Symptoms And Signs Of Uti In Children
In neonates, symptoms and signs of urinary tract infection are nonspecific and include poor feeding, diarrhea, failure to thrive, vomiting, mild jaundice , lethargy, fever, and hypothermia. Neonatal sepsis Neonatal Sepsis Neonatal sepsis is invasive infection, usually bacterial, occurring during the neonatal period. Signs are multiple, nonspecific, and include diminished spontaneous activity, less vigorous sucking… read more may develop.
Infants and children < 2 years with UTI may also present with poorly localizing signs, such as fever, gastrointestinal symptoms , or foul-smelling urine. About 4 to 10% of febrile infants without localizing signs have UTI.
In children > 2 years, the more classic picture of cystitis or pyelonephritis can occur. Symptoms of cystitis include dysuria, frequency, hematuria, urinary retention, suprapubic pain, urgency, pruritus, incontinence, foul-smelling urine, and enuresis. Symptoms of pyelonephritis include high fever, chills, and costovertebral pain and tenderness.
Physical findings suggesting associated urinary tract abnormalities include abdominal masses, enlarged kidneys, abnormality of the urethral orifice, and signs of lower spinal malformations. Diminished force of the urinary stream may be the only clue to obstruction or neurogenic bladder.
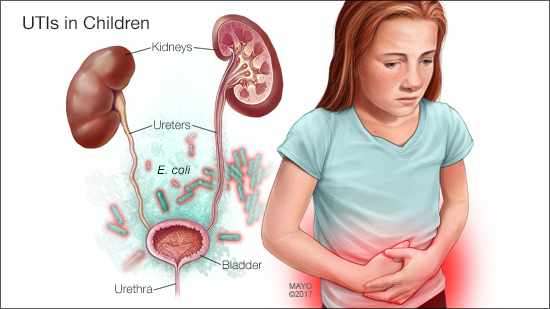
Types Of Utis In Children
Common types of UTIs include:
- Cystitis: this bladder infection is the most common type of UTI. Cystitis occurs when bacteria move up the urethra and into the bladder
- Urethritis: when bacteria infect the urethra
- Pyelonephritis: a kidney infection caused by infected urine flowing backward from the bladder into the kidneys or an infection in the bloodstream reaching the kidneys
Treatment For More Severe Utis
Kids with a more severe infection may need treatment in a hospital so they can get antibiotics by injection or IV .
This might happen if:
- the child has high fever or looks very ill, or a kidney infection is likely
- the child is younger than 6 months old
- bacteria from the infected urinary tract may have spread to the blood
- the child is dehydrated or is vomiting and cannot take any fluids or medicine by mouth
Kids with VUR will be watched closely by the doctor. VUR might be treated with medicines or, less commonly, surgery. Most kids outgrow mild forms of VUR, but some can develop kidney damage or kidney failure later in life.
Also Check: What Are The Symptoms Of A Severe Urinary Tract Infection
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection In Toddlers
A UTI is an infection in your childs urinary tract which includes their kidneys, the ureters that connect them to the bladder and the urethra where urine exits their body. Bacteria get into their urinary tract through the skin around their rectum and genitals or through the bloodstream from any part of their body .
Because it may not be obvious when a child has an infection, especially if theyre too young to voice their symptoms, UTIs in children sometimes go unnoticed. Urinary tract infections need to be treated immediately to prevent the infection from spreading and damaging the kidneys.
Urinary Tract Infections In Boys

- Urology
Urinary tract infections in boys are the result of bacteria getting into the bladder and staying there. UTIs are common in kids, especially girls and uncircumcised boys. E. Coli, responsible for over 75% of UTIs, doubles every 20 minutes in the bladder. That means if there are 100 bacteria of E. Coli in the bladder and you wait three hours to go to the bathroom, you will have over 50,000 bacteria in your bladder. The more bacteria in the bladder and the longer it stays there, the more likely you are to get a UTI.
There are many things that can be done to both treat urinary tract infections in boys and prevent them in the future.
Don’t Miss: Medicine To Stop Urinary Burning
Urinary Tract Infections In Babies
It can be hard to figure out whats wrong with babies when all they can do to communicate pain is cry. A fussy infant may have any number of health problems, from colds to rashes, but some medical problems are harder to identify than others. For example, many parents may not know that babies can get infections in their urinary tract. In fact, childhood urinary tract infections account for more than 1 million pediatrician visits each year in the US.
UTIs are usually caused by bacteria in the kidneys, ureters , or bladder. Sometimes the body can rid itself of this bacteria but when it cannot, the bacteria can build up and cause an infection. Bacteria and other infection-causing microbes may enter the urinary tract when an infant has a dirty diaper or when babies are wiped from back to front. Good hydration enabling frequent urination and maintaining proper hygiene can help prevent UTIs.
Check If It’s A Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms of a UTI may include:
- pain or a burning sensation when peeing
- needing to pee more often than usual during the night
- pee that looks cloudy
- needing to pee suddenly or more urgently than usual
- needing to pee more often than usual
- lower tummy pain or pain in your back, just under the ribs
- a high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
You May Like: What Is The Best Medicine For Urinary Tract Infection
About Urinary Tract Infections In Children
Urinary tract infections in children are fairly common, but not usually serious. They can be effectively treated with antibiotics.
A UTI may be classed as either:
- an upper UTI if it’s a kidney infection or an infection of the ureters, the tubes connecting the kidneys to the bladder
- a lower UTI if it’s a bladder infection or an infection of the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection In Children
A UTI is when bacteria gets into your urine and travels up to your bladder. As many as 8 in 100 of girls and 2 in 100 of boys will get UTIs. Young children have a greater risk of kidney damage linked to UTI than older children or adults.
How Does the Urinary Tract Work?
The urinary tract is the organs in your body that make, store, and get rid of urine, one of the waste products of your body. Urine is made in the kidneys and travels down to the bladder through the ureters . The kidneys make about 1½ to 2 quarts of urine a day in an adult, and less in children, depending on their age. In children, the bladder can hold 1 to 1½ ounces of urine for each year of age. For example, a 4-year-old childs bladder can hold 4 to 6 ouncesa little less than a cup.
The bladder stores the urine until it is emptied through the urethra, a tube that links the bladder to the skin, when you urinate. The urethra opens at the end of the penis in boys and in front of the vagina in girls.
The kidneys also balance the levels of many chemicals in the body and check the blood’s acidity. Certain hormones are also made in the kidneys. These hormones help control blood pressure, boost red blood cell production and help make strong bones.
Normal urine has no bacteria in it, and the one-way flow helps prevent infections. Still, bacteria may get into the urine through the urethra and travel up into the bladder.
Also Check: E Coli In Urinary Tract
Key Points About A Uti In Children
- A urinary tract infection is inflammation of part of the system that takes urine out of the body.
- Most infections are caused by bacteria from the digestive tract. The most common is Escherichia coli bacteria. These normally live in the colon.
- A UTI is not common in children younger than age 5. A UTI is much more common in girls because they have a shorter urethra.
- A UTI is unlikely in boys of any age, unless part of the urinary tract is blocked. Uncircumcised boys are more at risk for a UTI than circumcised boys.
- Symptoms vary by age, and can include fever, need to urinate often, pain, and crying.
Treatment For Urinary Tract Infections
Babies under 3 months usually need to have antibiotics directly into a vein through a drip to treat a urinary tract infection . This means they need to be treated in hospital.
Babies older than 3 months can usually be treated at home with oral antibiotics.
Your doctor will check your childs urine again after treatment to make sure the infection has cleared up.
If there are any concerns about how your childs urinary tract is working, your doctor might refer your child to a specialist for further advice and treatment.
If your baby needs hospital treatment for a UTI, it can be quite upsetting. It might help to know that most babies get over UTIs quickly and dont need ongoing treatment.
Read Also: Azithromycin For Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary Tract Infection In Babies What Causes Urinary Tract Infections In Babies
There are multiple ways bladder infections can occur at such a young age.
- Abnormality in the urinary tract There are some babies whose urinary tract is not fully developed or has some abnormality that makes urine flow backward causing the bladder not to empty properly.
- Bacteria Bladder infections in babies happen when bacteria invade the urethra and reach the bladder. Without immediate treatment, the infection caused by said bacteria can affect the kidneys and other parts of the urinary tract.
- Not changing diapers Bacteria present in a babys urine and stool combined with the warmth of a closed diaper is an excellent medium for bacteria to grow and spread.
- Bubble baths Bubble baths irritate babies genitals and urethras which can lead to bladder infections .
Eating Diet & Nutrition
Food choices do not help prevent or treat bladder infections in children, but drinking plenty of liquids may help. Talk with a health care professional about how much liquid your child should drink, depending on his or her age, size, and other health conditions.
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and other components of the National Institutes of Health conduct and support research into many diseases and conditions.
You May Like: Men’s Urinary Tract Problems
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Urinary Tract Infections In Children
BRETT WHITE, MD, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, Oregon
Am Fam Physician. 2011 Feb 15 83:409-415.
Acute urinary tract infections are relatively common in children, with 8 percent of girls and 2 percent of boys having at least one episode by seven years of age. The most common pathogen is Escherichia coli, accounting for approximately 85 percent of urinary tract infections in children. Renal parenchymal defects are present in 3 to 15 percent of children within one to two years of their first diagnosed urinary tract infection. Clinical signs and symptoms of a urinary tract infection depend on the age of the child, but all febrile children two to 24 months of age with no obvious cause of infection should be evaluated for urinary tract infection . Evaluation of older children may depend on the clinical presentation and symptoms that point toward a urinary source . Increased rates of E. coli resistance have made amoxicillin a less acceptable choice for treatment, and studies have found higher cure rates with trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole. Other treatment options include amoxicillin/clavulanate and cephalosporins. Prophylactic antibiotics do not reduce the risk of subsequent urinary tract infections, even in children with mild to moderate vesicoureteral reflux. Constipation should be avoided to help prevent urinary tract infections. Ultrasonography, cystography, and a renal cortical scan should be considered in children with urinary tract infections.
What Are The Treatments For Utis
Antibiotics, mainly. These medications kill bacteria. Kids usually take them for anywhere from 3 to 10 days . Your doctor might do another urine test after your child finishes the medicine to see if the infection has cleared up.
Make sure your child finishes all of their meds, even if they start to feel better. Stopping too soon can make germs resistant to antibiotics and cause another infection.
Most UTIs clear up in about a week. Some kids will have symptoms for a few weeks. Call your doctor if your child’s symptoms don’t start to improve after 3 days from when they started on antibiotics, or if they get worse.
Read Also: What Can You Do For Urinary Incontinence
Urinary Tract Infection In Children
, MD, Golisano Childrens Hospital
-
Urinary tract infections are caused by bacteria.
-
Infants and younger children who have urinary tract infections sometimes have structural abnormalities of their urinary system that make them more susceptible to urinary infection.
-
Newborns and infants may have no symptoms other than a fever, whereas older children have pain or burning during urination, pain in the bladder region, and a need to urinate frequently.
-
The diagnosis is based on an examination and culture of the urine.
-
Proper hygiene may help prevent urinary tract infections.
-
Antibiotics are given to eliminate the infection.
During infancy, boys are more likely to develop urinary tract infections. After infancy, girls are much more likely to develop them. UTIs are more common among girls because their short urethras make it easier for bacteria to move up the urinary tract. Uncircumcised infant boys , children who are premature Premature Newborn A premature newborn is a baby delivered before 37 weeks of gestation. Depending on when they are born, premature newborns have underdeveloped organs, which may not be ready to function outside… read more , and young children with severe constipation Constipation in Children Constipation refers to delay or difficulty in passing stool for a period of at least 1 month in infants and toddlers and a period of 2 months in older children … read more also are more prone to UTIs.
What Puts My Child At Risk Of Getting A Uti
UTIs are common. They are most common in babies under the age of 12 months but can affect children of any age.
There are some conditions which put babies and children at higher risk of UTIs:
- constipation
- an abnormality of the urinary tract
- neurological conditions where the bladder doesn’t empty properly
Don’t Miss: Kidney Stone In Urinary Tract
How Are They Treated
Your child will take antibiotics for a urinary tract infection. Give this medicine to your child as your doctor says. Do not stop it just because your child feels better. He or she needs to take all the medicine to get better. The number of days a child will need to take the medicine depends on the illness, the child’s age, and the type of antibiotic.
Have your child drink extra fluids to flush out the germs. Remind your older child to go to the bathroom often and to empty the bladder each time.
When Should You Call Your Doctor
Urinary tract infections in infants and young children need early evaluation and treatment. Call your doctor to make an appointment within 24 hours if your child has:
- A fever.
- Urine that looks pink, red, brown, or cloudy or is foul-smelling.
- Burning pain with urination.
- Frequent need to urinate without being able to pass much urine.
- Pain in the flank, which is felt just below the rib cage and above the waist on one or both sides of the back.
- Vaginal discharge with urinary symptoms.
- Symptoms similar to those of a previous UTI.
Call the doctor if your child isn’t feeling better within 48 hours after starting an antibiotic.
Also Check: Ways To Prevent Urinary Tract Infections
When Should I See A Doctor
See a doctor if your child:
- has signs or symptoms of a UTI
- has been diagnosed with a UTI and
- is not improving after two days of taking antibiotics
- is having trouble taking the antibiotics or is vomiting
- isnt drinking enough fluid
- develops back pain
In an emergency, always call 000 immediately. Otherwise, contact your local doctor or visit your nearest hospital emergency department. If its not an emergency but you have concerns, contact 13 Health . Qualified staff will give you advice on who to talk to and how quickly you should do it. You can phone 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
How Can You Prevent Utis In The Future

Change your baby’s diapers often to prevent bacteria from growing. As your child gets older, teach them good bathroom habits to prevent UTIs. Instruct girls to wipe from front to back. This helps to prevent bacteria in poop from getting into the vagina and urinary tract. Encourage your kids to go to the bathroom as soon as they feel the urge — not to hold it in.
Girls should avoid bubble baths and should not use perfumed soaps. And, they should wear cotton underwear — not nylon — to improve airflow and prevent bacteria from growing.
Have your kids drink lots of water, which helps flush bacteria out of the urinary tract. Extra water also prevents constipation, which can create blockages in the urinary tract that allow bacteria to grow.
Also Check: Natural Remedies For Male Urinary Tract Infection
How Does A Baby Get A Urinary Tract Infection
UTIgetbladdercanbabychild
. Also question is, how do I know if my baby has a UTI?
Symptoms of UTI include frequent or painfulurination, wetting during the day or night, leaking ordribbling, and foul-smelling urine. Fever, stomach aches inthe lower abdomen, and vomiting? may also be present.If your child develops symptoms of a UTI, callthe doctor to schedule an appointment as soon aspossible.
Additionally, can diaper cause UTI in babies? Babies are especially vulnerable to UTIsbecause they’re in diapers most of the time, which keepstheir genital area moist and warm and allows bacteria to breed.Plus, diapers don’t always keep their messes contained, sobacteria from bowel movements can easily get into thegenitals and sometimes cause an infection.
Herein, what causes urinary tract infection in babies?
Most UTIs in children occur because bacteria thatare normally found in the bowel cause an infection inthe urinary tract. These factors can increase yourchild’s chance of getting a UTI: Poor bathroomhabits, such as not changing out of wet underwear or not wipingproperly.
Is UTI dangerous for baby?
UTIs do not pose any danger to adeveloping fetus, and the infection is usually asymptomatic duringpregnancy . However, untreated UTIs can progressto kidney infections, which are far more serious.