When You Need Themand When You Dont
Antibiotics are medicines that can kill bacteria. Doctors often use antibiotics to treat urinary tract infections . The main symptoms of UTIs are:
- A burning feeling when you urinate.
- A strong urge to urinate often.
However, many older people get UTI treatment even though they do not have these symptoms. This can do more harm than good. Heres why:
Antibiotics usually dont help when there are no UTI symptoms.
Older people often have some bacteria in their urine. This does not mean they have a UTI. But doctors may find the bacteria in a routine test and give antibiotics anyway.
The antibiotic does not help these patients.
- It does not prevent UTIs.
- It does not help bladder control.
- It does not help memory problems or balance.
Most older people should not be tested or treated for a UTI unless they have UTI symptoms. And if you do have a UTI and get treated, you usually dont need another test to find out if you are cured. You should only get tested or treated if UTI symptoms come back.
Antibiotics have side effects.
Antibiotics can have side effects, such as fever, rash, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, headache, tendon ruptures, and nerve damage.
Antibiotics can cause future problems.
Antibiotics can kill friendly germs in the body. This can lead to vaginal yeast infections. It can also lead to other infections, and severe diarrhea, hospitalization, and even death.
Antibiotics can be a waste of money.
When should older people take antibiotics for a UTI?
10/2013
Treatment Options And Resistance
Increasing resistance to narrow spectrum antibiotics limits the available treatment options in all ages. There remains a difficult balance between the clinical, empirical management of UTIs using broad-spectrum antibiotics in all age ranges, and the development of antibiotic resistance in the community.12 Table 1 shows the level of resistance of E. coli to antibiotics used to treat UTI in 2018. Trimethoprim resistance in England is now at 28.6% of E. coli urine isolates, compared with only 2% for nitrofurantoin, and 6% for pivmecillinam.15 Nitrofurantoin is therefore a first-line antibiotic to consider in all patients . Nitrofurantoin attains low urinary concentrations in patients with poor renal function, so other antibiotics should be considered if estimated glomerular filtration rate is < 45 ml/min, including trimethoprim , pivmecillinam, or fosfomycin.
NICE and PHE now recommend cefalexin as a first-line treatment for oral treatment of pyelonephritis in the community as resistance to this antibiotic is now lower than resistance to co-amoxiclav and randomised controlled trials show that it is equally effective.16,17
Escherichia coli
| Antimicrobial tested against | |
|---|---|
|
Public Health England. Field Epidemiology Field Service NIS. Antibiotic drug-bug resistance profile workbooks . PHE 2018. |
|
| No. tested against given antimicrobial | 118,913 |
| No. resistant to given antimicrobial | 2,459 |
| 28.60% |
Sending Urine For Culture And Interpreting Results
Clinicians should be aware of the various indications for sending a patients urine for culture, including urinary symptoms in pregnancy, suspected pyelonephritis or sepsis, and suspected UTI in men. Clinicians should also consider risk factors for antimicrobial resistance, and should send urine for culture if the patient is a care home resident, has had a recent hospitalisation , or has travelled to a country with increased resistance . Some CCGs with high resistance in the community are recommending urine culture in all symptomatic patients. The results of the urine culture will help inform the choice of antibiotic. If an antibiotic has already been prescribed, this should be reviewed to see if it is still an appropriate choice. Refer to Box 2 for the full list of indications for sending urine for culture, and how to interpret urine culture results if a UTI is suspected.10
Read Also: How Does Myasthenia Gravis Affect The Urinary System
Do I Need To See A Doctor
Yes. Painful urination can be a symptom of a more serious problem. You should tell your doctor about your symptoms and how long youve had them. Tell your doctor about any medical conditions you have, such as diabetes mellitus or AIDS, because these could affect your bodys response to infection. Tell your doctor about any known abnormality in your urinary tract, and if you are or might be pregnant. Tell your doctor if youve had any procedures or surgeries on your urinary tract. He or she also need to know if you were recently hospitalized or stayed in a nursing home.
If your doctor thinks your pain may be from vaginal inflammation, he or she may wipe the lining of your vagina with a swab to collect mucus. The mucus will be looked at under a microscope to see if it has yeast or other organisms. If your pain is from an infection in your urethra , your doctor may swab it to test for bacteria. If an infection cant be found, your doctor may suggest other tests.
Preventing Future Urinary Tract Infections
BATHING AND HYGIENE
To prevent future urinary tract infections, you should:
- Choose sanitary pads instead of tampons, which some doctors believe make infections more likely. Change your pad each time you use the bathroom.
- Do not douche or use feminine hygiene sprays or powders. As a general rule, do not use any product containing perfumes in the genital area.
- Take showers instead of baths. Avoid bath oils.
- Keep your genital area clean. Clean your genital and anal areas before and after sexual activity.
- Urinate before and after sexual activity. Drinking 2 glasses of water after sexual activity may help promote urination.
- Wipe from front to back after using the bathroom.
- Avoid tight-fitting pants. Wear cotton-cloth underwear and pantyhose, and change both at least once a day.
DIET
The following improvements to your diet may prevent future urinary tract infections:
- Drink plenty of fluids, 2 to 4 quarts each day.
- Do not drink fluids that irritate the bladder, such as alcohol and caffeine.
RECURRING INFECTIONS
Some women have repeated bladder infections. Your provider may suggest that you:
- Use vaginal estrogen cream if you have dryness caused by menopause.
- Take a single dose of an antibiotic after sexual contact.
- Take a cranberry supplement pill after sexual contact.
- Have a 3-day course of antibiotics at home to use if you develop an infection.
- Take a single, daily dose of an antibiotic to prevent infections.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Incontinence After Prostate Surgery
Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
If you are a healthy adult man or a woman who is not pregnant, a few days of antibiotic pills will usually cure your urinary tract infection. If you are pregnant, your doctor will prescribe a medicine that is safe for you and the baby. Usually, symptoms of the infection go away 1 to 2 days after you start taking the medicine. Its important that you follow your doctors instructions for taking the medicine, even if you start to feel better. Skipping pills could make the treatment less effective.
Your doctor may also suggest a medicine to numb your urinary tract and make you feel better while the antibiotic starts to work. The medicine makes your urine turn bright orange, so dont be alarmed by the color when you urinate.
Can I Get A Prescription For A Uti Without Going To The Doctor
Your telehealth doctor can write a prescription for antibiotics to treat your bladder infection during your virtual appointment.
Your doctors office will send the prescription to your pharmacy, and you will be able to pick up your medicine as soon as it is ready.
This is one of the added benefits of seeing a doctor online to treat your bladder infection–your prescription is fast-tracked to the pharmacy instead of you having to physically go to your pharmacy and drop it off.
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection After Period
How K Health Can Help
Did you know you can get affordable UTI treatment with the K Health app? Download K to check your symptoms using our AI-driven symptom checker and, if needed, text with a doctor in minutes. K Healths board-certified, U.S.-based doctors can provide a treatment plan and, if required, a prescription to resolve your symptoms as soon as possible.
The Link Between Sex And Utis
To understand why sex causes UTIs, it helps to know that most UTIs are caused by bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract.
Over 80% of UTIs are caused by E. coli bacteria. These germs are normal and common inside our intestines, where they help with digestion without making us sick.
The other 20% of bacteria that cause UTIs are mostly:
-
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
-
Enterobacter species
These types of bacteria are also common in the digestive tracts of healthy people.
Bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract can often be found on the skin around the rectum. In people with typically female genitals, the rectum is in the back, the urethra is in the front, and the vagina is in the middle. Having sex can force bacteria from the rectal area forward, toward the vagina and the urethra. Anything that pushes germs toward the opening of the urethra increases your chance of infection.
Some types of contraceptives contribute to sex-related UTIs as well. Spermicides, including the spermicides on some condoms, change the interaction between bacteria and skin cells by making it easier for bacteria to attach to the inside of the urethra. Contraceptive diaphragms are also associated with UTIs. In addition to containing a spermicide, a diaphragm can press on the urethra and cause urine to become trapped. This interferes with how urine flow can help wash bacteria out of the urethra.
Recommended Reading: Azo Urinary Pain Relief Walgreens
Prevention Of New Urinary Tract Infections
Your telehealth doctor will also provide you with recommendations on how to keep yourself from getting another UTI. These may include:
- Drinking plenty of water
- Wiping from front to back
- Emptying your bladder completely after sexual activity
- Avoiding deodorant sprays, douches, and powders in the groin region
- Changing your birth control from diaphragms or spermicide-treated condoms or unlubricated condoms to something else
Following the above recommendations will help to ensure that bacteria are flushed from your system on a regular basis. The more often bacteria are flushed from your system, the less time bacteria have to grow and create an infection.
Amoxicillin/potassium Clavulanate Cefdinir Or Cephalexin
How it Works: is another combination drug that belongs to the penicillin class of antibiotics. and belong to a different class of antibiotics thats closely related to penicillins.
All three antibiotics kill bacteria by destroying one of its most important components: the cell wall, which normally keeps bacteria structurally intact.
Common doses:
-
Amoxicillin/clavulanate: 500 twice a day for 5 to 7 days
-
Cefdinir: 300 mg twice a day for 5 to 7 days
-
Cephalexin: 250 mg to 500 mg every 6 hours for 7 days
Notable side effects: Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and rash are common side effects of these antibiotics. In rare cases, all three have the potential to cause the dangerous skin reactions, SJS and TEN.
If you have a penicillin allergy, your healthcare provider wont prescribe amoxicillin/clavulanate. They may or may not prescribe cefdinir or cephalexin since there is a small chance that a person with a penicillin allergy may also be allergic to these two.
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection Blood In Pee
How Do Antibiotics Treat A Uti
UTIs can be caused by many different types of germs including bacteria or fungi and in rare cases, even viruses. But bacterial UTIs are the most common.
If you have a bacterial UTI, the only way to treat it is by getting rid of the bacteria thats causing it. Thats where antibiotics come in. They either stop those bacteria from growing or directly kill the bacteria altogether.
Its worth noting that antibiotics only treat UTIs and other infections caused by bacteria. If you have a fungal or viral UTI, antibiotics wont help.
Which Antibiotic Will Work Best
Your doctor will take a urine sample to confirm that you have a UTI. Then the lab will grow the germs in a dish for a couple of days to find out which type of bacteria you have. This is called a culture. Itâll tell your doctor what type of germs caused your infection. Theyâll likely prescribe one of the following antibiotics to treat it before the culture comes back:
Which medication and dose you get depends on whether your infection is complicated or uncomplicated.
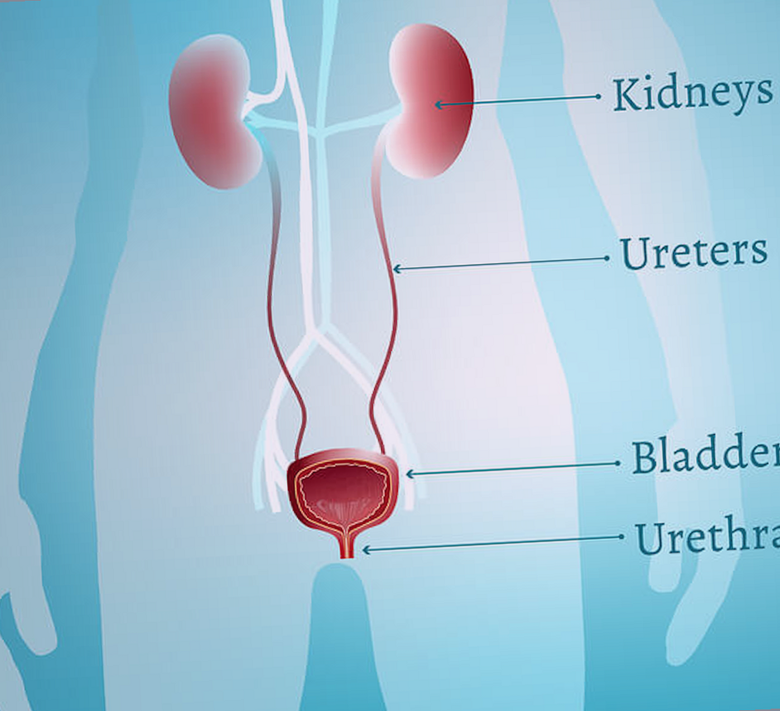
âUncomplicatedâ means your urinary tract is normal. âComplicatedâ means you have a disease or problem with your urinary tract. You could have a narrowing of your ureters, which are the tubes that carry urine from your kidneys to your bladder, a narrowing in the urethra which transports urine from the bladder out of the body, or, you might have a blockage like a kidney stone or an enlarged prostate . It’s also possible you have a urinary fistula or a bladder diverticulum.
To treat a complicated infection, your doctor might prescribe a higher dose of antibiotics. If your UTI is severe or the infection is in your kidneys, you might need to be treated in a hospital or doctor’s office with high-dose antibiotics you get through an IV.
Your doctor will also consider these factors when choosing an antibiotic:
- Are you over age 65?
- Are you allergic to any antibiotics?
- Have you had any side effects from antibiotics in the past?
Read Also: Symptoms Of Pinworms In Urinary Tract
Recognizing The Symptoms Of A Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections do not always present with obvious signs and symptoms. The most common symptom of a urinary tract infection is a frequent and urgent need to urinate.
Other symptoms include:
- A strong, persistent need to urinate, even after just having gone
- Pain or burning during urination
- Frequent, small amounts of urine
- Urine that is cloudy in appearance
- Urine that is red, bright pink or cola-colored
- Urine that has a strong smell
- Pain, pressure or soreness in the pelvis, lower belly, back or sides
These symptoms do not always indicate a UTI. Frequent urination can also be a symptom of sexually transmitted infections or other vaginal infections. Only a doctor or nurse can properly check for a UTI.
If the infection travels to the kidneys, you may experience:
- Pain in your mid-back
- Fever
- A recent exam or urinary surgery
When Should I Call My Healthcare Provider
- Fever.
- Back pain.
- Vomiting.
If you have any of these symptoms, or your other symptoms continue after treatment, call your healthcare provider. A UTI can spread throughout your urinary tract and into other parts of your body. However, treatment is very effective and can quickly relieve your symptoms.
Also Check: How Does Someone Get A Urinary Tract Infection
Antibiotics For Recurrent Infections
Doctors sometimes advise that women with repeat infections use preventive antibiotic therapy. This may include taking a small dose of antibiotics daily or on alternate days, taking antibiotics after sexual intercourse , or taking antibiotics only when you develop symptoms. Talk with your doctor about which treatment strategy is right for you.
What Your Doctor May Ask
There are risk factors that make you more susceptible to getting urinary tract infections. Your doctor may go down a list of risk factors with you during your visit. Certain things your doctor may ask you about are:
- Your sexual activity
- Type of birth control you are on
- Whether you have gone through menopause
- Whether you have a suppressed immune system
- Whether you have used a catheter recently
Make sure to answer your doctors questions with as much detail as possible. Even the smallest detail can help your telehealth provider in prescribing the right treatment for your bladder infection.
Though some of your doctors questions may seem personal and probing, try to remember that your physician is simply doing his or her job. Your doctor is not delving into your personal life for any other reason than to help you overcome the pain and discomfort in which you are.
Recommended Reading: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Help With Urinary Tract Infections
Can Home Remedies Quickly Treat A Uti
As resistance to antibiotics is becoming more common, many people are looking for ways to avoid using them. While this can be a good thing in some cases, it can draw out your illness in other instances.
The most commonly asked about home remedy for UTIs is cranberry. Drinking cranberry juice or taking cranberry tablets has been long-touted as a natural alternative for treating UTIs. The thought is that cranberry makes your urine more acidic which, in turn, kills the bacteria causing your infection.
Unfortunately, cranberry does not treat UTIs very well. On the flip side, though, it can be useful for helping to prevent infections if youre prone to them. This seems to also be the case for other acidic fruits like lemon. Just be sure if youre going to try this for preventing future UTIs that you drink unsweetened juice, as sugar actually helps bacteria to grow.
Do I Really Need To Take Antibiotics For A Uti
In most cases, it makes sense to start antibiotics if you know you have a bacterial UTI since this is the only way to treat it.
While it is possible for a UTI to go away on its own, this doesnt always happen. Plus, youll still have to deal with uncomfortable UTI symptoms like pain during urination while waiting to see if the UTI will go away. And if it doesnt, the infection can travel up your urinary tract and cause a more serious infection in your kidneys called pyelonephritis. If youre pregnant, have underlying health conditions, or are older than 65 years old, you should not try to treat a UTI without antibiotics.
You May Like: What Can I Do To Prevent Urinary Tract Infections