Utis In The Elderly: Symptoms And Treatment
Urinary tract infections are the most common type of bacterial infection in older adults. According to the National Institutes of Health, UTIs affect around 10% of men and 20% of women older than 80. Seniors may also experience different and more severe symptoms than younger adults do, including agitation, mental confusion, and sudden changes in behavior.
When left untreated, UTIs in the elderly can cause serious problems, including permanent kidney damage and sepsis a generalized and potentially life-threatening infection.
Read on to understand how UTIs can affect the elderly and how to recognize symptoms of this common infection.
Urinary Tract Infection In Elderly
Many elderly adults in modern society tend to suffer from infections of the urinary tract, and this is somewhat burdensome for caregivers. Caregivers may experience caregiver burnout and/or fatigue as they try to care for their loved ones with urinary tract infections. Thus, it is crucial to be aware of the causes, signs and symptoms, and prevention mechanisms for elderly adults with urinary tract infections. It is also important to remember that assisted living caregivers are trained on how best to support elderly residents with urinary tract infection, in order to help alleviate the burden from the shoulders of the family caregivers.
Urinary tract infections, also referred to as UTIs, are more common in older adults who are 65 years and above. In fact, urinary tract infections are the second most common cause of hospital admissions in community-dwelling senior citizens of age 65 and older. There has been a sudden rise in the number of seniors diagnosed with urinary tract infections, particularly more so among women affected than men. Within the past few years, more than 10% of women over 65 years have been diagnosed with urinary tract infections, with the number increasing to over 30% among women over 80 years of age.
Can I Prevent Urine Infections
Unfortunately, there are few proven ways to prevent urine infections. No evidence has been found for traditional advice given, such as drinking cranberry juice or the way you wipe yourself.
There are some measures which may help in some cases:
- It makes sense to avoid constipation, by eating plenty of fibre and drinking enough fluid.
- Older women with atrophic vaginitis may wish to consider hormone replacement creams or pessaries. These have been shown to help prevent urine infections.
- If there is an underlying medical problem, treatment for this may stop urine infections occurring.
- For some people with repeated urine infections, a preventative low dose of antibiotic taken continuously may be prescribed.
Recommended Reading: How Does Botox Work For Urinary Incontinence
Older Adults Should Have Other Symptoms Too
When your loved ones doctor suspects a UTI, be sure to mention whether these symptoms are also present:
- Fever over 100.5 °F
- Worsening urinary frequency or urgency
- Sudden pain with urination
- Tenderness in the lower abdomen, above the pubic bone
Having at least two of the symptoms above, along with a positive urine culture, will confirm a UTI.
Are Frequent Utis A Sign Of Diabetes Or Is A Uti A Symptom Of Diabetes
A review from 2005 found that an astounding 50% of people with diabetes have some type of dysfunction of their bladder- thats half of every man and woman with diabetes. There are quite a few theories which we have already discussed, but again, most of the newer theories and research have only been conducted on rats.
Another fact this review highlights is that women who have Type 1 diabetes have a higher risk for kidney infections , which can potentially damage the kidneys function long term. This may lead to the need for a kidney transplant as the damage becomes severe.
Dont Miss: Probiotics For Urinary Tract Infection
You May Like: Azo Urinary Pain Relief Walgreens
Quality Assessment / Risk Of Bias
Two review authors assessed the risk of bias of included studies independently, with any discrepancies being resolved by consensus, or through discussion with a third reviewer , if necessary. The risk of bias was assessed using a modified version of the assessment checklist developed by Downs and Black . Quality items that pertained to interventions and trial studies were removed as they were not deemed to be appropriate for the studies included in this review. An additional five quality items were added to the quality assessment to determine if studies described the criteria used for confusion, UTI and bacteriuria, and if their criteria for UTI and confusion were valid and reliable. Criteria for confusion were deemed valid and reliable if accepted criteria were utilised, including: the Confusion Assessment Method, the Organic Brain Syndrome Scale or the Diagnosis and Statistical Manual criteria . Similarly, criteria for UTI were deemed valid and reliable if established criteria for UTI were utilised, including: the McGeer Criteria, the revised McGeer Criteria, the Loeb Criteria, or the Revised Loeb Criteria . The modified checklist finally consisted of 14 quality items, grouped into: reporting, internal validity, external validity and criteria . The risk of bias for each quality item was reported as low risk of bias, high risk of bias, unclear risk of bias or not applicable.
Table 2 Quality Assessment Criteria
Institutionalized Older Adults & Catheterized Patients
Similar to other populations, the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI in nursing home residents requires the presence of genitourinary symptoms in the setting of a positive urine culture. In older adults who are cognitively intact, the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI is relatively straightforward. However, nursing home residents often suffer from significant cognitive deficits, impairing their ability to communicate, and chronic genitourinary symptoms , which make the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI in this group particularly challenging. Furthermore, when infected, nursing home residents are more likely to present with nonspecific symptoms, such as anorexia, confusion and a decline in functional status fever may be absent or diminished . In the setting of atypical symptoms, providers are often faced with the challenge of differentiating a symptomatic UTI from other infections or medical conditions. The high prevalence of bacteriuria plus pyuria in this population often leads to the diagnosis of UTI. Although bacteriuria plus pyuria is necessary for diagnosis of a laboratory-confirmed UTI, alone it is not sufficient for making the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI. To date, universally accepted criteria for diagnosing UTI in this population do not exist, making it difficult for providers to distinguish a symptomatic UTI from other conditions in the presence of new nonspecific symptoms.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Urinary Incontinence
What Causes Utis In Seniors
You know seniors are more likely to contract a UTI than a kid or a younger adult, but what exactly causes the UTI in the first place? UTIs are caused by bacteria or fungi thats entered the urinary tract. This often happens due to a blockage of urine flow and stored urine in the bladder.
The most common UTI-causing bacteria: E. coli. E. coli is responsible for about 85% of all UTIs in adults. It can contaminate food, such as ground beef and raw vegetables, which ends up in your stool. Since the anus and the urethra are so close to one another, especially in females, good bathroom habits are essential protection against UTIs.
Seniors who reside in a hospital or another care facility and have a catheter in place are also at high risk of contracting a UTI. Catheters provide an easy entry point for UTI-causing bacteria, and it doesnt help that UTI-causing bacteria commonly infiltrate catheters.
Causes Of Urinary Incontinence
Incontinence can happen for many reasons. For example, urinary tract infections, vaginal infection or irritation, constipation. Some medicines can cause bladder control problems that last a short time. When incontinence lasts longer, it may be due to:
- Weak bladder muscles
- Overactive bladder muscles
- Weak pelvic floor muscles
- Damage to nerves that control the bladder from diseases such as multiple sclerosis, diabetes, or Parkinsons disease
- Blockage from an enlarged prostate in men
- Diseases such as arthritis that may make it difficult to get to the bathroom in time
- Pelvic organ prolapse, which is when pelvic organs shift out of their normal place into the vagina. When pelvic organs are out of place, the bladder and urethra are not able to work normally, which may cause urine to leak.
Most incontinence in men is related to the prostate gland. Male incontinence may be caused by:
- Prostatitisa painful inflammation of the prostate gland
- Injury, or damage to nerves or muscles from surgery
- An enlarged prostate gland, which can lead to Benign Prostate Hyperplasia , a condition where the prostate grows as men age.
Read Also: Signs And Symptoms Of Urinary Incontinence
Why Are Seniors At Risk For Utis
Men and women older than 65 are at greater risk for UTIs. This is because both men and women tend to have more problems emptying their bladder completely as they age, causing bacteria to develop in the urinary system.
In older men, this often happens because of a common condition called benign prostatic hyperplasia , or an enlarged prostate gland. The enlarged prostate blocks the flow of urine and prevents the bladder from fully emptying.
As women age, the bladder muscles weaken and prevent the bladder from emptying completely, increasing the risk of infection. Women also produce lower amounts of estrogen after menopause. This creates an imbalance of good and bad bacteria in the vagina, which can lead to infection.
Other risk factors for UTIs in older adults include:
- Using a catheter to empty the bladder
- Having kidney stones, which can block the flow of urine
- Having a suppressed immune system, which lowers the bodys defense against infection
Empty Your Bladder After Sex
Following sex, be sure to use the bathroom and empty your bladder as soon as possible. You should also drink extra water to flush any bacteria out of the urinary tract.
If you suspect you have a urinary tract infection and need relief from your symptoms, schedule a diagnostic evaluation at Primary Care & Walk-In Medical Clinic online, , or visit the clinic in person.
You Might Also Enjoy
Don’t Miss: Natural Supplements For Urinary Incontinence
A Pharmacist Can Help With Utis
You can ask a pharmacist about treatments for a UTI. A pharmacist can:
- offer advice on things that can help you get better
- suggest the best painkiller to take
- tell you if you need to see a GP about your symptoms
Some pharmacies offer a UTI management service and can prescribe antibiotics if they’re needed.
How Dangerous Is A Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infection often occur in older adults, it happens when a bacterial infection affect the bladder which is supposed to be a sterile environment, the seriousness of urinary tract infections and how dangerous it could be can vary from a minor medical issue easy to solve with antibiotics to a life threatening condition,
it also depends on the overall state of health for the affected person and whether or not the infection spread to other parts and organs of the body or not.
In most cases with UTIs symptoms are mainly related to bladder irritation such as a burning sensation while urinating, blood in the urine, pain and urge to urine frequently, oral antibiotics treatment usually result in quick improvement.
In older adults specially ones with dementia, a UTI can cause delirium which is a worsening situation for their mental state and that can be dangerous because it put them at risk of failing and hurting themselves.
A urinary tract infection can become even more serious when it affects the other parts of the body like the kidney or it spreads to the bloodstream, in this situation a life threatening low blood pressure may occur, intravenous antibiotics may be used to treat this spreading UTI.
Note: There is a condition that is often confused with urinary tract infections but it isnât, Asymptomatic bacteriuria which happens when a urine culture grows bacteria, even though the person may not show any symptoms,
Read Also: Amoxicillin For Urinary Tract Infection Dosage
Treatment Considerations In Older Adults
Dr N: She told me that her incontinence had definitely gotten worse in the last couple of weeks. I had noticed that another physician had sent a urine culture that had grown more than 105 CFU/mL of E coli that was sensitive to all antibiotics. Assuming that this was asymptomatic bacteriuria, it was not treated with antibiotics. A repeat urine culture again showed more than 105 CFU/mL of E coli, again it was pan sensitive. Given her symptoms, I treated her with a 7-day course of an antibiotic. However the antibiotics didnt really make a difference.
Studies have shown that treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria does eradicate bacteriuria. However, reinfection rates , adverse antimicrobial drug effects, and isolation of increasingly resistant organisms occur more commonly in the therapy vs nontherapy groups. No differences in genitourinary morbidity or mortality were observed between the 2 groups.
Read Also: Yeast Infection Symptoms Womenâs Health
Simple Ways To Prevent A Uti In Elderly Women
Urinary tract infections, or UTIs, are more than a painful medical condition. Left untreated, these infections can spread through the body. The leading cause of sepsis, an untreated UTI can ultimately result in death. For caregivers of elderly patients, learning how to recognize a UTI can be tricky as the symptoms are varied. Fortunately, there are three easy ways to avoid the onset of the infection to begin with.
Recommended Reading: How Does One Get A Urinary Tract Infection
When Should You Have A Urine Test
You should get a urine test if you have new or worsening urinary symptoms like these:
- Pain when urinating.
- Blood in the urine
- A strong urge to urinate often
You should also get a urine test if you have a fever or if a blood test suggests that you have an infection. But before you get a urine test, your doctor should make sure you dont have other symptoms, like a cough, that may be caused by something else.
If you dont have UTI symptoms, you might still need a urine test if you are scheduled to have:
- Prostate surgery.
- Kidney stones removed.
- Bladder tumors removed.
This report is for you to use when talking with your healthcare provider. It is not a substitute for medical advice and treatment. Use of this report is at your own risk.
09/2014
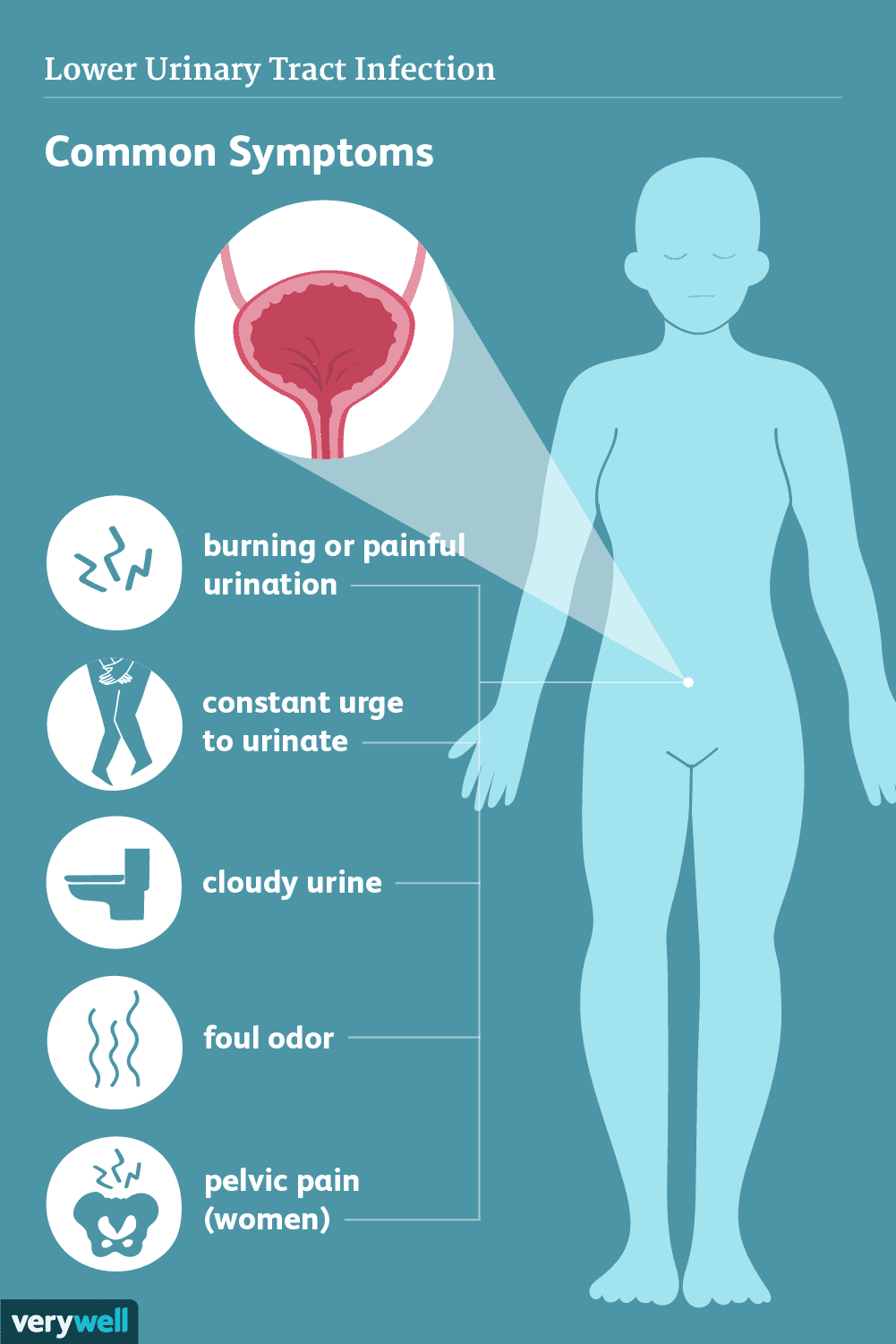
Senior Uti Do You Know The Symptoms
Urinary tract infections, or UTIs, are the most common bacterial infection in older adults,affecting women more often than men.
UTIs can typically be treated effectively with antibiotics once diagnosed.Unfortunately, not all UTIs are treated quickly, and some aren’t even identified, particularly in seniors.
What is a UTI?
A UTI is an infection in the urinary tract. The urinary tract includes the kidneys, bladder, ureters and the urethra which carries urine out of the body. They are most commonly caused by bacteria but can also be a fungal infection.
A lower UTI is a common infection, affecting the lower part of the urinary tract, the urethra and urinary bladder. Infection of the urethra is urethritis while a bladder infection is cystitis. An upper UTI affects the kidneys.
What causes a UTI?
A typical bacterial UTI is caused by bacteria, often fecal bacteria, entering the urethra through the urethral opening where urine is released from the body. Usually, the body can fight off these bacteria and prevent infection. However, if the immune system is too weak, the bacteria multiply, causing infection.
Fungal UTIs usually stem from fungus in the bloodstream. Fungal UTIs are relatively uncommon, impacting mainly those with illnesses that compromised their immune system.
What are the symptoms of a UTI?
When typical, healthy adults get a UTI, the symptoms are usually easy to identify, and the infection is simple to diagnose:
If left untreated, a person may experience:
You May Like: Stages Of Urinary Tract Infection
Why Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Usually Doesnt Warrant Antibiotics
Clinical studies overwhelming find that in most people, treating asymptomatic bacteriuria with antibiotics does not improve health outcomes.
A 2015 clinical research study found that treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria in women was associated with a much higher chance of developing a UTI later on, and that these UTIs were more likely to involve antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Even for frail nursing home residents, there is no proof that treating asymptomatic bacteriuria improves outcomes, but it does increase the presence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Despite the expert consensus that this condition doesnt warrant antibiotics, inappropriate treatment remains very common. A 2014 review article on this topic notes overtreatment rates of up to 83% in nursing homes.
Is there a role for cranberry to treat or manage urine bacteria?
The use of cranberry juice or extract to prevent UTIs has been promoted by certain advocates over the years, and many patients do prefer a natural approach when one is possible.
However, top quality clinical research has not been able to prove that cranberry is effective for this purpose. In a 2016 study of older women in nursing homes, half were given cranberry capsules daily. But this made no difference in the amount of bacteria or white blood cells in their urine.
A 2012 systematic review of high-quality research studies of cranberry for UTI prevention also concluded that cranberry products did not appear to be effective.
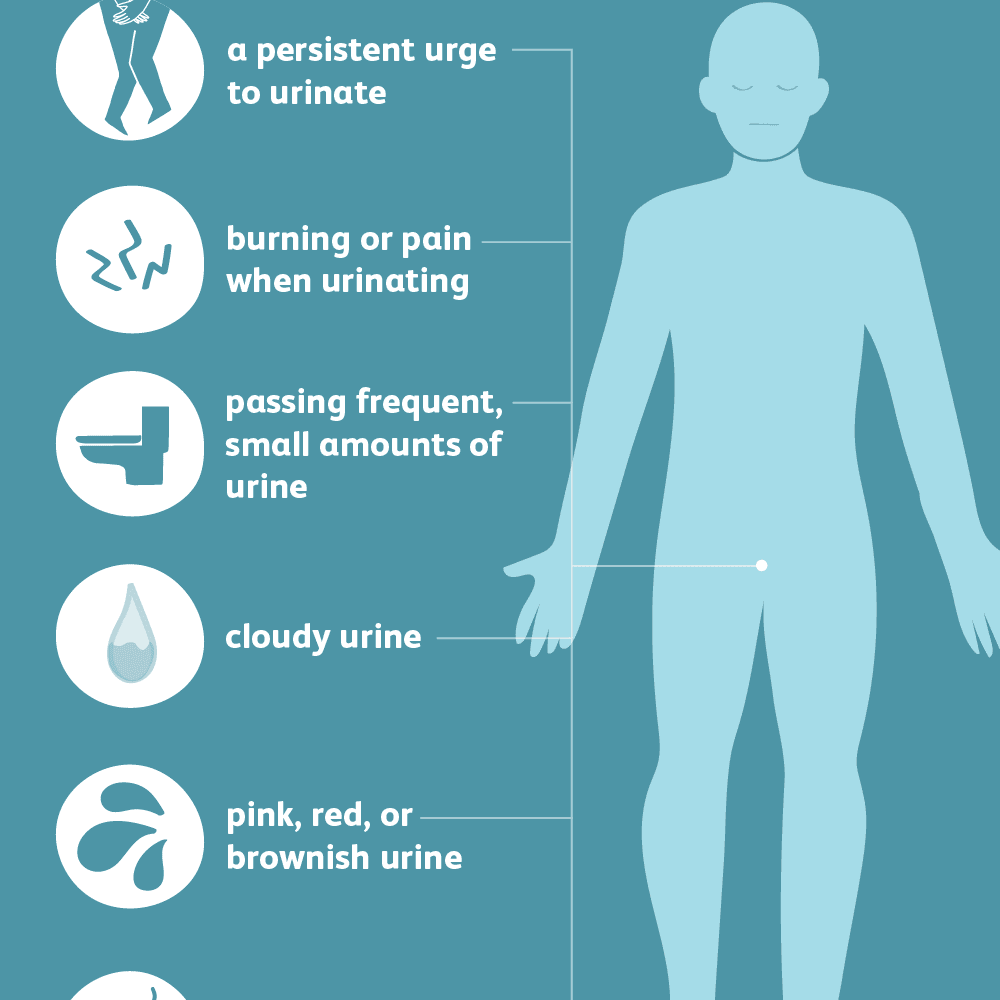
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Utis In The Elderly
Detecting UTI symptoms in seniors can be tricky because many of them affect behavior, so they can be missed or attributed to more serious illnesses.
The classic, universal symptoms for UTIs are frequent urination, burning pain, cloudy urine and lower back pain. But because senior citizens immune systems are not functioning at optimal levels, the symptoms will take a different turn and produce some unsettling side effects:
- Confusion
Why is this?
Don’t Miss: Is Cranberry Juice Good For Your Urinary Tract