Antibiotics For A Uti
The form of antibiotic used to treat a bacterial UTI usually depends on which part of the tract is involved.
Lower tract UTIs can usually be treated with oral antibiotics. Upper tract UTIs require intravenous antibiotics. These antibiotics are put directly into your veins.
Sometimes, bacteria develop resistance to antibiotics. To reduce your risk of antibiotic resistance, your doctor will likely put you on the shortest treatment course possible. Treatment typically lasts no more than 1 week.
Results from your urine culture can help your doctor select an antibiotic treatment that will work best against the type of bacteria thats causing your infection.
Treatments other than antibiotics for bacterial UTIs are being examined. At some point, UTI treatment without antibiotics may be an option for bacterial UTIs by using cell chemistry to change the interaction between the body and the bacteria.
There are no home remedies that can cure a UTI, but there are some things that you can do that can help your medication work better.
These home remedies for UTIs, like drinking more water, may help your body clear the infection faster.
More Tips To Help Remove And Prevent Burning When Urinating
- Drink plenty of water during the day to increase urine flow to help facilitate the elimination of bacteria.
- Maintain good intimate hygiene and clean the genital area from front to back to prevent new infections.
- Wash your hands before and after going to the bathroom.
- Use condoms during all sexual relations.
- Urinate after sexual encounters to prevent bacteria from entering the body.
- Favor cotton underwear and natural fabrics.
This article is merely informative, oneHOWTO does not have the authority to prescribe any medical treatments or create a diagnosis. We invite you to visit your doctor if you have any type of condition or pain.
If you want to read similar articles to How To Get Rid Of Burning When Urinating, we recommend you visit our Healthy living category.
Causes Of Pain Or Burning With Urination
Burning or pain during urination is typically caused by inflammation of the urethra or bladder. In women, inflammation in the vagina or in the region around the vaginal opening can be painful when exposed to urine. Inflammation that results in burning or pain is usually caused by infection but sometimes by noninfectious conditions. Sometimes acidic foods and certain drinks act as irritants and cause burning or pain during urination.
Recommended Reading: Urinary Tract Infection In Children
When To See A Doctor For Urethritis
For temporary, mild urethritis that comes from using a new soap or lotion, you may not need to see your health-care provider. But other cases of urethritis may need to be checked.
- If you are experiencing pain with urination following a medical procedure, contact your physician to discuss the need for evaluation or treatment. The pain may be an expected side effect of the procedure, or it may signify the beginning of an infection.
- All other cases of burning with urination require medical attention within 24 hours.
Urethritis is probably not an emergency, but you will want to get relief promptly. If you are experiencing other signs of illness, such as fever, nausea, vomiting, back, and abdominal pain, you may need emergency care. These symptoms could mean the infection has moved beyond the urethra. These potentially serious conditions require immediate evaluation by your doctor or in an emergency department.
If you have an object lodged in your urethra or another injury to your penis, seek immediate medical care at a hospital’s emergency department. These situations can progress rapidly into a life-threatening infection.
Signs And Symptoms Of A Urinary Tract Infection
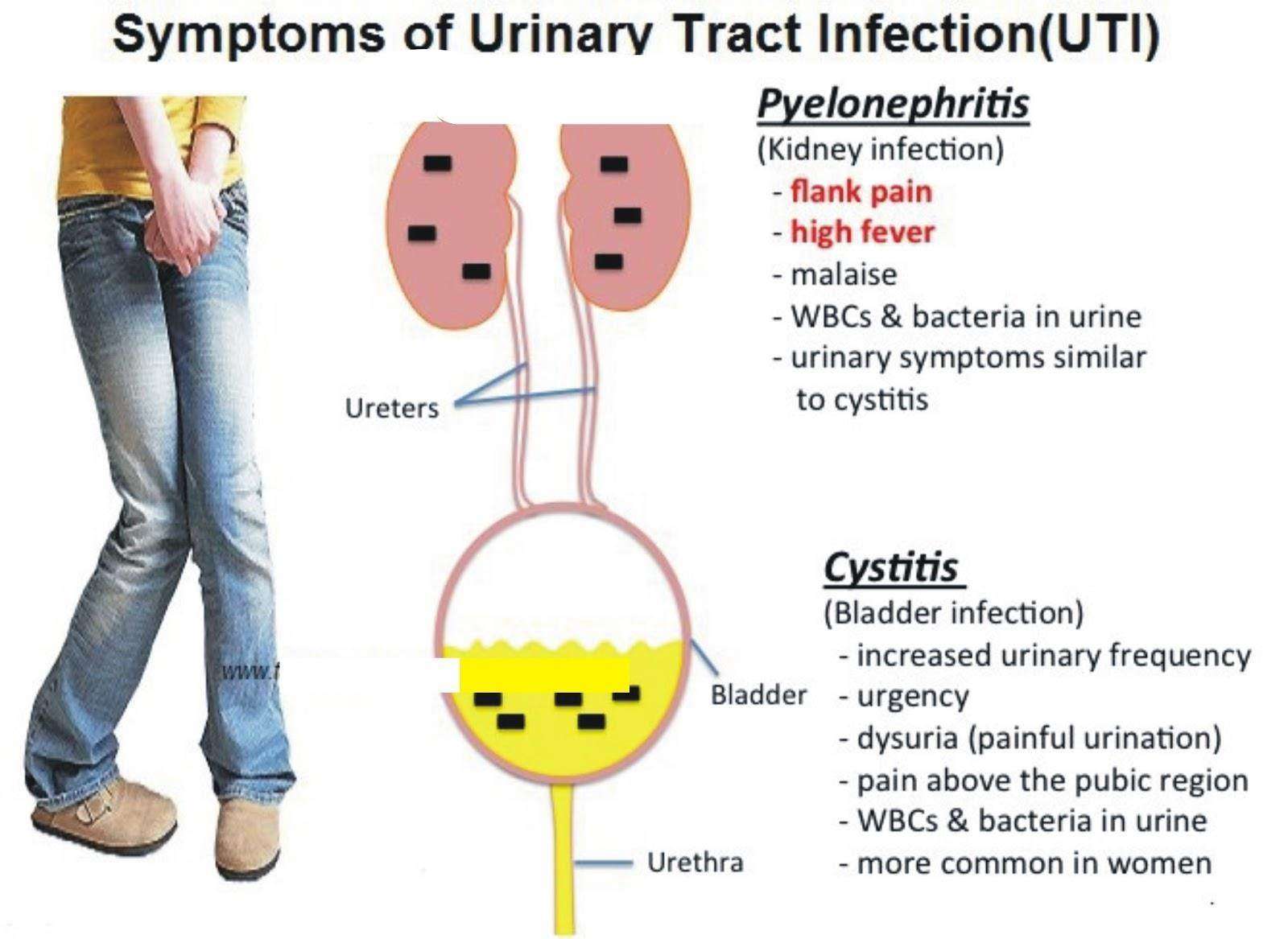
Urinary tract infections may go unnoticed at first, especially if the initial symptoms are mild. Symptoms generally worsen and magnify as the infection spreads. One of the first symptoms is often a frequent urge to urinate coupled with small amounts of urine or the feeling of being unfinished after urinating. This may lead to straining. An itching or burning sensation during urination is common as well. Other symptoms, like blood in the urine, may be more obvious and suggest a more serious infection.
Most urinary tract infection symptoms are consistent between genders, but some symptoms are more prevalent in one gender than the other. Urinary tract infections are more common in adult females than males. Other diagnosis, such as a low grade infection of the prostate and sexually transmitted infections should be carefully considered.
-
Frequent urges to urinate, with only small amounts of urine
-
Cloudy or dark urine
-
Pain in the back just below the ribs
For either sex, back pain below the ribs is associated with kidney infections and should be taken seriously. If you experience kidney pain coupled with a fever, weakness, chills or nausea, seek medical attention immediately to prevent complications.
Recommended Reading: Hill’s Science Diet Adult Urinary & Hairball Control
Itching Urination After Urinating No Pain Or Skin Rash
Posted by Dr. Chris
HaroldG55 Asked :
I have been experiencing intense itching while urinating which settles but does not go away completely after I stop urinating. The itching sensation is like inside the penis and no matter how much I rub the area or try to scratch around the penis, nothing relieves it. Sometimes the itching gets quite extreme when I am sitting for long periods and cannot go to the toilet and it suddenly strikes and makes me jump up in my seat.
This has been going on for just over a week but over the past 2 days I noticed smelly mucus in my underwear which I dont think is semen because it just comes on its own with no sexual activity. My greatest fear is that this is a sexually transmitted disease but I am wondering if there are other causes. I have no skin rash on my penis and there is no pain when I urinate. The itching is quite intense during urination so I can say that it is bordering on burning to some extent. What else could cause this itch?
Any response by the Health Hype team does not constitute a medical consultation and the advice should be viewed purely as a guide. Always consult with your doctor before making any changes to your current treatment program. The information provided in this article is not an authoritative resource on the subject matter and solely intends to guide the reader based on the questions asked and information provided.
Dr. Chris Answered :
Diagnosis Of Urinary Tract Infection
Because viral infections of the bladder and kidneys are relatively rare, most UTIs require antibiotics. Leaving a UTI untreated can cause the symptoms to worsen and may result in permanent kidney damage or a weakened bladder failure to treat a UTI may make future UTIs more common and serious.
If your doctor discovers that your infection has spread to your kidneys, the treatment may be much more involved. Depending on the severity of the infection, hospitalization may be required to fully treat the kidney infection.
You May Like: Back Pain Causing Urinary Problems
Treatment For Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections are treated with antibiotics, which kill the bacteria responsible for the infection. Some of the most common antibiotics prescribed by doctors to treat UTIs include Amoxicillin, Bactrim or Ciprofloxacin. If a patient has developed a resistance to one type of medication, the doctor will prescribe a different antibiotic. If you have a history of urinary tract infections, be sure to mention this to the doctor as it may precipitate a change in what drugs are prescribed.
In addition to antibiotics, the doctor may recommend that the patient take the over-the-counter drug phenazopyridine, commonly sold as AZO or Uristat. This drug will not cure the UTI, but it does help to treat its symptoms and relieve discomfort. The primary purpose of phenazopyridine is relief from the itching or burning sensation that often accompanies a UTI it may also help relieve the frequency and urgency of urination. Be aware that this drug can cause bodily fluids like urine and tears to turn bright orange, so dont be alarmed if this occurs.
If the UTI is severe and has spread to the kidneys, the patient may require hospitalization. Antibiotics will be delivered intravenously, and additional treatment may be required as well to ensure kidney health and prevent the infection from entering the bloodstream.
Burning Sensation After Peeing: Why And What To Do
The medical term for painful or burning urination is dysuria. The burning sensation can occur either during urination or directly afterwards. This condition is more common in women because of the female anatomy. Women have short urethras and the close proximity of the urinary tract to the anus and vagina. Some men are more predisposed to urinary infections because of having certain underlying medical conditions.
You May Like: Tips For Urinary Tract Infection
What Causes A Urinary Tract Infection
Most urinary tract infections are bacterial in nature. When fecal bacteria from the anus makes its way into the urethra, the bacteria can multiply and travel upward to the bladder and kidneys. This condition is even more common in people whose urine flow is obstructed by kidney stones or an enlarged prostate. This is because urine becomes trapped in the bladder or surrounding systems. The resulting buildup of urine creates the sort of warm, damp environment that bacteria thrive in, and the decrease in urination prevents the urethra from flushing out pathogens as it normally might.
There are several ways that fecal bacteria can get into the urinary tract:
-
Swimming in unsanitary water
Even when none of these situations are common, bacterial migration can still occur. Women are more prone to urinary tract infections than men due to their short urethras. Women are also in particular risk of contracting a UTI because of the proximity of their vagina, anus and urethra enabling bacterial migration between these locations. For some women, chronic or recurring UTIs become common.
While most urinary tract infections are caused by the bacteria E. coli, its important to know that not every UTI is caused by fecal bacteria. Other types of bacteria can cause bladder and kidney infections, and certain fungi may be responsible for infections as well. Viral infections of the urinary tract are not common.
Whats Chlamydial Urethritis In Men
Chlamydial urethritis in men is an infection of the urethra caused by the sexually transmitted disease chlamydia. The urethra carries urine from the bladder, through the penis, and to the outside of the body.
This condition often causes swelling and inflammation of the urethra, accompanied by penile discharge. But as with many STDs, men often dont show symptoms. An infected person and all recent and current sexual partners must receive treatment for STDs to prevent reinfection.
The bacteria Chlamydia trachomatiscauses chlamydial urethritis. Its spread through oral, anal, and vaginal sex. Both men and women can develop this common type of infection.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , chlamydia is the most prevalent STD in the United States. Many of these cases are in adolescents and young adults.
People who have unprotected sex with multiple partners are more likely to contract chlamydial urethritis than those who practice safe sex and are in a monogamous relationship. Sexually active people before the age of 25 are also more likely to contract STDs in general, including chlamydia, according to the Mayo Clinic.
Don’t Miss: What Can I Do To Prevent Urinary Tract Infections
Condom Use During Sex
Non-lubricated latex condoms may increase friction and irritate the skin during sexual intercourse. This may increase the risk of a UTI.
However, there are many reasons to use condoms. Theyre important for reducing the spread of sexually transmitted infections and preventing unwanted pregnancy.
To help prevent friction and skin irritation from condoms, be sure to use enough water-based lubricant during sex.
Avoid using condoms that have been coated with spermicide.
Diagnosis And Treatment For Discharge And An Itchy Urethra
If youâre experiencing an itchy urethra, penile discharge, or any other symptoms of an STD, speak with your healthcare provider as soon as possible. They may recommend testing for sexually transmitted infectionsâincluding gonorrhea and chlamydiaâto help diagnose the cause of your STD symptoms.
You may prefer to get tested from the comfort of your home. In this case, you can order our at-home Chlamydia & Gonorrhea Test. If you receive a positive result on this test, you have the option to speak with a physician in our networkâwho may prescribe medication to treat the infection, if appropriate.
Also consider taking the at-home STD Test for menâwhich checks for 6 common sexually transmitted infections, including chlamydia, gonorrhea, hepatitis C, HIV, syphilis, and trichomoniasis.
References
1. Diagnosis and Treatment of Urethritis in Men. American Family Physician. URL. Accessed May 15, 2020.
2. Korenromp EL, Sudaryo MK, de Vlas SJ, et al. What proportion of episodes of gonorrhoea and chlamydia becomes symptomatic?. Int J STD AIDS. 2002 13:91â101. doi:10.1258/0956462021924712
3. Chlamydia – CDC Fact Sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. URL. Accessed May 15, 2020.
4. Gonorrhea – CDC Fact Sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. URL. Accessed May 15, 2020.
5. Chlamydia Treatment. National Health Service. URL. Accessed May 15, 2020.
6. Gonorrhea – Diagnosis and Treatment. Mayo Clinic. URL. Accessed May 15, 2020.
Don’t Miss: Botox For Urinary Incontinence Side Effects
Urethritis Caused By Stds
Urethritis is where the urethra becomes inflamed mainly causing discomfort or pain whilst urinating, or causing a more frequent urge to urinate. It can also cause an unpleasant itchiness of the urethra. Although urethritis is not an STD, it may be caused by one. If your itchy urethra or penis is accompanied by pain whilst urinating you may require a more complete sexual health screen against bacterial infections such as chlamydia and gonorrhoea. Our Profile 3 test can diagnose a range of bacteria which may be causing such symptoms.
Urinary Tract Infection Diagnosis
If you think you might have a UTI, dont worry. Diagnosing one requires a simple urinalysis. You urinate into a cup, and your clinician examines the urine for signs of infection. The standard course of treatment is three to five days of antibiotics.
In some cases, especially if your infections keep coming back, your practitioner may order a urine culture, a specific test for UTIs. A culture identifies the bacteria causing your infection so your clinician can choose the most effective antibiotic to treat it. The results of a urine culture are typically not available for two to four days.
Recommended Reading: Over The Counter Urinary Tract Infection Remedy
Southern Cross Medical Library
The purpose of the Southern Cross Medical Library is to provide information of a general nature to help you better understand certain medical conditions. Always seek specific medical advice for treatment appropriate to you. This information is not intended to relate specifically to insurance or healthcare services provided by Southern Cross. For more articles go to the Medical Library index page.
How Long Will The Effects Last
For most UTIs, the symptoms go away within 24 hours after you begin treatment. Take all of the medicine your healthcare provider prescribes, even after the symptoms go away. If you stop taking your medicine before the scheduled end of treatment, the infection may come back.
Without treatment, the infection can last a long time. If it is not treated, the infection can permanently damage the bladder and kidneys, or it may spread to the blood. If the infection spreads to the blood, it can be fatal.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Urinary Retention Last After Botox
What Should I Do If I Have Symptoms Of Urethritis
- If you suspect that you have urethritis then contact your local genitourinary clinic – find one from the Family Planning Association’s ‘Find a Clinic’ service – or see your GP.
- You may be asked to have tests for HIV, hepatitis and syphilis, as people with inflammation of the urethra sometimes have these conditions as well.
- Men who have sex with men may also need to have swabs taken from the back of the throat and back passage .
- The GUM clinic will protect your confidentiality but, if they confirm you have an infection, they may want to contact anyone you had sex with up to three months before you were diagnosed. This is called ‘contact tracing’.
- Medicines called antibiotics will usually clear an infection. The antibiotic prescribed depends on the cause. Make sure you complete the course.
- If your urethritis is due to an infection such as gonorrhoea it is vital that you have another test after you have been treated to make sure the infection has been cured. This will usually be done seven days after treatment.
- Tell your sexual partner to see their doctor or go to a GUM clinic, even if they have no symptoms. Many women with sexually transmitted infections do not have symptoms.
- Don’t have sex until you and your sexual partner have completed tests and treatment. You should wait seven days after you have had your treatment course to avoid passing on the infection: your doctor will advise.
Does My Child Have A Bladder Infection
If you notice that your child has to pee more often or if he/she complains that peeing hurts, your child may have urethritis. This happens when the urethra becomes inflamed.
The urethra is the tube that drains urine out of the body. For girls, the urethra is the opening above the vagina. For boys, the urethra is the opening on the tip of the penis.
Depending on your childs age, it can be difficult to figure out what is wrong. You may need to ask the same question in different ways using terms your child understands.
Talk to your health care provider to determine if your child should be evaluated. Symptoms of urethritis are similar to a bladder infection . Symptoms include:
- Pain or burning in the urethra when urinating
- Pain around the vagina or penis
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Not wanting to urinate, which can cause accidents
- Not wanting to drink to avoid urinating
- Lower abdominal pressure or pain
If you suspect urethritis and bring your child to a health care provider, assure your child that the visit will be painless. All your child needs to do is pee in a cup, which is usually fun for kids.
In children, urethritis is usually caused by a chemical irritation not an infection. Chemicals like soap, bubble baths or skin lotions that get inside the urethra can cause the irritation. Symptoms usually resolve within three days after the last exposure to the irritant.
How can you prevent urethritis?
You May Like: Sore Throat And Urinary Tract Infection