Proven Ways How To Relieve Chronic Urinary Retention
Urinary retention is the inability to urinate even with the desire or encouragement of it. Urine retention happening when urine buildup in the bladder and cannot emptied it perfectly.
Furthermore, chronic urinary retention is the inability to urinate suddenly in an enlarged, full, painless urinary state with or without urination.
What are cause chronic urinary retention?
Urinary retention may occur by location, drug factors and other factors such as anxiety, urethral pathology, trauma, and so on. Drug factors may affect urination, lower blood pressure, decrease glomerulus filtration, leading to decreased urine production.
Other factors such as anxiety, urethral pathology disorder, trauma and so on that can increase tension of abdominal muscles, anal elbows, external anal spinkter cannot be relaxed well. The cause might affecting the urethral lumen or urethral wall, urethral compression or neurological dysfunction. Urinary tract infections or pain may trigger retention. Read more about How to Relieve Chronic Nasal Congestion.
Etiology of urinary retention
Urinary retention can be distinguished by the site of nerve damage:
That is damage in the center of the micturition of the S2-S4 sacral spinal cord is as high as Th1 L1. Damage occurs in the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves either partially or completely.
Clinical overview of urinary retention
Results of urinary retention
When To See A Doctor
Anyone experiencing symptoms of acute urinary retention should go to the emergency room.Chronic urinary retention is not a medical emergency, but it does usually indicate a potentially serious underlying problem.
A person should schedule an appointment with a doctor for urinary retention that lasts longer than a few days or that goes away and then returns.
People who experience temporary urinary retention due to medication or anesthesia may not need medical treatment if the symptoms disappear and do not return.
Although anyone can develop urinary retention, it is more common as a person ages. Males are also more likely than females to have urinary retention due to prostate issues and partial blockages of the urethra.
Some other risk factors include:
What Is Urinary Retention
Urinary retention is a condition where your bladder doesnt empty all the way or at all when you urinate. Your bladder is like a storage tank for urine. Urine is made up of waste thats filtered out of your blood by your kidneys. Once filtered, the urine moves to your bladder where it waits till its time to move through the urethra and out of the body.
When you have urinary retention, it can be acute or chronic . Acute means that it comes on quickly and it could be severe. Chronic urinary retention means that youve had the condition for a longer period of time.
The acute form of urinary retention is an emergency. In this case, youll need to see a healthcare provider right away. The chronic form happens most of the time in older men, but it can also occur in women.
Read Also: Nature’s Sunshine Urinary Maintenance
How Is It Diagnosed
To diagnose urinary retention, a doctor will first ask about the history of your symptoms and perform a physical exam. The physical will include an examination of your genitals and rectum to look for any symptoms affecting those areas that may also affect the urinary tract.
Some other tests that may be used to confirm a diagnosis
likely be inserted to help quickly drain the urine. Local anesthesia will be used to make sure you dont feel pain or discomfort from the catheter.
If a catheter doesnt work or cant be used because of an injury or other condition, a doctor may insert a suprapubic catheter into the skin above your bladder to drain the urine.
Diagnosis Of Urinary Retention

When a person seeks treatment for urinary retention, the doctor will do a physical exam and ask about symptoms and medications.
For men, the doctor may do a rectal exam to check the size of the prostate, a walnut-sized gland located between the bladder and the penis. An enlarged prostate might press the urethra and cause urinary retention. Doctors might order blood tests to screen for prostate cancer, which is very common among older men.
The doctor also may order tests including:
- Urinalysis to check for infection or blood in urine.
- Ultrasound to see how much urine remains in the bladder after voiding.
- Cystoscopy, a test where a tiny camera is inserted through the urethra, allowing the doctor to see the inside of the urethra and bladder.
- CT scan, which looks for stones or other blockages of the urine flow.
- Urodynamic tests of urine flow.
- Electromyography , which measures how well the muscles and nerves work around the bladder and the urethra.
In some cases, doctors also might order an MRI test of the pelvic region and/or the brain to determine the cause of the urinary retention.
You May Like: Medicine To Take For Urinary Tract Infection
Grading The Strength Of Evidence For Individual Comparisons And Outcomes
The overall strength of evidence for select clinical outcomes within each comparison will be evaluated based on four required domains: study limitations directness consistency and precision .13 A fifth domain, reporting bias, will be assessed when the strength of evidence is moderate or high based on the first four domains.13 Risk of bias will be rated as low, medium, or high according to study design and conduct. Consistency will be rated as consistent, inconsistent, or unknown/not applicable . Directness will be rated as either direct or indirect. Precision will be rated as precise or imprecise. Other factors that may be considered in assessing strength of evidence include dose-response relationship, the presence of confounders, and strength of association. Based on these factors, the overall evidence for each outcome will be rated as:13
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Postoperative urinary retention is not an uncommon problem, and it should have management from an interprofessional healthcare team. Its diagnosis and treatment rely on an interprofessional approach through all perioperative stages. Surgeons should identify patients preoperatively who are at the highest risk of developing POUR, educate them on their increased potential of developing POUR, and consider prescribing a prophylactic alpha-blocker . Intraoperatively, the anesthesia team should keep in mind that POUR correlates with the volume of intravenous fluids given, and the surgeon should keep in mind that the length of operation has a link to the development of POUR.
A trial without a catheter can then follow in 1 to 3 days by the floor nurse at the order of the surgeon/hospitalist. It is essential after removal of a foley to closely monitor the patient’s ability to void to avoid a second episode of extreme bladder retention and confirm a low postvoid residual bladder scan before considering the trial without catheter a success. If a patient does fail a trial without a catheter, the patient should receive an outpatient urology consultation. These interprofessional measures can ensure the best possible patient outcomes with POUR.
Recommended Reading: What’s The Signs Of A Urinary Tract Infection
What Specialists Treat Urinary Retention
Urologists are most often involved in the care of patients with urinary retention. However, urogynecologists also treat women with urinary retention. Internists, family physicians, and emergency-room physicians also frequently treat urinary retention and will refer you to a urologist or urogynecologist if it is not improving.
Effective Urine Retention Home Remedies For Urine Blockage
What is Urine Retention? In simple words, urinary retention means an inability to empty the bladder completely. This problem is very common in old people. It can be a very painful and serious health condition.
Urine retention can be fatal so you should seek medical advice as soon as possible. In the meantime, you can use natural home remedies for urine retention to get relief from pain and urine blockage.
There is two types of urine retention which is acute urine retention and chronic urine retention.
- In acute urine retention, you stop urinating completely which can be painful and life-threatening. Although this problem lasts for a short period of time but still needs immediate medical attention.
- While chronic urine retention is not life-threatening but it lasts for a longer period of time. People with chronic urine retention problem can urinate but cannot empty the bladder completely. Chronic urine retention can cause UTI and urinary incontinence in which you lost control of the bladder.
Contents
Urine Retention Home Remedies
You May Like: Physical Therapy For Urinary Problems
What Exams And Tests Assess The Causes Of Urinary Retention
Medical evaluation for urinary retention includes a medical and physical examination as well as laboratory tests to find the cause of the problem.
On physical examination, the bladder may be visible and/or palpable . A rectal examination in a male may demonstrate an enlarged prostate, an enlarged prostate with hard areas suspicious for prostate cancer, or prostate tenderness suggestive of prostatitis. A penile examination can identify abnormalities of the penile skin and the meatus, the opening at the tip of the penis that urine passes through, or signs of prior penile surgery such as prior hypospadias repair. Examination of the genitalia in a female may demonstrate a large cystocele . A rectal examination in both males and females may reveal fecal impaction.
A bladder scan is often used to determine how much urine is in the bladder to confirm the diagnosis of urinary retention.
A renal and bladder ultrasound may be helpful to determine if there is hydronephrosis or bladder stones.
A pelvic ultrasound or CT of the abdomen/pelvis may be indicated to check for pelvic, abdominal, or retroperitoneal conditions.
A catheter can be placed in the urethra. This is a thin, flexible tube. It goes up the bladder and drains the urine into a bag.
Other lab tests may be done, depending on your doctor’s conclusions from your medical interview and exam.
Should I Be Worried About Urinary Retention
Urinary retention affects people of all ages and occurs in both sexes. However, it is most common in older men who have an enlarged prostate gland. It develops slowly over time. You may not notice it until you are unable to urinate. This causes swelling and discomfort in your bladder. It is a condition that is diagnosed in millions of adults due to various causes, but it doesnt have to control your life. If youre struggling from one or more of the symptoms of urinary retention, you may need to visit a urologist. Diagnosis is important in case of urinary retention as treatment starts with identifying an underlying medical cause.
You May Like: Can Cranberry Juice Cure A Urinary Tract Infection
What Foods Are Bad For Urinary Retention
Urinary retention is a condition in which you cannot empty your bladder completely. While no direct connection exists between diet and urinary retention, certain foods may aggravate urinary retention
- Acidic and spicy foods: A few people complain of bladder issues with acidic and spicy foods. Acidic foods include citrus fruits and their juices, pineapple, vinegar, tomatoes and tomato products. Spicy foods include hot peppers, curry, chili sauce and powder, etc. Cuisines like Mexican, Thai and Indian are usually spicy.
- Artificial sweeteners: Some people feel discomfort and pressure in the lower abdominal area when they consume artificial sweeteners, such as Saccharin, Aspartame, and Acesulfame K.
- Constipation: Constipation may cause urinary retention. Processed foods, such as white bread, sweets, hot dogs, french fries and fast food, may cause constipation. Skipping meals may also increase the risk of constipation and one should avoid missing meals when they have urinary retention.
- Caffeinated foods and drinks: As a diuretic, caffeine may aggravate symptoms associated with urinary retention, such as urgency. Caffeine is present in a variety of different foods and beverages, including chocolate, coffee and tea. An individual may need to limit caffeine intake to avoid urinary retention.
Uti From Catheter Use
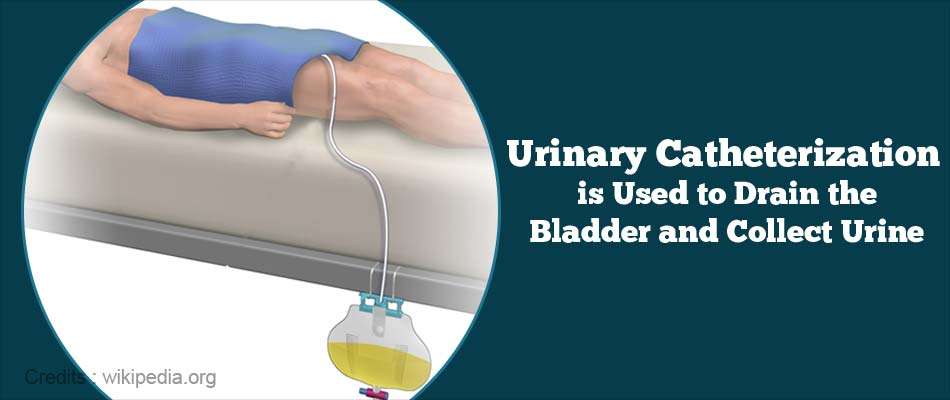
Placement of a urinary catheter provides an opportunity for bacteria to enter the urinary tract. Bacteria may come from the patients anus and perineum or from the health workers hands. Health workers must take great care, using sterile technique, when placing a catheter. If you are performing clean intermittent catheterization, you must follow the same sterile procedures every time you handle the catheter.
Read Also: Pomegranate Juice For Urinary Tract Infection
Your Urology Specialist Can Help
Having difficulty urinating is an uncomfortable and inconvenient experience. While urinary retention remedies are good practice in preventing future health concerns, not being able to urinate is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention.
Managing mild urinary retention symptoms is possible, but it is always best to see a urology specialist for a professional opinion to learn about traditional treatment options. Schedule an appointment with us, or visit your local emergency room, if you start showing symptoms of urinary retention.
This content was originally published in March 2019 and was refreshed in January 2021.
Treating And Preventing Urinary Retention
Treatment will differ depending on the severity of the condition. The following are potential treatments:
Bladder drainage: Involves inserting a tube called a catheter up through the urethra and into the bladder for drainage. Those suffering from acute cases of urinary retention will see immediate relief of their distressful symptoms. This procedure can be done in an office or in a hospital setting, with the patient receiving local anesthesia. In the rare case that the urethra is blocked not allowing a catheter to travel upward the doctor can pass the tube directly through the lower abdomen into the bladder. People with chronic cases of urinary retention may require intermittent, occasional, or long-term catheterization if other treatments do not work.
Urethral dilation: A treatment for urethral strictures a cause of urinary retention that works by inserting increasingly wider tubes into the urethra to widen the stricture. A stricture, by definition, is an abnormal narrowing of a passage that may be due to scar tissue. Local anesthesia is always utilized, and if necessary, the patient will receive sedation and regional anesthesia.
Read Also: Royal Canin Feline Urinary So Dry
What Are The Complications Of Urinary Retention And Its Treatments
Some complications of urinary retention and its treatments may include:
- Urinary Tract Infections Because urine is normally sterile and the normal flow of urine usually prevents bacteria from infecting the urinary tract, developing urinary retention means an abnormal urine flow gives bacteria at the opening of the urethra a chance to infect the urinary tract.
- Bladder damage If your bladder is stretched too far or for extended periods, the muscles may become permanently damaged and lose their ability to properly contract.
- Kidney damage Sometime urinary retention can cause urine to flow back into the kidneys. This is called reflux and can damage or scar the kidneys.
- Urinary incontinence Transurethral surgery to treat an enlarged prostate can result in urinary incontinence in some men. Its often temporary with most men gaining bladder control in a few weeks or months after surgery. The removal of tumours or cancerous tissue in the bladder, prostate, or urethra may also result in urinary incontinence.
Causes Of Urinary Retention
There are many different causes.
Blockage In men, the urethra may be constricted by an enlarged prostate a common condition for men over 50. In women, blockage can be caused by certain types of pelvic prolapse, including Cystocele and Rectocele .
Other blockage reasons for both men and women include urethral stricture and urinary stones.
Infection / Swelling In men, prostatitis , can cause swelling that blocks the free flow of urine. Urinary Tract Infections and Sexually Transmitted Diseases can also cause swelling that leads to urinary retention.
Nerve Problems Urinary retention could be caused by a problem with the nerves that control the bladder. If the nerves are damaged, it can cause a breakdown in the signals between the brain and bladder. Some causes of nerve damage include:
- Stroke
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection Natural Cures Garlic
When To Seek Medical Care
A person who has any of the following symptoms should see a health care provider right away:
- complete inability to urinate
- electromyography
Physical Exam
A health care provider may suspect urinary retention because of a patient’s symptoms and, therefore, perform a physical exam of the lower abdomen. The health care provider may be able to feel a distended bladder by lightly tapping on the lower belly.
Postvoid Residual Measurement
This test measures the amount of urine left in the bladder after urination. The remaining urine is called the postvoid residual. A specially trained technician performs an ultrasound, which uses harmless sound waves to create a picture of the bladder, to measure the postvoid residual. The technician performs the bladder ultrasound in a health care provider’s office, a radiology center, or a hospital, and a radiologist — a doctor who specializes in medical imaging — interprets the images. The patient does not need anesthesia.
A health care provider may use a catheter — a thin, flexible tube — to measure postvoid residual. The health care provider inserts the catheter through the urethra into the bladder, a procedure called catheterization, to drain and measure the amount of remaining urine. A postvoid residual of 100 mL or more indicates the bladder does not empty completely. A health care provider performs this test during an office visit. The patient often receives local anesthesia.
Medical Tests
Helpful Tips For Managing Urinary Retention And Incontinence
Urinary incontinence is a prevalent issue, with anywhere from 25-50 percent of women reporting an episode in the past year.
Managing urinary conditions can be frustrating and time consuming, but there are helpful tips and lifestyle changes that can reduce the burden this condition causes.
Topics in this Post
Don’t Miss: Sore Throat And Urinary Tract Infection