Other Symptoms Of Utis
If the person has a sudden and unexplained change in their behaviour, such as increased confusion, agitation, or withdrawal, this may be because of a UTI.
These pages explain what a UTI is, the different types of UTIs, their symptoms and treatments, and gives tips on how they may be prevented.
Presentation And Diagnosis Of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria And Symptomatic Uti In Older Adults
Dr N: Do you feel ill from the bladder infection that you can tell?
Mrs M: Just in my head. I dont have any of the accompanying symptoms. Theres no odor, theres no burning or anything like that. But for the past at least half-dozen years, it just has been there, thats all. Every time they took a test, there was a very small amount of E coli. Whatever that means.
Dr N: For me, its just so challenging. Were taught in medical school that you dont treat asymptomatic bacteriuria in people. It doesnt help them. The problem when people have chronic urinary symptoms is that we are trying to determine if this is now a symptomatic bacterial infection and how do I figure out what is a UTI sign or symptom in somebody who has these chronic voiding problems to begin with. So, thats always been the tricky part. She has been hospitalized a couple of times for UTIs. She basically presented with dizziness, had trouble walking, confusion, and low blood pressure. She was admitted and found to have a UTI based on urine cultures. She was treated with antibiotics intravenous fluids and got better.
Complicated Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infection in patients with renal calculi, those with pyelonephritis, prostatitis, orchitis, patients with long-standing indwelling catheters or those using intermittent self-catherisation are likely to be complicated. These patients are likely to have an infection that involves other parts of the renal tract apart from the urinary bladder. They often need hospitalisation and surgical intervention like nephrostomy tubes or ureteric stents.
Intravenous antibiotics are usually prescribed for this group of patients. Treatment can be modified based on known multi-drug resistant organism colonisation or previous urine culture result. Usually, patients with complicated UTI require a 10â14 day course of antibiotic treatment.
Also Check: Royal Canin Urinary Canine Treats 17.6 Oz
Utis In The Walking Well
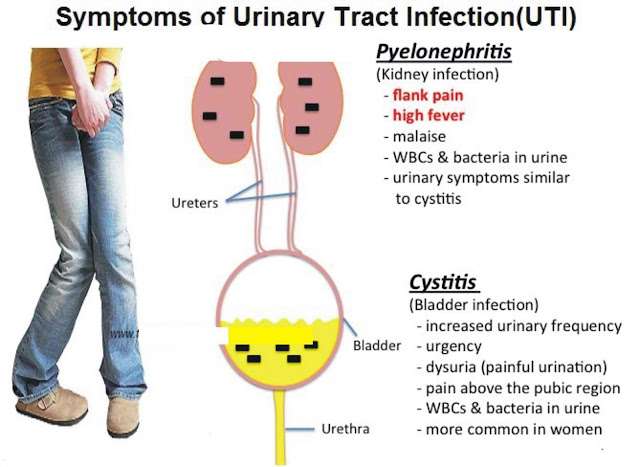
Urethritis: The primary symptoms of this condition, which results from urethral inflammation and/or infection, are dysuria and purulent discharge. The incidence of urethritis secondary to sexually transmitted disease caused by Chlamydia or Gonococcus has been increasing in this population, according to the CDC. The reason for this is a decrease in condom use, which would prevent STDs.7 Other pathogens include adenovirus, Escherichia coli, herpes simplex, Mycoplasma, and Trichomonas .8
Prostatitis: This condition is an inflammation or infection of the prostate gland. See TABLE 1 for the prostatitis classification system used by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.9
Cystitis: Cystitis, an inflammation or infection of the urinary bladder, is seen more often in females in this population. One of the more common causes is poor hygiene resulting in urethral contamination with fecal bacteria that then pass directly into the bladder. In males, cystitis most commonly results from urinary tract obstruction it usually is secondary to BPH and urinary retention, but it may be secondary to bladder enervation resulting from spinal-cord injury or multiple sclerosis. Diabetes is frequently associated with cystitis since glycosuria provides an ideal environment for infection. In dementia, infection is usually caused by poor hygiene, as noted above. Patients who have received radiation therapy to the perineum also are prone to cystitis.13
Residential Aged Care Setting
A 2018 Australian national aged care antimicrobial prescribing survey indicated that UTI was the second most common clinical indication for antimicrobial prescription. Moreover, cystitis has been consistently the most frequently reported known indication for prescriptions for prophylaxis in 2016â2018. Encouragingly, prescriptions for ASB were reported to have fallen from 46% in 2016 to 2.1% in 2018.
For people residing in aged care facilities, recommendations for the initiation of antibiotics for UTI have been established., , ASB should not be treated with antimicrobial therapy, for either treatment or prophylaxis, as antibiotic therapy does not reduce the rate of complications associated with this condition, and has been shown to paradoxically increase the risk of subsequent UTI., , Additionally, unnecessary antimicrobial treatment is associated with the development and progression of antimicrobial resistance, adverse drug events, such as liver function derangement to beta-lactam antibiotics and the development of Clostridiodes difficile infection., –
Don’t Miss: What Are The First Signs Of A Urinary Tract Infection
Why Are Women And Older Adults More At Risk
E. coli or other bacteria cause UTIs, which are infections in your kidneys, bladder, ureters or urethra. Unfortunately, women are more likely to get them mainly because of their anatomy.
A womans urethra is shorter than a mans and closer to the anus. The urethra is also close to the vagina, which can collect bacteria during sex. So bacteria from both the anus and vagina have easy access to a womans urinary tract.
Post-menopausal women are also at higher risk because pH changes in the vagina make it more susceptible to infection.
Both men and women are more likely to get UTIs as they age. Certain medical conditions, such as bladder prolapse in women and enlarged prostate in men, cause incomplete bladder emptying in older adults. Urine that stays in your bladder too long can encourage bacteria to grow.
Some newer drugs for diabetes can also promote sugar in the urine and create conditions ideal for a UTI, Dr. Vasavada adds.
Why Are Urinary Tract Infections Common In Older Adults
Seniors are more vulnerable for many reasons, including their overall susceptibility to infections due to a weakened immune system.
As you get older, your immune response changes its part of normal aging, explains Anna Dowd, APN, a gerontological nurse practitioner in the greater Chicago area.
According to the National Institutes of Health , the following conditions make older individuals more susceptible to UTIs:
- Diabetes
- Urine retention
- Use of a urinary catheter
- Bowel incontinence
- Urinary incontinence
- Immobility
- Surgery of any area around the bladder
- Kidney stones
People with incontinence are at an increased risk for UTIs because of the close contact that adult briefs and other incontinence products have with their skin. While these products can help contain messes and prevent embarrassment associated with accidents, they can also introduce bacteria into the urethra. Women are more prone to UTIs because the female urethra is much shorter, allowing bacteria to travel to the bladder more easily.
Also Check: Urinary Tract Infection Antibiotic Macrobid
Ways To Prevent A Uti
Antibiotics and natural medicines are available to help clear up UTIs, but there are preventative measures you can take to help ensure your body is able to stave off infections that tend to occur through the normal course of life. Read on to see three ways weve discovered through careful research to help prevent urinary tract infections in older women.
How Utis Are Diagnosed
In most cases, if you think you have a UTI, you should visit a health care provider and give a urine sample for testing. A urinalysis is a test that looks for white blood cells, red blood cells, bacteria, and or other chemicals such as nitrites in your urine. A proper urinalysis can pinpoint an infection and a urine culture can help your health care provider choose the best antibiotic for treatment. It is vital to get a urinalysis and culture performed to make sure you have an infection and require care. Use of antibiotics when not needed, can be tricky, and can lead to greater rates of bacterial antibiotic resistance.
It should be noted that some individuals get a urinalysis result that shows bacteria, but the individuals are not having any symptoms of a UTI. This event is common in older adults. If the individual has bacteria in their urine, but has no symptoms, treatment is not right. Treatment should be given to individuls who have bacteria and associated UTI symptoms.
In closing, it should be noted that studies on cranberry juice and linked supplements are mixed. Some studies show that cranberry supplements can be helpful and other studies show that they dont help stop UTIs before they happen. Be sure to read about the pros and cons of cranberry products, and decide if theyre right for you. For now, practice these tips to lower your risk of getting a UTI.
Recommended Reading: Magnetic Therapy For Urinary Incontinence
How To Help Your Loved One Avoid Utis
Do you give the older adult in your life cranberry juice or probiotics to prevent a UTI? These products wont hurt them, but whether theyll help is unclear.
We dont have enough research to support their effectiveness in UTI prevention, although their medical benefits cant be ruled out completely, says Dr. Goldman.
Instead, he recommends these tried-and-true prevention strategies:
- Encourage sufficient fluid intake
- Promote genital and urinary hygiene
- Ask the doctor about low-dose vaginal cream for postmenopausal women
Dr. Goldman says researchers are also studying D-Mannose for UTI prevention. The supplement, which has few side effects, sticks to bladder receptors that normally attract the E. coli bacteria usually responsible for UTIs.
Researchers also believe D-Mannose may keep bad bacteria from colonizing the digestive tract, which can harbor the bacteria responsible for UTIs in women.
Following these tips should help your aging relative stay healthy, productive and out of the hospital.
Ongoing Management Of Uti
Dr N: So, shes going to come in next week and give a urine sample. Well see if the E coli has been cleared and then try to figure out what the next step will be.
Urine testing should be in response to symptoms as outlined in the Figure. Repeated urine testing as a test of cure is not warranted among older patients. Among patients with recurrent symptomatic UTI , use of chronic suppressive antibiotics for 6 to 12 months are effective at reducing UTI episodes and should be considered.68 Nitrofurantoin given at 50 mg daily is used in older patients with minimal adverse effects and no growth of nitrofurantoin-resistant fecal flora after 1 year of treatment.69 Six months of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole , trimethoprim , and nitrofurantoin are also effective,70 but trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole resistant E coli fecal isolates were more common in patients treated with trimethoprim-based regimens.71
Also Check: Mesh Sling For Urinary Incontinence
How Is A Uti Diagnosed
To find out whether you have a UTI, your doctor or nurse will test a clean sample of your urine. This means you will first wipe your genital area with a special wipe. Then you will collect your urine in midstream in a cup. Your doctor or nurse may then test your urine for bacteria to see whether you have a UTI, which can take a few days.
If you have had a UTI before, your doctor may order more tests to rule out other problems. These tests may include:
- A cystogram. This is a special type of x-ray of your urinary tract. These x-rays can show any problems, including swelling or kidney stones.
- A cystoscopic exam. The cystoscope is a small tube the doctor puts into the urethra to see inside of the urethra and bladder for any problems.
What Is The Prognosis For A Person With A Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections typically respond very well to treatment. A UTI can be uncomfortable before you start treatment, but once your healthcare provider identifies the type of bacteria and prescribes the right antibiotic medication, your symptoms should improve quickly. Its important to keep taking your medication for the entire amount of time your healthcare provider prescribed. If you have frequent UTIs or if your symptoms arent improving, your provider may test to see if its an antibiotic-resistant infection. These are more complicated infections to treat and may require intravenous antibiotics or alternative treatments.
Donât Miss: Can A Bladder Infection Cause Lower Back Pain
Recommended Reading: How To Treat E Coli Urinary Tract Infection
Why Are Seniors At Risk For Utis
Men and women older than 65 are at greater risk for UTIs. This is because both men and women tend to have more problems emptying their bladder completely as they age, causing bacteria to develop in the urinary system.
In older men, this often happens because of a common condition called benign prostatic hyperplasia , or an enlarged prostate gland. The enlarged prostate blocks the flow of urine and prevents the bladder from fully emptying.
As women age, the bladder muscles weaken and prevent the bladder from emptying completely, increasing the risk of infection. Women also produce lower amounts of estrogen after menopause. This creates an imbalance of good and bad bacteria in the vagina, which can lead to infection.
Other risk factors for UTIs in older adults include:
- Using a catheter to empty the bladder
- Having kidney stones, which can block the flow of urine
- Having a suppressed immune system, which lowers the bodys defense against infection
What Can I Do To Prevent Recurrent Utis
The majority of UTIs, about 90%, are caused by E. coli, a bacteria that naturally occurs in your intestines where its helpful. When this bacteria comes in contact with your urinary tract system, however, it can be harmful and lead to a UTI.
For most people, simple hygiene and lifestyle changes can help prevent recurrent UTIs. To help stop a UTI before it starts, try implementing these tips:
- Avoid spreading E. coli by washing your genitals with warm water and mild soap before and after sex.
- Drink plenty of fluids to flush out any wandering bacteria from the urinary system.
- Be sure to urinate after having sex to keep bacteria from lingering in the urethra.
- When you feel the urge to urinate, go postponing urination increases your risk of developing a UTI.
- Be sure to wipe from front to back to avoid spreading E. coli to the vagina.
Ready to learn more about UTIs and how they affect older women? Experiencing symptoms of a UTI? Contact our Littleton office or book an appointment online now and the help you need!
Don’t Miss: Natural Ways To Cure Urinary Tract Infection
Utis Secondary To Chronic Disease
Diabetes Mellitus: UTIs affect millions of people each year and are responsible for billions of dollars in health care spending. Elderly people with diabetes are thought to be at increased risk for UTIs, presumably secondary to immunologic, neurologic, or anatomical abnormalities.19 In the geriatric population, there is a fivefold increase in a diabetic patients susceptibility to UTI complications. Risk factors include duration of diabetes, high glycosylated hemoglobin level, glycosuria, and pyuria.20
A critical step in the infection process is the adhesion of pathogenic bacteria to the bladder mucosa. The high prevalence of gram-negative pathogens such as E coli and Klebsiella may be due to the pathogens ability to adhere to the urinary tract mucosa.21 This increased adherence in the presence of glycosuria and decreased functionality of neutrophils in diabetic patients results in an increased incidence of UTI. The low urinary pH caused by bacterial metabolism does not inhibit bacterial growth in this population.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria in the diabetic patient requires special assessment. Women with type 2 diabetes and asymptomatic bacteriuria have been found to have an increased risk of developing a UTI during 18-month follow-up .22
How Do You Get A Urinary Tract Infection
Because of the differences in anatomy, women are much more likely to get UTI than men. The opening of a womans urethra is located in close proximity to her vagina and anus which can both be potential sources of infection. The female anatomy creates more opportunities for fungi and bacteria to enter the urinary tract through the urethra. In addition, the length of the female urethra is shorter than a males, allowing an infection to spread more quickly from the urethra to the bladder and on up through the urinary tract.
Beyond anatomical differences, sexual activity and menopause also make women more vulnerable to UTIs than men. Sexual intercourse increases the potential for fungi and bacteria to enter a womans urethra. Frequent intercourse and intercourse with multiple partners increase the potential for infection even more. 80% of pre-menopausal women with UTI report having had sexual intercourse within the previous 24 hours. Post-menopausal womens bodies produce lower levels of estrogen than pre-menopausal women. Estrogen may be helpful in preventing the overgrowth of E. coli bacteria in the urethra and vagina. As a womans estrogen levels decrease, E. coli may be allowed to grow unchecked and cause an infection.
You May Like: Discomfort In Urinary Tract Male
What Causes A Urinary Tract Infection
The main cause of UTIs, at any age, is usually bacteria. Escherichia coli is the primary cause, but other organisms can also cause a UTI.
In older adults who use catheters or live in a nursing home or other full-time care facility, bacteria such as Enterococci and Staphylococci are more common causes.
Why Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections Are Most Common In Women And Seniors
Urinary tract infections can develop in anyone at any time. However, recurrent infections may become a problem for women and the elderly.
At Primary Care & Walk-In Medical Clinic, the skilled team of physicians offers comprehensive care for people of all ages suffering from discomfort and pain of a urinary tract infection. The medical staff also specializes in treating recurrent infections of the urinary tract to protect your general health.
You May Like: Natural Remedy For Urinary Tract Infection In Humans
Treatment Considerations In Older Adults
Dr N: She told me that her incontinence had definitely gotten worse in the last couple of weeks. I had noticed that another physician had sent a urine culture that had grown more than 105 CFU/mL of E coli that was sensitive to all antibiotics. Assuming that this was asymptomatic bacteriuria, it was not treated with antibiotics. A repeat urine culture again showed more than 105 CFU/mL of E coli, again it was pan sensitive. Given her symptoms, I treated her with a 7-day course of an antibiotic. However the antibiotics didnt really make a difference.
Studies have shown that treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria does eradicate bacteriuria.41 However, reinfection rates , adverse antimicrobial drug effects, and isolation of increasingly resistant organisms occur more commonly in the therapy vs nontherapy groups. No differences in genitourinary morbidity or mortality were observed between the 2 groups.42