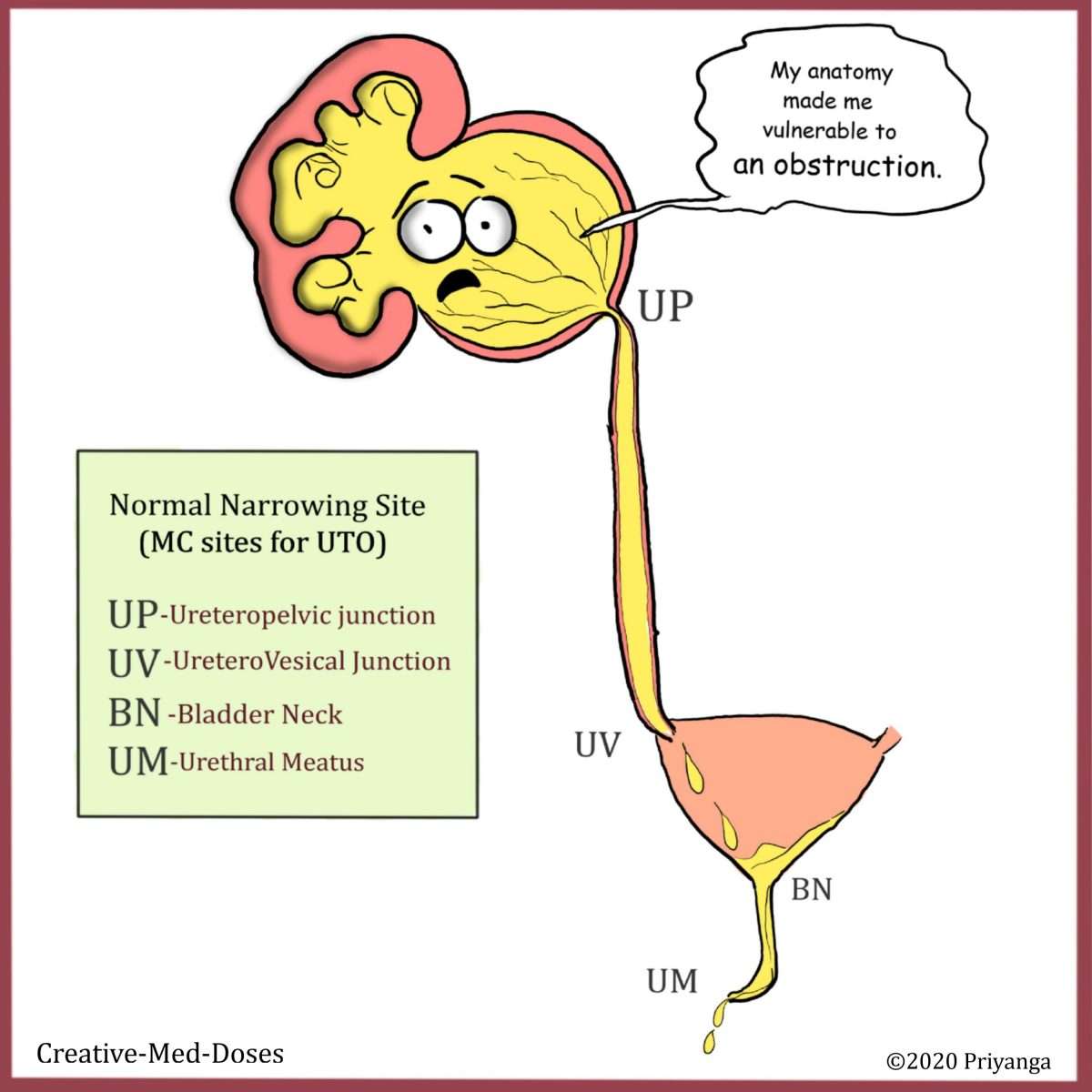
Obstructive Uropathy Can Cause Kidney Damage
An obstruction along the urinary tract can increase pressure and slow urine flow. Urinary tract obstruction can be sudden or slow to develop over a number of days, weeks, or months. During this process, damage may be done to one or both of your kidneys.
Most of the time, urine flows from your kidneys at a very low pressure. If there is an obstruction, urine backs up and creates urinary blockage.
The urine later reaches the small tubes of the kidney and the holding area called the renal pelvis. This leads to the kidney to swell up, which increases pressure on its inside structures.
The increased pressure due to the urinary tract obstruction may lead to kidney damage and loss of kidney function. Urine flow obstruction can then lead to kidney stones, as well as a kidney infection due to bacteria in the urinary tract not being flushed out.
Kidney failure may also result when both kidneys are obstructed.
Over time, renal pelvis and ureter distention can also thwart the rhythmic muscular contractions that normally move urine from the kidney down through the ureter and into the bladder.
Permanent damage may then result when scar tissue replaces the normal muscular tissue of the ureter walls.
Read Also: Urinary Tract Infection After Period
Who Gets Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
- Lower urinary tract symptoms are a common problem, especially for older men. It has been reported that 30% of men over the age of 65 suffer from potentially troublesome LUTS. The prevalence of storage symptoms increases from 3% in men aged 40-44 years to about 40% in those aged 75 years or older.
- One study found that the prevalence of nocturia in men aged over 85 was about 69% compared to 49% in women.
- Around one third of men will develop urinary tract symptoms, of which the principal underlying cause is benign prostatic hyperplasia .
- Once symptoms arise, their progress is variable and unpredictable with about one third of patients improving, one third remaining stable and one third deteriorating.
Surgery For Male Urinary Dysfunction
At NYU Langone, doctors often recommend surgery for men with certain types of male urinary dysfunction, including benign prostatic hyperplasia and stress incontinence thats caused by prostate surgery. Rarely, surgery is required to treat neurogenic voiding dysfunction.
The goal of surgery is to improve bladder function. There are several types of prostate surgery, and the one thats best for you often depends on your symptoms and the size of the prostate.
Recommended Reading: What To Do To Prevent Urinary Tract Infections
Symptoms Of Bladder Outlet Obstruction
Women and men with bladder outlet obstruction have similar symptoms. Lower urinary tract symptoms involve the urinary sphincter, urethra, bladder, and prostate in men. The preferred term for lower urinary tract symptoms in men is prostatism.
Some of these symptoms include:
- Incomplete bladder emptying
Acute and chronic kidney failures are also common complications of urinary obstruction.
How Is It Diagnosed
Prompt diagnosis of bladder outlet obstruction is critical. This becomes even more serious in cases of acute bladder outlet obstruction. A doctor will need to consider several factors. The doctor should consider what type of condition the patient has. This may include primary bladder neck obstruction, for example.
Some symptoms associated with bladder neck obstruction may rather be linked to another condition. For this reason, the doctor needs to consider all possibilities. Treatment for stress urinary incontinence differs from a case where BPH causes bladder obstruction.
There are several tests that a doctor may request if they suspect a patient has bladder outlet obstruction.
The doctor will start by asking the patient a few questions. The healthcare provider asks the patient about the symptoms they experience. This will allow the doctor to get a better idea of what may be the issue. It can also help the doctor confirm if the cause behind their symptoms may be bladder outlet obstruction.
A physical examination is needed during the initial diagnosis process. The doctor will feel the abdomen area of the patient. This will help them identify an abnormal growth in the abdomen. The doctor will also be able to feel if the bladder is larger than it should be. These may be signs that urine is pushing back into the urinary system.
Once this process is done, the doctor will ask the patient to undergo additional tests. These tests will assist in confirming what the issue is.
Read Also: Azo Urinary Pain Relief Maximum Strength
Diagnosing Prostate Enlargement Or Urethra Strictures
Tests that may allow doctors to determine what is causing a urinary obstruction.
- Cystoscopypassing a scope through the urethra into the bladder
- Urodynamicstests of the nerve supply to the bladder and pressures within the bladder
- Uroflow studiestests of the pressure and flow of urine from the bladder
- Ultrasoundmeasurement of how much urine is left in the bladder after the patient feels like the bladder has been emptied
Acute Upper Urinary Tract Obstruction
See also the separate Urolithiasis article.
- Advise patients that most stones < 5 mm in diameter will pass spontaneously, as will 50% of those between 5-10 mm however, most stones > 10 mm in diameter will require intervention:
- Acute symptoms rarely last for more than 72 hours. Pain and vomiting require management – for severe pain, an anti-inflammatory, usually IM diclofenac 75 mg, repeated after 30 minutes if there is no response or, alternatively, diclofenac suppositories 100 mg PR, or morphine .
- Patients with renal colic may be managed at home provided they are able to maintain good fluid intake and urinary output, pain is controlled, they have good social support, are not elderly or have significant other co-morbidities and that they fully understand the need to contact a doctor urgently if fever, rigors, or increasing or abrupt recurrence of pain take place. They should also be urgently referred to urology for outpatient investigation.
Also Check: Urinary Tract Infection Diagnosis Test
Uti Causes And Risk Factors
The most common cause of a UTI in the urethra is a sexually transmitted disease. Chlamydia and gonorrhea are two STDs that can cause a UTI. STDs are also the most common cause of UTIs in younger men.
Prostate problems can also cause UTIs. An enlarged prostate is common in older men and can block the flow of urine. This can increase the odds that bacteria will build up and cause a UTI.
Prostatitis, which is an infection of the prostate, shares many of the same symptoms as UTIs.
Diabetes and other medical issues that affect your immune system can also make you more likely to get a UTI.
Urinary Tract Infection In Men
Approved by: Maulik P. Purohit MD, MPH
Urinary Tract Infection is generally caused by a microbe, such as bacteria. Men are at a decreased risk of developing a UTI than women, because of the anatomical structure of the male urinary system. The infection can occur more frequently with increasing age, due to a blockage in the urinary tract, having a bladder catheter, or with a decreased immune system.
Recommended Reading: Azo Urinary Pain Relief Side Effects
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider About Boo
- Whats the cause of my bladder outlet obstruction?
- Whats the best treatment option for me?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
If you have symptoms of a bladder outlet obstruction, dont hesitate to see your healthcare provider. Pay attention to your pee. Is your urine stream normal? Or does very little pee come out, despite your fluid intake? Are you peeing slower than normal? Or do you have trouble starting to pee, no matter how hard you try? Are you in pain? All of these are reasons to get checked out by your healthcare provider to avoid kidney and bladder complications.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 02/09/2022.
References
Whats Bladder Outlet Obstruction
Bladder outlet obstruction is when the neck at the very bottom of your bladder gets blocked. The neck is where your bladder connects to your urethra, which carries urine out of your body. A blockage stops or slows down the flow of pee. Possible blockages include scar tissue, bladder stones, a large gland, cancer or a tumor.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Urinary Incontinence In Men
Voiding Dysfunction And Urinary Retention
Bladder outlet obstruction may occur following SUI surgical procedures. This complication manifests as prolonged complete urinary retention, persistently elevated postvoid residual urine volume, or as variably bothersome and poorly categorized lower urinary tract symptoms including combinations of obstructive symptoms and urinary urgency or UI. These last two groups are difficult to identify and are often not recognized as having BOO by many investigators. The incidence of postoperative voiding problems across various procedures is variable and is difficult to compare. Historically the incidence of postoperative voiding difficulties lasting > 4 weeks occurred in 3% to 7% of patients undergoing Burch procedures, in 4% to 8% of those undergoing transvaginal needle suspensions, and in 3% to 11% of patients undergoing sling procedures.10 The incidence of voiding dysfunction, including urinary retention and de novo urgency and urge UI, following midurethral sling procedures ranges from approximately 2% to 25%.16,19,20,22,40,46-53
Recurrence of SUI symptoms following urethrolysis or sling incision may occur in 15% to 20% of patients.62,68 Patients should be counseled regarding this possibility preoperatively because some may wish to continue performing intermittent catheterization rather than risk recurrent SUI.
Peter Twining, in, 2007
Final Thoughts On Bladder Outlet Obstruction
Bladder neck obstruction may be a problem for many years with few symptoms before a diagnosis and treatment are pursued. But, when bladder neck obstruction is treated, the symptoms typically disappear.
The treatment of bladder outlet obstruction will often depend on the cause, and sometimes, surgery may be required to help improve symptoms. Medication or natural remedies can help treat the cause of bladder neck obstruction.
Other ways to improve bladder health include double-void urination, scheduling bladder trips, watching water intake, avoiding dietary triggers, quitting smoking, and trying kegel exercises to help relax the bladder.
Also Read:
Also Check: Ways To Cure Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms Of Urinary Obstruction
Symptoms depend on the cause, location, and duration of the obstruction. When the obstruction begins quickly and distends the bladder, ureter, and/or the kidney, it usually causes pain. If the kidney is distended, renal colic can develop. Renal colic is an excruciating pain between the ribs and hip on the affected side that comes and goes every few minutes. The pain may extend into a testis or the vaginal area. People may have nausea and vomiting.
Obstruction of one ureter does not reduce how much people urinate. Obstruction can stop or reduce urination if blockage affects the ureters from both kidneys or if it affects the urethra. Obstruction of the urethra or bladder outlet may cause pain, pressure, and distention of the bladder.
People who have slowly progressive obstruction that causes hydronephrosis may have no symptoms, or they may have attacks of dull, aching discomfort in the flank on the affected side. Sometimes, a kidney stone temporarily blocks the ureter and causes pain that occurs intermittently.
Obstruction that leads to hydronephrosis may cause vague digestive tract symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. These symptoms sometimes occur in children when hydronephrosis results from a birth defect in which the junction of the ureter and renal pelvis is too narrow .
Hydronephrosis: A Distended Kidney
|
In hydronephrosis, the kidney is distended because the flow of urine is obstructed. Urine backs up behind the obstruction and remains in the kidneys small tubes and central collecting area . |
Normally, urine flows out of the kidneys at extremely low pressure. If the flow of urine is obstructed, urine backs up behind the point of blockage, eventually reaching the small tubes of the kidney and its collecting area , swelling the kidney and increasing the pressure on its internal structures. Such kidney distention is called hydronephrosis. The elevated pressure due to the obstruction may ultimately damage the kidney and can result in loss of its function.
When the flow of urine is obstructed, stones Stones in the Urinary Tract are more likely to form. An infection may develop when the flow of urine is obstructed because bacteria that enter the urinary tract are not flushed out. If both kidneys are obstructed, kidney failure Kidney Failure may result.
Long-standing distention of the renal pelvis and ureter can also inhibit the rhythmic muscular contractions that normally move urine down the ureter from the kidney to the bladder . Scar tissue may then replace the normal muscular tissue in the walls of the ureter, resulting in permanent damage.
Partial and complete obstruction tend to cause similar problems, but most problems, and particularly kidney damage, are more severe when obstruction is complete.
You May Like: Antibiotics For Feline Urinary Tract Infection
Inserting A Stent Or Tube For Urinary Obstruction
If the blockage is in the kidney or ureter, then a tube can be placed in the ureter between the kidney and the bladder to help the flow of urine. This is placed with the help of a lighted scope that is inserted into the urethra.
Another alternative is a tube that is inserted through the back into the kidney. Placing these tubes gives temporary relief of a blockage of the ureter. A second procedure may later be necessary to completely eliminate the cause of such an obstruction. Placing a scope into the kidney through the back or into the ureter through the bladder allows the physician to remove obstructing lesions such as stones . Alternatively, a shock-wave procedure may be used to help break up small stones.
Symptoms Of Urinary Problems
Urinary symptoms commonly experienced with prostate problems include:
- the need to urinate frequently during the night
- urinating more often during the day
- urinary urgency the urge to urinate can be so strong and sudden that you may not reach the toilet in time
- the urine stream is slow to start
- urine dribbling for some time after finishing urination
- a sensation that the bladder isn’t fully emptied after urination
- lack of force to the urine flow, which makes directing the stream difficult
- the sensation of needing to go again soon after urinating.
Although these symptoms often do not need treatment, see your doctor if they are causing you difficulty, as they can be successfully treated.
Read Also: Can I Use Azithromycin For Urinary Tract Infection
How Is A Bladder Outlet Obstruction Evaluated And Diagnosed
Tests may include:
- Blood tests to check for kidney damage.
- Urine cultures to test for infection.
- Ultrasound of your kidneys and bladder to find where the pee blockage is occurring.
- Urine testing to look for blood in your pee.
- A scope to look for narrowing of your urethra.
- Urodynamic evaluation .
- Ultrasound .
What Are The Symptoms Of Ureteral Obstruction

Signs of ureteral obstruction reveal themselves in different ways. Patients who have stones may have severe pain. When the blockage is gradual and slow, it usually come on slowly and builds over time. In some cases symptoms may be mild at first, but can quickly get worse. Symptoms of a blocked ureter or urinary tract obstruction include:
- Pain in your abdomen, lower back or sides below your ribs .
- Fever, nausea or vomiting.
- Gastrointestinal issues such as Crohns disease, diverticulitis or swollen appendix.
- Ureteral stones, which are kidney stones that move to the ureter.
- Genetic disorders that cause narrowing of the ureter or other abnormalities of the urinary tract. One disorder is ureteropelvic junction obstruction, which is a blockage of the ureter at its connection to the kidney.
Don’t Miss: Is Caffeine Bad For Urinary Tract Infection