Antibiotics For More Complicated Urinary Tract Infections
A different antibiotic may be better for a more severe or stubborn UTI. This may include a UTI that:
- Spreads to the kidneys
- Comes back
- Is not responding to treatment
Additionally, there is a medical category of complicated UTIs that may require a different antibiotic regimen.
Complicated UTIs include UTIs that occur:
- In a person with a childhood history of UTIs
- In a person with a weakened immune system
- In a child or postmenopausal woman
- During pregnancy
- With a medical condition, like diabetes
- With an abnormality of the urinary tract, like a stone, obstruction, catheter or kidney deformity
In these cases, a urine culture may be done to make the choice of antibiotic. A urine culture grows the bacteria from the urine so that it may be identified under a microscope and tested for antibiotic sensitivity. The best antibiotic will be determined by the culture and sensitivity results.
No matter what antibiotic your health care provider prescribes, it is important to take the entire course as directed. Stopping early can lead to antibiotic resistance.
If your antibiotic doesnt seem to be working and symptoms dont go away or come right back, let your health care provider know.
Will Uti Go Away On Its Own Without Antibiotics Symptoms
However, the body can often heal urinary tract infections on its own without minor complications, without the help of antibiotics. By some estimates, 25-42% of uncomplicated UTIs resolve on their own. In these cases, people can try various home remedies to speed up their recovery. Complicated urinary tract infections require treatment.
How Long Should I Take Antibiotics
Your doctor will let you know. Typically, for an uncomplicated infection, you’ll take antibiotics for 2 to 3 days. Some people will need to take these medicines for up to 7 to 10 days.
For a complicated infection, you might need to take antibiotics for 14 days or more.
If you still have symptoms after completing antibiotics, a follow-up urine test can show whether the germs are gone. If you still have an infection, you’ll need to take antibiotics for a longer period of time.
If you get UTIs often, you may need a prolonged course of antibiotics. And if sex causes your UTIs, you’ll take a dose of the medicine right before you have sex. You can also take antibiotics whenever you get a new UTI if youâre having symptoms and a positive urine culture.
Recommended Reading: Tart Cherry Juice For Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms Of Urinary Tract Infections
During the first stage, the urinary tract infection might not show any symptoms. It is only when the bacteria have invaded the urinary tract that symptoms appear. There are two types of urinary tract infections, and the symptoms are different.
An upper urinary tract infection comes with:
- Lack of appetite
- Drinking more water than usual
A lower urinary tract infection will present symptoms such as:
- Polydipsia
- The dog is in pain when urinating
- The urine might contain traces of blood
- The dog urinates significantly more than usual
- The dog tries to urinate, but cannot
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection
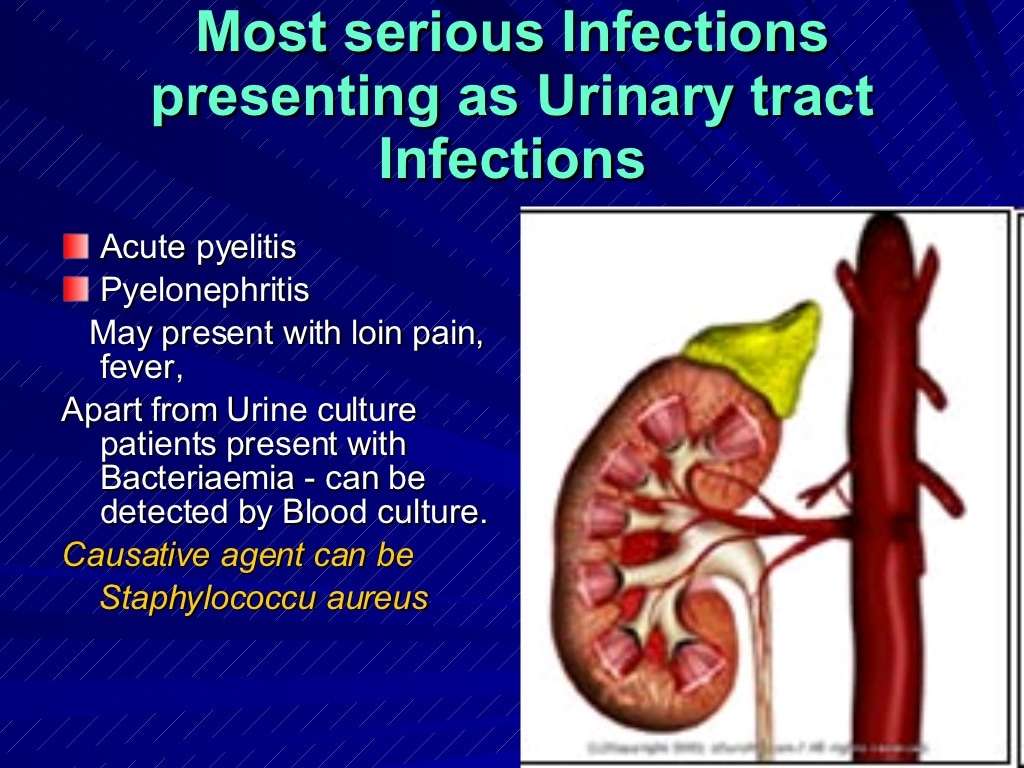
The urinary tract is comprised of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra . A urinary tract infection is an infection caused by pathogenicorganisms in any of the structures that comprise the urinary tract. However, this is the broad definition of urinary tract infections many authors prefer to use more specific terms that localize the urinary tract infection to the major structural segment involved such as urethritis , cystitis , ureterinfection, and pyelonephritis . Other structures that eventually connect to or share close anatomic proximity to the urinary tract are sometimes included in the discussion of UTIs because they may either cause or be caused by UTIs. Technically, they are not UTIs and will be briefly mentioned in this article.
UTIs are common, leading to between seven and 10 million doctor visits per year . Although some infections go unnoticed, UTIs can cause problems that range from dysuria to organ damage and even death. The kidneys are the active organs that produce about 1.5 quarts of urine per day in adults. They help keep electrolytes and fluids in balance, assist in the removal of waste products , and produce a hormone that aids in the formation of red blood cells. If kidneys are injured or destroyed by infection, these vital functions can be damaged or lost.
Read Also: Azo Urinary Tract Defense Directions
How Do You Cure Uti Without Antibiotics
To cure urinary tract infections within 24 hours without taking harmful antibiotics, you can use the home remedies listed here: Take plenty of probiotics. This increases the percentage of good bacteria that fight the bacteria that cause bladder infections. Take khomucha or milk kefir, a natural probiotic drink.
What If I Take Too Much
Taking an extra dose of azithromycin by accident is unlikely to harm you or your child. It may, however, increase the chance of temporary side effects, such as feeling or being sick or diarrhoea.
Talk to your pharmacist or doctor if you’re worried, or if you or your child accidentally take more than 1 extra dose.
You May Like: Why Am I Prone To Urinary Tract Infections
Why Do Antibiotics Sometimes Not Work For A Urinary Tract Infection
If an antibiotic doesnt work it is likely that the bacteria causing the UTI is not susceptible or is resistant to the antibiotic you are taking.
Antibiotic resistance occurs when the bacteria that is causing the infection is no longer affected by a particular antibiotic and is able to continue to grow and multiply. Inappropriate and unnecessary antibiotic use contributes to the increasing problem of antibiotic resistance.
If you felt better for a little while and then came down with the symptoms of a UTI again, it is also possible that you have a new or recurrent UTI.
Another possibility if you continue to experience symptoms of a UTI despite antibiotic treatment, is that you have another type of infection that mimics that symptoms of a UTI and you need a different antibiotic or other treatment. Sexually transmitted infections such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, for example, produce symptoms that mimic a UTI. Vaginal yeast infections can also cause burning when you pee.
Common Side Effects With Antibiotic Use
Each antibiotic is responsible for its own unique list of side effects, and the list is usually extensive. Be sure to discuss your individual antibiotic side effects with your healthcare provider. However, there are side effects that are common to most antibiotics, regardless of class or drug:
Related: Common Side Effects from Antibiotics, Allergies and Reactions
Recommended Reading: Can Smoking Weed Cause Urinary Problems
Amoxicillin/potassium Clavulanate Cefdinir Or Cephalexin
How it Works: is another combination drug that belongs to the penicillin class of antibiotics. and belong to a different class of antibiotics thats closely related to penicillins.
All three antibiotics kill bacteria by destroying one of its most important components: the cell wall, which normally keeps bacteria structurally intact.
Common doses:
-
Amoxicillin/clavulanate: 500 twice a day for 5 to 7 days
-
Cefdinir: 300 mg twice a day for 5 to 7 days
-
Cephalexin: 250 mg to 500 mg every 6 hours for 7 days
Notable side effects: Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and rash are common side effects of these antibiotics. In rare cases, all three have the potential to cause the dangerous skin reactions, SJS and TEN.
If you have a penicillin allergy, your healthcare provider wont prescribe amoxicillin/clavulanate. They may or may not prescribe cefdinir or cephalexin since there is a small chance that a person with a penicillin allergy may also be allergic to these two.
Adhesion On Urinary Catheters
The adhesion on urinary catheters was assayed using the standard crystal violet staining method with a few revisions . In brief, a 3-cm urinary catheter was placed into a 6-well board with 4.5 ml LB broth, and 50 l bacterial culture was added to the well. After incubation for 6 h, unattached cells were removed with sterile water, and attached cells were stained with 1% crystal violet for 20 min. The dye bound to the adherent cells was then solubilized with ethanol-acetone and the optical density of the solution was measured at 570 nm.
You May Like: Can Peyronies Cause Urinary Problems
Do I Really Need To Take Antibiotics For A Uti
In most cases, it makes sense to start antibiotics if you know you have a bacterial UTI since this is the only way to treat it.
While it is possible for a UTI to go away on its own, this doesnt always happen. Plus, youll still have to deal with uncomfortable UTI symptoms like pain during urination while waiting to see if the UTI will go away. And if it doesnt, the infection can travel up your urinary tract and cause a more serious infection in your kidneys called pyelonephritis. If youre pregnant, have underlying health conditions, or are older than 65 years old, you should not try to treat a UTI without antibiotics.
For Pharyngitis Or Tonsillitis
Adult dosage
Your doctor may prescribe 500 mg in a single dose on day 1, followed by 250 mg once per day on days 2 through 5.
Child dosage
The typical dosage is 12 mg/kg of body weight once per day for 5 days.
Child dosage
This drug should not be used for this condition in children who are younger than 2 years.
Disclaimer: Our goal is to provide you with the most relevant and current information. However, because drugs affect each person differently, we cannot guarantee that this list includes all possible dosages. This information is not a substitute for medical advice. Always speak with your doctor or pharmacist about dosages that are right for you.
Read Also: Will Az Pack Help A Urinary Tract Infection
What Should I Avoid While Taking Azithromycin
Antibiotic medicines can cause diarrhea, which may be a sign of a new infection. If you have diarrhea that is watery or bloody, call your doctor before using anti-diarrhea medicine.
Azithromycin could make you sunburn more easily. Avoid sunlight or tanning beds. Wear protective clothing and use sunscreen when you are outdoors.
For Acute Middle Ear Infection
Child dosage
The typical dosage is 30 mg/kg of body weight taken as a single dose, or 10 mg/kg of body weight once per day for 3 days. The doctor may also prescribe 10 mg/kg of body weight on day 1, followed by 5 mg/kg per day on days 2 through 5.
Child dosage
This drug should not be used in children who are younger than 6 months.
Also Check: Nature’s Sunshine Urinary Maintenance
What Are Possible Complications Of A Urinary Tract Infection
Most UTIs cause no complications if they spontaneously resolve quickly or if treated early in the infection with appropriate medications. However, there are a number of complications that can occur if the UTI becomes chronic or rapidly advances. Chronic infections may result in urinary strictures, abscesses, fistulas, kidney stones, and, rarely, kidney damage or bladder cancer. Rapid advancement of UTIs can lead to dehydration, kidney failure, sepsis, and death. Pregnant females with untreated UTIs may develop premature delivery and a low birth weight for the infant and run the risks of rapid advancement of the infection.
Warnings For People With Certain Health Conditions
For people with myasthenia gravis: If you have myasthenia gravis, taking this drug may worsen your symptoms. Be sure to discuss your condition with your doctor before taking azithromycin.
For people with certain heart problems: If you have an abnormal heart rhythm, including a condition called QT prolongation, taking this drug can increase your risk of having an arrhythmia that may be fatal. People with decompensated heart failure are also at risk. Ask your doctor if this drug is safe for you.
Also Check: Cephalexin For Urinary Tract Infection
What Are The Dangers Of Uti
The main danger of untreated UTIs is that the infection can spread from the bladder to one or both kidneys. When bacteria â â â â â â the kidneys, they can cause damage that irreversibly impairs kidney function. In people who already have kidney problems, this can increase the risk of kidney failure.
What Are The Possible Side Effects Of Azithromycin
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction or a severe skin reaction .
Seek medical treatment if you have a serious drug reaction that can affect many parts of your body. Symptoms may include: skin rash, fever, swollen glands, muscle aches, severe weakness, unusual bruising, or yellowing of your skin or eyes.
- severe stomach pain, diarrhea that is watery or bloody
- fast or pounding heartbeats, fluttering in your chest, shortness of breath, and sudden dizziness or
- liver problems—nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, stomach pain , tiredness, itching, dark urine, clay-colored stools, jaundice
Older adults may be more likely to have side effects on heart rhythm, including a life-threatening fast heart rate.
Common side effects may include:
- nausea, vomiting or
- stomach pain.
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Read Also: What Not To Eat With A Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary Tract Infection Antibiotics
Antibiotics are the treatment of choice for a urinary tract infection.
Your veterinarian will perform a sensitivity test to see how the bacteria in the urine react to certain drugs, then check if your dog is allergic to any drugs and then prescribe the proper antibiotics.
If the right antibiotic is prescribed, the number of bacteria in the dog’s urine will decrease.
However, your veterinarian may prescribe the antibiotic without performing the urine culture test.
A urinary tract infection is often treated with antimicrobials.
These are usually taken for 2 to 3 weeks, depending on how much the infection has spread.
The most common antibiotics and antimicrobials are:
- cephalexin
Implications For Research And Practice

Based on the data we analysed, a pragmatic approach is required when considering prescribing long-term antibiotics in older patients with recurrent UTI. Although long-term antibiotics may reduce the risk of UTI recurrence in women, this benefit diminishes on cessation of treatment. Little is known about optimal prophylaxis period, long-term effects on health, risk of antibiotic resistant infections, effect in older men, effect in frail care home residents or impact on important patient-centred outcomes. These unknowns must be balanced against benefits and patient preferences.
Future research efforts on recurrent UTI should focus on improving the design and reporting of trials and developing a core set of outcomes to allow better synthesis of trial data. Antibiotic prophylaxis should be compared with non-antibiotic prophylaxis with some evidence of efficacy rather than those with little or poor evidence of efficacy. Researchers should address unanswered questions regarding long-term effects, duration of use, adverse effects and antibiotic resistance.
Also Check: Does Cranberry Juice Clean Urinary Tract
How Do Antibiotics Treat A Uti
UTIs can be caused by many different types of germs including bacteria or fungi and in rare cases, even viruses. But bacterial UTIs are the most common.
If you have a bacterial UTI, the only way to treat it is by getting rid of the bacteria thats causing it. Thats where antibiotics come in. They either stop those bacteria from growing or directly kill the bacteria altogether.
Its worth noting that antibiotics only treat UTIs and other infections caused by bacteria. If you have a fungal or viral UTI, antibiotics wont help.
Monitoring Response To Therapy
Patients with a simple, uncomplicated UTI may not require rigorous monitoring. However, patients with complicated, relapsing, or recurrent infections should be monitored very closely. The following protocol is recommended to monitor response to therapy in patients with relapsing, recurrent, or refractory UTI.3
Recommended Reading: How To Manage Urinary Incontinence
Warnings For Other Groups
For pregnant women:
Azithromycin hasnt been evaluated in clinical studies of pregnant women. However, when used during pregnancy, the drug hasnt been found to increase the risk of pregnancy loss, birth defects, or other problems.
One study in pregnant rats did show increased risk of fetal death and delays in development after birth. However, most animal studies of the drug havent shown any increased risk of birth defects. And keep in mind that animal studies dont always predict what will happen in humans.
Before taking azithromycin, talk with your doctor if youre pregnant or plan to become pregnant. This drug should be used only if its clearly needed.
For women who are breastfeeding:
Azithromycin does pass into the breast milk of lactating women. Because of this, the drug may cause side effects in a child whos breastfed. These side effects may include diarrhea, vomiting, and rash.
Before taking azithromycin, talk with your doctor about whether its safe for you to breastfeed.
All possible dosages and drug forms may not be included here. Your dosage, drug form, and how often you take the drug will depend on:
- your age
- how severe your condition is
- other medical conditions you have
- how you react to the first dose