What Are The Symptoms Of A Uti In An Elderly Person
In some elderly people, mental changes and confusion may be the only signs of a UTI. Older adults with a UTI are more likely to be tired, shaky, and weak and have muscle aches and abdominal pain. Symptoms of a UTI in the bladder may include: Some people may have bacteria in the bladder or urinary tract, but not feel any symptoms.
Potential Causes of Vaginal Bleeding. Urinary Tract Infections Urinary tract infections can be very painful, reduce ones ability to go to the bathroom properly, and in severe cases can lead to blood in the urine. Additionally, the infection can lead to spotting or dribbling of urine, which might occur when the woman doesnt realize it.
What Is An Asymptomatic Urinary Tract Infection In Older Adults
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is defined as the presence of bacteria in the urine, without clinical signs or symptoms suggestive of a UTI . Asymptomatic pyuria is defined as the presence of white blood cells in the urine, in the absence of urinary tract specific-symptoms. UTI is one of the most commonly diagnosed infections in older adults.
Tips To Prevent Utis In Seniors
Since seniors are at increased risk for contracting a UTI, they must practice healthy habits to cut down their chances of contracting the disease. They can do this by:
- Staying hydrated. Water helps to flush bacteria from the urethra.
- Thoroughly cleaning and drying their genital area after every washroom trip. For this, clean your genitals by wiping from front to back, moving any bacteria away from the urethral opening.
- Changing incontinence briefs frequently.
- Avoiding bladder irritants like caffeine and alcohol.
- Urinating as soon as the urge hits.
Recommended Reading: Azo Urinary Tract Defense Antibacterial Plus Urinary Pain Relief Tablets
Weakening Of The Bladder Muscles And Pelvic Floor
Both can lead to increased urinary retention and incontinence. Incontinence is at an increased risk due to the close contact of incontinence pads and other incontinence products with their skin. These products introduce bacteria into the urethra.
Other Causes:
- Immobility
- Surgery of an area around the bladder
Institutionalized Older Adults & Catheterized Patients
Similar to other populations, the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI in nursing home residents requires the presence of genitourinary symptoms in the setting of a positive urine culture. In older adults who are cognitively intact, the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI is relatively straightforward. However, nursing home residents often suffer from significant cognitive deficits, impairing their ability to communicate, and chronic genitourinary symptoms , which make the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI in this group particularly challenging. Furthermore, when infected, nursing home residents are more likely to present with nonspecific symptoms, such as anorexia, confusion and a decline in functional status fever may be absent or diminished . In the setting of atypical symptoms, providers are often faced with the challenge of differentiating a symptomatic UTI from other infections or medical conditions. The high prevalence of bacteriuria plus pyuria in this population often leads to the diagnosis of UTI. Although bacteriuria plus pyuria is necessary for diagnosis of a laboratory-confirmed UTI, alone it is not sufficient for making the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI. To date, universally accepted criteria for diagnosing UTI in this population do not exist, making it difficult for providers to distinguish a symptomatic UTI from other conditions in the presence of new nonspecific symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Urinary Tract Infection Antibiotics Walmart
What Is Asymptomatic Bacteriuria
Asymptomatic bacteriuria means having significant quantities of bacteria in the urine, but no clinical signs of inflammation or infection.
In other words, in asymptomatic bacteriuria, a urine culture will be positive.
When bacteria are present in the bladder but not provoking an inflammatory reaction, this can also be called bacterial colonization of the bladder.
How Can Utis In The Elderly Be Prevented
Once a UTI infection is gone, prevention should consist of maintaining a more set schedule. Some older people start a urination schedule, setting up alarms to remind themselves to urinate. Implementing better hygiene to keep the midsection area clean and dry is also key. Seniors should regularly wear and change loose, breathable cotton underwear that can be cleaned easily. A ritual of wiping from front to back when using the bathroom is also critical.
Some urologists claim that there is an ingredient in cranberry juice that prevents bacteria, especially E coli, from adhering to the bladder wall. The ingredient is A-type proanthocyanidins or PACs. There is debate in the medical and healthcare communities as to whether there are enough PACs in cranberry juice to actually stop bacteria from grabbing on to the bladder wall. You could say that the theory has caused a healthy, sweet and sour debate! Essentially, all of these preventative measures mentioned boil down to one theme: better care.
You May Like: Does Cvs Minute Clinic Do Urinary Tract Infections
Other Symptoms Of Utis
If the person has a sudden and unexplained change in their behaviour, such as increased confusion, agitation, or withdrawal, this may be because of a UTI.
These pages explain what a UTI is, the different types of UTIs, their symptoms and treatments, and gives tips on how they may be prevented.
What Is Urinary Sepsis
Urinary is a serious infection that can result in and premature death if treatment is delayed or absent. Also known as systemic inflammatory response syndrome, this condition may occur in individuals who have a urinary catheter or those diagnosed with a severe urinary tract infection . Timely and aggressive treatment is essential to a good prognosis, generally involving the administration of antibiotic medications, intravenous fluids, and, in some cases, surgery.
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs as a result of the immune system‘s overactive inflammatory response to a bacterial infection. Under normal circumstances, the immune system controls the body’s inflammatory response, keeping swelling restricted to the site of infection. When the immune system overreacts and inflammation spreads, the body’s defenses overcompensate and blood clots form throughout the circulatory system. As numerous, tiny blood clots circulate unchecked throughout the body, the delivery of oxygenated blood becomes compromised and organ functions are jeopardized.
You May Like: Natural Remedies For Urinary Urgency
Causes Of Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs are usually caused by bacteria from poo entering the urinary tract.
The bacteria enter through the tube that carries pee out of the body .
Women have a shorter urethra than men. This means bacteria are more likely to reach the bladder or kidneys and cause an infection.
Things that increase the risk of bacteria getting into the bladder include:
- having sex
-
do not use scented soap
-
do not hold your pee in if you feel the urge to go
-
do not rush when going for a pee try to fully empty your bladder
-
do not wear tight, synthetic underwear, such as nylon
-
do not drink lots of alcoholic drinks, as they may irritate your bladder
-
do not have lots of sugary food or drinks, as they may encourage bacteria to grow
-
do not use condoms or diaphragms with spermicidal lube on them try non-spermicidal lube or a different type of contraception
What Is A Uti
UTIs happen when bacteria enter the body through the urethra, which is the opening that carries urine from the bladder, and the immune system isnt able to fight off the bacteria. As a result, the bacteria multiply and can spread to the bladder and kidneys, causing an infection.
Typically, women are more susceptible to UTIs because the urethra is shorter, meaning bacteria doesnt have to travel as far to reach the kidneys or bladder. However, seniors are also at a higher risk of a UTI because of weaker immune systems, chronic health conditions, urinary incontinence, reliance on catheters, or other factors.
UTIs can be treated with medication to kill off the bacteria. However, if left untreated, a UTI can cause kidney infections, kidney failure, sepsis, and other health problems. In fact, the infection can even spread into the bloodstream, leading to life-threatening infection and a long road to recovery. However, with proper care and attention, many UTIs can be avoided.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Relief From A Urinary Tract Infection
How Do You Get Urinary Tract Infections
The design of the human body makes it so it isnt hard to get a bacterial UTI, because the infection comes from outside, through the urethra. Bacteria in the genital area can enter the urethra and the urinary tract, either because wiping after going to the bathroom, sexual activity, or unsanitary conditions. Once the bacteria have entered the urethra, the body tries fight them off, but sometimes the bacteria multiply and cause an infection.
In the case of a fungal infection, usually the fungus gets to the urinary tract through the blood stream. Those who develop this type of infection are usually ill with a disease that has compromised their immune system, such as AIDS.
In general, women get more UTIs than do men and this increases with age. Statistics show that many women get more than one. Almost 20% of women who have had one UTI will go on to have a second. Of this 20%, 30% of those will have a third, and in turn, 80% of these women will have more.
Why Is Sepsis So Serious For People Who Are Aging

Sepsis is a very serious illness for anyone at any age, but it can be particularly devastating for seniors. Older severe sepsis survivors are more than three times more likely to see a drop in cognitive abilities that can make it impossible for them to return to their previous living arrangements. This often results in admission into a chronic healthcare facility. As well, the risk of dying from severe sepsis or septic shock rises as you get older.
Sepsis doesnt affect just the patient, researchers have discovered. The stress of having a family member who is so ill can take a toll on spouses or partners too, especially if they are the primary caregivers. For example, a study published in 2012 found that the wives of older sepsis survivors were at greater risk of developing depression, as much as three to four times the average. Depression can be very serious, affecting quality of life and even the ability to function independently.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get A Urinary Tract Infection From Intercourse
How Long Can You Have Sepsis Before It Kills You
According to researchers at the University of Michigans Institute of Healthcare Policy & Innovation , many patients die in the months and years after sepsis, but it is not known if these patients are dying because of the sepsis itself or because of other health conditions they may have. In this study, 40% of patients who survived the first 30 days of a hospitalization died within the next two years.
Can A Child Get An Infection At Any Age
Other infections occur at all ages but have specific considerations in children. Several severe bacterial infections are preventable by routine immunization early in childhood. Certain children are at particular risk of bacterial infections. Sometimes doctors diagnose bacterial infections by the typical symptoms they cause.
Recommended Reading: What Can I Do To Prevent Urinary Tract Infections
Uti In The Elderly: Signs Symptoms And Treatments
Urinary tract infections arent just a nuisance in the senior populationthey can cause serious health problems. A UTI occurs when bacteria in the urethra, bladder or kidneys multiplies in the urine. Left untreated, a UTI can lead to acute or chronic kidney infections, which could permanently damage these vital organs and even lead to kidney failure. UTIs are also a leading cause of , an extreme and potentially life-threatening response to an infection.
How Does Sepsis Occur In People Who Are Aging
Researchers believe that as we go through the aging process, our immune system becomes less effective at fighting infections. This results in older people contracting more infections and they are more severe. Every infection we get means we have a risk of developing sepsis.
As well, as people age, they may develop chronic illnesses, such as diabetes, COPD, kidney disease, or heart failure. Its not unusual to see someone with two or more chronic diseases.
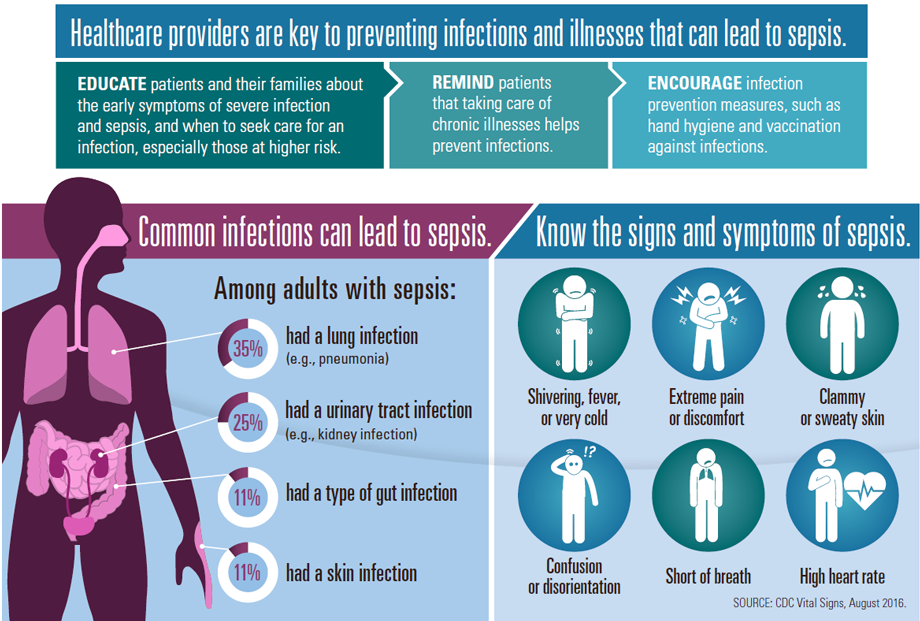
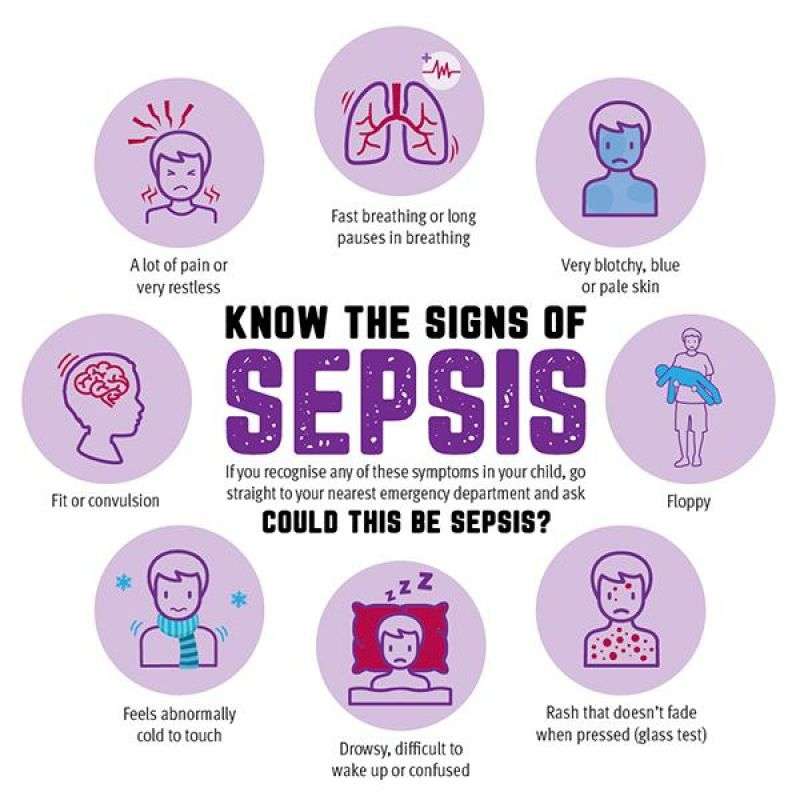
Any type of infection can cause sepsis, from the flu to an infected bug bite, but the most common infections that trigger sepsis among older people are respiratory, such as pneumonia, or genitourinary, such as a urinary tract infection . In 2020, COVID-19 emerged as another strong risk factor for sepsis among older adults. Infections can also happen through infections in the mouth due to abscesses or other injuries, or skin sores, either from a simple skin tear because the skin may be dry or fragile, or a pressure injury from sitting in a wheelchair or lying in bed. There are many ways an infection can take hold.
Since infections might not be obvious, if an older person becomes confused or behaves in an unusual manner, or if confusion or disorientation worsens, this could be a sign of an infection.
Recommended Reading: Sacral Nerve Stimulation For Urinary Incontinence
What Causes Urosepsis
It is known that infections of the urinary tract occur when an infectious organism travels up the urethra. Women more commonly face urinary tract infections as a result, owing to their shorter urethras compared to men. If a urinary tract infection were to spread into the blood, urosepsis has occurred. The following are specific causes leading to the condition:
- Use of an indwelling catheter: Commonly used in hospital settings and in those unable to use the bathroom, a catheter is a tube thats inserted through the urethra that empties the bladder into a bag. Improper emptying of this bag may cause microorganisms to ascend through the catheter, leading to infection.
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia : The enlargement of the prostate can impede urine flow. Urine accumulating in the bladder may lead to microorganism growth.
- Kidney stones: Blockage of urine through the ureter or any other structure of the urinary system can lead to the promotion of bacteria growth.
- Urinary tract infection by E. coli: A common bacterium found in our gastrointestinal tract. It has the potential for spreading.
- Sexually transmitted diseases: Chlamydia infection may lead to the development of urosepsis.
While not direct causes, certain conditions can cause urinary tract infections, leading to urosepsis. They are:
- Diabetes mellitus
Are Any Tests Needed
In some cases the diagnosis may be obvious and no tests are needed. A test on a urine sample can confirm the diagnosis and identify what germ is causing the infection. Sometimes a dipstick test can provide enough information immediately. In other cases the urine sample is sent to a laboratory for further examination under a microscope. This result takes several days.
Further tests are not usually necessary if you are otherwise well and have a one-off infection. However, your doctor may advise tests of your kidney or bladder if an underlying problem is suspected. If you are a man, you may be advised to have some tests for your prostate gland.
An underlying problem is more likely if the infection does not clear with antibiotic medication, or if you have:
- Symptoms that suggest a kidney is infected .
- Recurring urine infections .
- Had problems with your kidney in the past, such as kidney stones or a damaged kidney.
- Symptoms that suggest a blockage to the flow of urine.
Relevant tests may include:
Recommended Reading: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Cause Urinary Tract Infections
Tips For Preventing Utis In The Elderly
The following lifestyle and personal hygiene changes can significantly reduce a seniors risk of developing a urinary tract infection.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Drink cranberry juice or use cranberry tablets, but NOT if the elder has a personal or family history of kidney stones.
- Avoid or limit caffeine and alcohol, which irritate the bladder.
- Do not douche or use other feminine hygiene products.
- After toileting, always wipe from front to back .
- If incontinence is not an issue, wear breathable cotton underwear and change them at least once a day.
- Change soiled incontinence briefs promptly and frequently.
- Keep the genital area clean and dry.
- Set reminders/timers for seniors who are memory impaired to try to use the bathroom instead of an adult brief.
How Is It Diagnosed
If doctors suspect that a UTI is present, they will test a urine sample in the office or send it to a laboratory for a urinalysis.
A urine culture can confirm which bacteria are causing the infection. Knowing the specific type of bacteria allows the doctor to determine a suitable treatment plan.
A condition called asymptomatic bacteriuria is also common in older adults. ASB occurs when there are bacteria in the urine, but they do not cause any signs or symptoms of infection.
Although ASB is common in older adults, it does not typically require treatment, unless it causes other clinical symptoms.
The standard treatment for a UTI is antibiotics, which kill the bacteria causing the infection. Doctors will prescribe an antifungal medication instead if a fungus is causing the UTI.
It is essential that people take the antibiotic or antifungal medication precisely according to the prescription, even if they begin to feel better. Completing the entire prescription will help to destroy all of the infectious bacteria.
Read Also: Azithromycin For Urinary Tract Infection
Summary Of The Evidence
Following this review, it is evident that all of the studies which have explored the association between suspected UTI and confusion are methodologically flawed, due to poor case definition for UTI or confusion, or inadequate control of confounding factors introducing significant bias. Subsequently, no accurate conclusions about the association between UTI and confusion can be drawn. One study of acceptable quality shows an association between confusion and bacteriuria. However, this sample of patients in whom they tested bacteriuria and pyuria were patients already suspected of having a UTI, introducing a bias into their calculation . In summary, none of the 22 publications had sufficient methodological quality to enable valid conclusions.