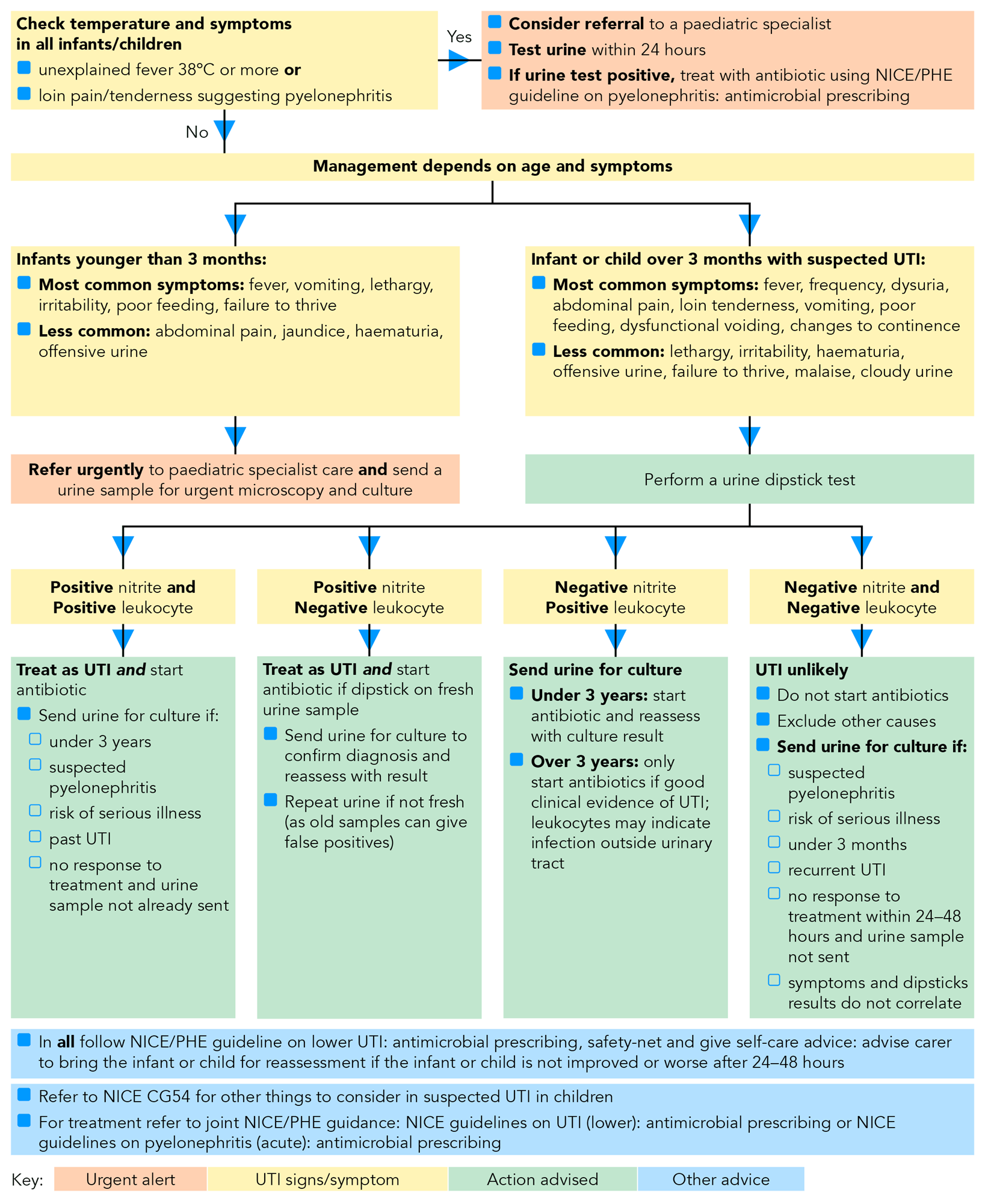
How Are Urinary Tract Infections Diagnosed
Your doctor will review your medical history and do a physical exam. Other tests may include:
- Urinalysis. Lab testing of urine is done to check for various cells and chemicals, such as red and white blood cells, germs , or a lot of protein.
If UTIs become a repeated problem, other tests may be used to see if the urinary tract is normal. These tests may include:
- Intravenous pyelogram . This is a series of X-rays of the kidney, ureters , and bladder. It uses a contrast dye injected into a vein. This can be used to find tumors, structural abnormalities, kidney stones, or blockages. It also checks blood flow in the kidneys.
- Cystoscopy. In this test, a thin, flexible tube and viewing device is put in through the urethra to examine the bladder and other parts of the urinary tract. Structural changes or blockages, such as tumors or stones can be found.
- Kidney and bladder ultrasound. This imaging test uses high-frequency sound waves to make images of the bladder and the kidneys on a computer screen. The test is used to determine the size and shape of the bladder and the kidneys, and check for a mass, kidney stone, cysts, or other blockages or abnormalities.
Increase Knowledge And Develop Skills
Changing key practices related to UTI management and treatment requires education for front-line staff, as well as residents and their families.
Strategy E: Deliver classroom education to staff
- Education can bring together staff to learn and discuss issues associated with the overuse of antibiotics, symptoms that indicate a UTI, and new organizational processes related to UTI assessment documentation.
- There are different ways to deliver education in your LTCH: classroom education, bullet rounds, online learning platforms, and orientation for new staff.
Strategy G: Use coaching to reinforce practices and support staff
- Coaches provide one-on-one education, supervision, assessment, feedback, and emotional support to front-line staff as they adopt the key practice changes in the UTI Program.
- Coaching for Beliefs and Consequences
Prevention Of Utis: A Focus On Immunomodulation
Vaccines remain the gold standard for preventive infectious-disease control. While E.coli-vaccine research continues, the expression of multiple suites of virulencefactors by UPEC strains remains a stumbling block. Despite these challenges datafrom animal models showing that antibody titers correlate with bacterial load andinfection duration suggest that vaccine-based prophylaxis can beeffective.4 Immunomodulation using bacteria-derived preparations offers analternative route for prophylaxis. Several bacterial lysate therapies are availablefor UTI prevention. Of these, OM-89 is the best studied and consists of 18 strainsof UPEC.9
Recommended Reading: Signs Of Urinary Blockage In Cats
Iii Proper Techniques For Urinary Catheter Maintenance
Urinate Before And After Sex
Sexual activity increases the chances of getting a UTI, especially if youre a woman. Thats because bacteria can easily get into the urethra during sex.
To reduce your risk, pee immediately before and after sex. The idea is to flush out bacteria that may cause UTIs.
Its also a good idea to gently wash your genital area before sex. This can help keep the area clean and reduce the chance of bacteria spreading to your urethra.
Read Also: Is Honey Good For Urinary Tract Infection
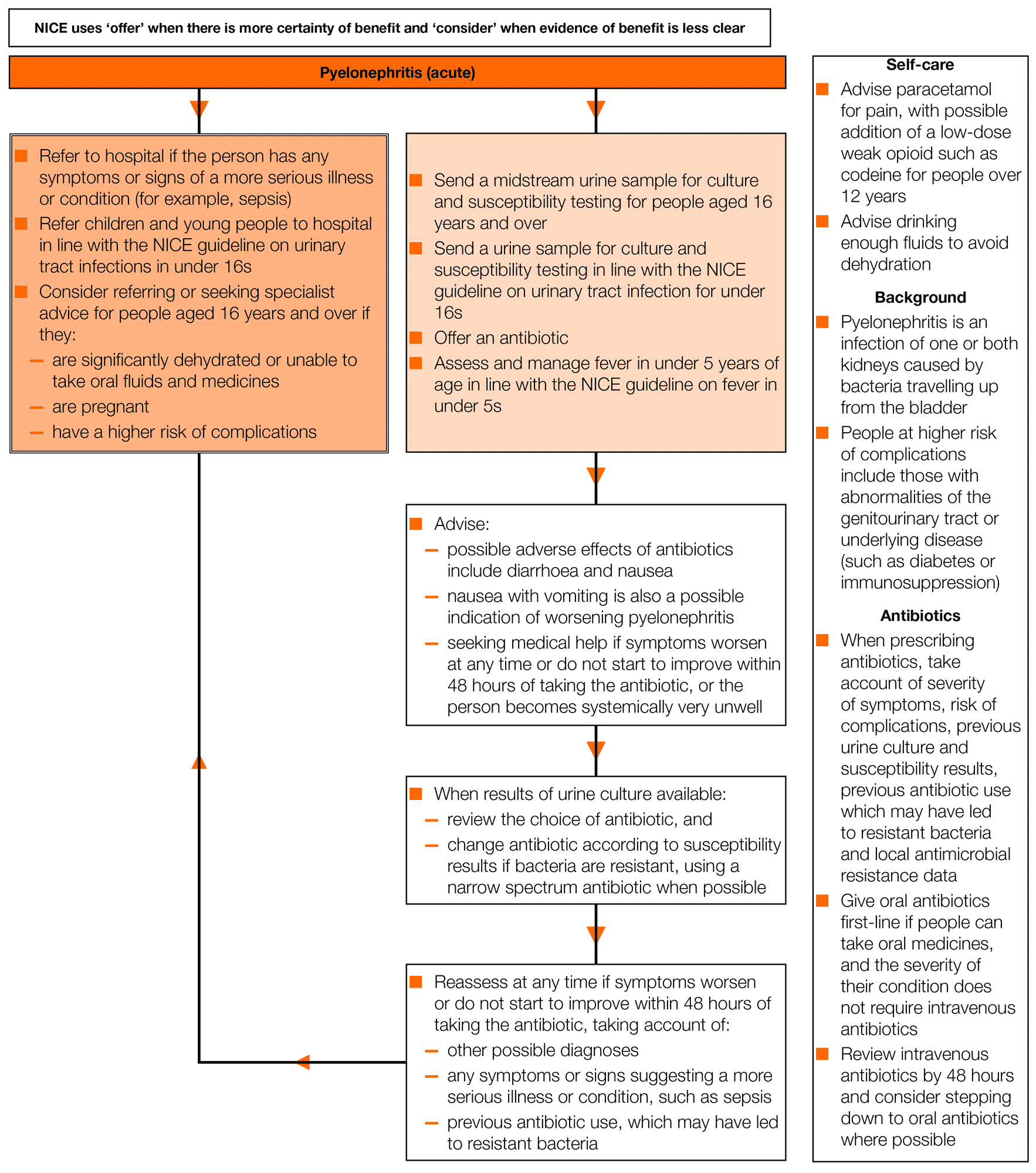
Acute Uncomplicated Lower Uti : Guideline Recommendations
Definitions of uncomplicated cystitis vary between guidelines. The 2018 EuropeanAssociation of Urology guidelines define uncomplicated UTI as acute,sporadic, or recurrent cystitis limited to nonpregnant, premenopausal women withno relevant anatomical or functional abnormalities in the urinarytract.12 The relevance of any urinary tract abnormality is the keyfactor in whether a UTI should be treated as complicated or uncomplicated. Thisis emphasized in the current German S3 guidelines, which define uncomplicatedUTI on the basis of no relevant functional and anatomical abnormalities, norelevant renal dysfunctions, or no relevant comorbidities/differential diagnosesfavoring UTI or more serious outcomes.13 From the perspective ofthe German S3 guidelines, infection in pregnant women, postmenopausal women,young men, and diabetics with stable glycemic control can receive the samecategorization as uncomplicated when patients are otherwise healthy and withoutrelevant comorbidities.13
Coconut Oil For Urinary Tract Infection
Image: Shutterstock
1 cup pineapple or juiced pineapple
What You Have To Do
Consuming one cup of cut pineapple every day can help treat and prevent urinary tract infection. You can also drink pineapple juice every day.
How Often Should You Do This
Eat at least one cup of pineapple every day until the infection clears.
Why This Works
If your doctor has prescribed antibiotics to treat your UTI, supplementing the drugs with a daily dose of pineapple can expedite the process of recovery. The enzyme bromelain in pineapple enhances the effect of the antibiotic treatment of urinary tract infections .
You May Like: Artificial Sphincter For Urinary Incontinence
Diagnostics And Symptom Scoring
Classical diagnostics in acute uncomplicated cystitis involve: taking history todetermine experience of recurrence and complicating factors determiningsymptoms including frequency, urgency, and dysuria physical examination of thegenitals and assessment of suprapubic and flank pain urinalysis using teststrips, flow cytometry or microscopy and urine culture. The delay involved inurine culture generally makes the test impractical, resulting in empiricaltreatment of most acute uncomplicated cystitis cases.
Novel data on the sensitivity and specificity of uranalysis and an increasedunderstanding of the benign nature of ABU have led to a refocusing on symptomsscoring as a measure of diagnosis and treatment success.22,23 The AcuteCystitis Symptom Score is an 18-item, validated, self-reported measure ofsymptoms that comprises four sections which assess: typical symptoms symptoms for differential diagnosis quality of life and additionalsigns and symptoms. With 94% sensitivity and 90% specificity, this system isanalogous to microbiological assessments.24 The Spanish and Portugueseversions of the questionnaire are currently being validated.
Sterilizing Washcloths For Home Use
Sterilizing washcloths for washing and personal hygiene to help prevent recurrent UTIs may be recommended. This extra step is probably unnecessary for most patients with recurrent infections, but for the more resistant or severe cases, it may be very helpful. Home sterilization of washcloths is only one part of an ongoing program to help prevent these infections. Use only those washcloths purchased for this purpose and remember to wipe correctly, front to back.
Wash the washcloths with hot water and soap in a clothes washer. If a clothes washer is unavailable, use soap and hot water in the sink.
Boil the washcloths in water for at least 20 minutes .
Take the washcloths out of the water and allow to dry or use a clothes dryer.
When dry, place each washcloth in a separate sealable plastic bag, such as a zip-lock bag. Leave the bags open do not seal them yet.
Place the bags containing washcloths in a microwave oven. Put a large glass of cold water in the center of the microwave oven. Do not place the bags with the washcloths in the water.
Put the microwave oven on high power, set the timer for 5 minutes, and turn it on. Replace the glass with a new glass of cold water, and run the microwave oven on high power for an additional 5 minutes.
Let the bags cool, then close the bags. The sterile washcloth is now inside a sterile bag.
Tips for UTI prevention may be summarized as follows:
Chief, Division of Infectious Disease, Navy Medical Center, San Diego
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get A Urinary Tract Infection Male
What Do We Need To Change And Are We Ready To Make Those Changes
During this phase, long term care homes look at the practice changes and assess both their need for the program and what they should focus on in addition to making sure they are ready to get started. At the end of this phase, LTCHs will have a good understanding of whether they are ready to move forward with implementing the Program.
Use the two worksheets below to help assess for need and fit of the program, and whether your LTCH is ready to implement. Once you have confirmed your readiness, you will then move on to establishing the implementation team that will support the implementation of the program.
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection
UTIs are common infections that happen when bacteria, often from the skin or rectum, enter the urethra, and infect the urinary tract. The infections can affect several parts of the urinary tract, but the most common type is a bladder infection .
Kidney infection is another type of UTI. Theyre less common, but more serious than bladder infections.
Read Also: Can Stress Cause Urinary Tract Infection
Ii Proper Techniques For Urinary Catheter Insertion
Drink Plenty Of Fluids
![Urinary Tract Infections [UTI]](https://www.urinaryhealthtalk.com/wp-content/uploads/urinary-tract-infections-uti-medgeeks.png)
Stay hydrated throughout the day. This will make you pee more frequently, which flushes bacteria out of your urinary tract.
Water is the best choice. Aim for 6 to 8 glasses per day. If its hard for you to drink that much water, you can also increase your fluid intake by drinking sparkling water, decaffeinated herbal tea, milk, or smoothies made with fruits and vegetables.
Try to limit or avoid alcohol and caffeinated drinks, which may irritate the bladder.
You May Like: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia With Urinary Frequency
What Are The Symptoms Of A Urinary Tract Infection
These are the most common symptoms of a UTI:
- Frequent urination
- Pain or burning when passing urine
- Urine looks dark, cloudy, or reddish in color
- Urine smells bad
- Feeling pain even when not urinating
- Pain in the back or side, below the ribs
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Despite an strong urge to urinate, only a small amount of urine is passed
- Women may feel an uncomfortable pressure above the pubic bone
The symptoms of UTI may look like other conditions or medical problems. Always see a health care provider for a diagnosis.
Urinary Tract Infections: What You Need To Know To Reduce Your Risk
Have you ever experienced pain or burning while urinating, the urge to urinate frequently, or lower abdominal pain and fever? These could be symptoms of a urinary tract infection.
A urinary tract infection, also known as a UTI, occurs when bacteria or other germs enter the urinary tract. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recently reported that UTIs are the third most common healthcare-associated infection, accounting for more than 93,000 infections in hospitals alone.
The urinary tract consists of our kidneys, which filter the body of waste by making urine. The urine drains into our bladder by tubes called ureters. The bladder stores the urine until you are ready to urinate. The urine then leaves our body by the urethra.
Sometimes, a drainage device to remove the urine from the body is needed for a patient in a hospital or other care facility. This tube is called a urinary catheter and is inserted through the urethra by specially trained healthcare personnel. The catheter is connected to a drainage tube and a bag. The urine is emptied regularly from this drainage bag. It is estimated that 15-25 percent of hospitalized patients and 5 percent of long-term care residents have one of these catheters.
Because the catheter provides a direct pathway for the germs to travel into the bladder, there is an increased risk of a UTI. When this occurs, it is called a catheter-associated urinary tract infection or CAUTI.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Yeast Infection Treatment
Assess Capacity For Sustaining The Gains
Once the program is underway, it is recommended that your team understand what program elements and other factors may influence sustainability by completing the Sustainability Assessment Tool. Results from completing this tool can be used to develop a sustainability action plan to maintain, as well as build, your team’s capacity for sustainability.
Immunology Of The Urinary Tract
The kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra form the urinary tract. The proximityof the urethra to the intestine makes colonization by uropathogenicEscherichia coli afrequent occurrence, particularly in catheterized patients. Ascending movementthrough the urethra can lead to bladder infections, and further ascent throughthe ureter may lead to inflammation and protease release resulting in kidneydamage and hematogenic dissemination of the infection.2
Colonization of the bladder by uropathogenic bacteria with and withoutcatheterization.3
Adapted by permission from Springer Nature: Nature, Nature ReviewsMicrobiology, Urinary tract infections: epidemiology, mechanisms ofinfection and treatment options. Flores-Mireles AL, Walker JN, CaparonM, Hultgren SJ. 2015.
Also Check: Urinary Incontinence Pads For Elderly
Indications For Specialist Referral
Most patients with recurrent uncomplicated UTI may be treated successfully by family physicians.32 Specialist referral for recurrent uncomplicated UTI is indicated when risk factors for complicated UTI are present . Referral is also indicated when a surgically correctable cause of UTI is suspected or the diagnosis of UTI as a cause for recurrent lower urinary tract symptoms is uncertain. Prior to referral, culture of the urine while symptomatic and 2 weeks after sensitivity-adjusted treatment may aid in confirming the diagnosis of UTI, as well as guiding further specialist evaluation and management.
How Are Urinary Tract Infections Treated
Your health care provider will figure out the best treatment based on:
- How old you are
Treatment for UTIs may include:
- Other medications to ease pain
- Heat to ease pain
You may also need to make lifestyle changes such as:
- Drinking plenty of water to help wash bacteria out of the urinary tract
- Avoiding coffee, alcohol, and spicy foods
- Quitting smoking
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of A Urinary Tract Infection Male
Latin America: Progress Towards Regional Guidelines
Close to one-tenth of the worlds population lives in Latin America. Theunique ethnic makeup of patients, alongside local variation in the availabilityof medicines, antibiotic resistance, and health care practices necessitates thecreation of regional guidelines on the treatment of UTI. Prescription ofantibiotics for recurrent UTI without consideration of preventive measures iscommon in many Latin American countries. In a global survey of E.coli susceptibility in 10 countries, the mean sensitivity totrimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole was 71.2% in the sole representative LatinAmerican country, Brazil, it was 54.4%.46
The current Brazilian guidelines were based on systematic review and expertopinion, organized by the Urogynecology Committee of the Brazilian Federation ofGynecology and Obstetrics Associations . Thecommittee included papers that cover genital prolapse, stress urinaryincontinence, overactive bladder, mixed urinary incontinence, painful bladdersyndrome, and recurrent UTI. Guideline sections covering genital prolapse andstress urinary incontinence have been published in the Brazilian Journal ofGynecology and Obstetrics.47,48 The guidelines forrecurrent UTI have yet to be published in a peer-reviewed journal, but areavailable online as a guide for members of FEBRASGO they recommend behavioralmodification, followed by immunomodulatory prophylaxis ,and, finally, by either continuous or postcoital antimicrobial prophylaxis.
Why Was The Uti Program Developed
- It is common to find bacteria in the urine of the elderly but it does not always mean that they have a UTI.
- Older people are often given antibiotics for what health care providers and other caregivers assume to be UTIs.
- It can be harmful to treat somebody with antibiotics when they dont need them.
- Antibiotic use can increase the risk of antibiotic resistance, which can make it more difficult to treat future infections.
For more information on the overuse of antibiotics in long term care homes, see infographic.
Recommended Reading: How To Clear Urinary Tract
Summary Of Major Recommendations
Educate personnel in correct techniques of catheter insertion and care.
Catheterize only when necessary.
Insert catheter using aseptic technique and sterile equipment.
Secure catheter properly.
Category II. Moderately Recommended for Adoption
Periodically re-educate personnel in catheter care.
Use smallest suitable bore catheter.
Avoid irrigation unless needed to prevent or relieve obstruction.
Refrain from daily meatal care with either of the regimens discussedin text.
Do not change catheters at arbitrary fixed intervals.
Category III. Weakly Recommended for Adoption
Consider alternative techniques of urinary drainage before usingan indwelling urethral catheter.
Replace the collecting system when sterile closed drainage has beenviolated.
Spatially separate infected and uninfected patients with indwellingcatheters.
Avoid routine bacteriologic monitoring.
* Refer to Introduction of manual for full explanation of the rankingscheme for recommendations.