Why Are Women And Older Adults More At Risk
E. coli or other bacteria cause UTIs, which are infections in your kidneys, bladder, ureters or urethra. Unfortunately, women are more likely to get them mainly because of their anatomy.
A womans urethra is shorter than a mans and closer to the anus. The urethra is also close to the vagina, which can collect bacteria during sex. So bacteria from both the anus and vagina have easy access to a womans urinary tract.
Post-menopausal women are also at higher risk because pH changes in the vagina make it more susceptible to infection.
Both men and women are more likely to get UTIs as they age. Certain medical conditions, such as bladder prolapse in women and enlarged prostate in men, cause incomplete bladder emptying in older adults. Urine that stays in your bladder too long can encourage bacteria to grow.
Some newer drugs for diabetes can also promote sugar in the urine and create conditions ideal for a UTI, Dr. Vasavada adds.
History And Physical Examination
Suspect urethral warts when patients with genital warts present with pyuria or urethral discharge. Intraurethral warts may be a cause of recurrent meatal warts. Urethral and bladder involvement with condylomata is often associated with immunosuppression. HIV-positive men who practice receptive anal intercourse may present with anal and intra-anal warts. Other groups of immunosuppressed persons may develop perianal lesions but not intra-anal warts, which are due to transfer of the virus inside the anus.
Carefully assess the external genitalia of patients presenting with a typical sexual history and symptoms suggestive of urethral involvement. Include investigations to exclude other, concomitant sexually transmitted diseases . Offer current sexual partners of the patients an examination and treatment for macroscopically visible warts and other STDs. If screening of male partners is to be offered, specimens obtained from penile and urethral brushing for HPV DNA detection appear to be the most accurate. Semen may be an alternative to urethral brushing.
Also Check: Help For Female Urinary Incontinence
Prevention Of Utis In The Elderly
Its important to address the issue in advance in the attempt to prevent UTIs in seniors. Several urinary tract infection prevention methods exist, including:
- Reminding the individual to drink plenty of water , as proper hydration keeps the urinary tract in good health
- Avoiding consumption of alcohol and caffeine as much as possible
- Encouraging the senior to use the restroom frequently, at least every three hours
- Promptly caring for soiled materials due to incontinence
- Wiping from front to back when using the restroom
- Promoting good hygiene, such as daily showers, and avoiding baths and special care should be taken if the senior citizen uses a urinary catheter
Read Also: Why Do Older Adults Get Urinary Tract Infections
How Can You Avoid Genital Warts
- Get vaccinated against HPV.
- Certain types of HPV vaccines protect against the low-risk HPV that causes 90% of genital warts.
- HPV vaccine is safe for all females 9 to 26 years old.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends all 11-12 year old girls get the HPV vaccine.
Recommended Reading: Foods To Help Urinary Tract
How Many Is Too Many Utis
Three or more UTIs in one year indicates a recurrent infection, according to the ACOG.
Recurrent urinary tract infections are treated with antibiotics. A week or two after you finish the antibiotic treatment, your doctor may perform a urine test to make sure the infection is cured.
Your doctor may also ask you about factors that increase the risk of a recurrent UTI, including:
- Young age at first UTI
Read Also: How To Help With Urinary Tract Infection
I Feel Like I Have A Uti But My Tests Are Negative
Sound familiar? Unfortunately the standard tests used to diagnose UTIs dipstick tests and mid-stream urine cultures miss about half of infections. The figure is likely to be even higher for chronic infections.
But some doctors are more likely to rely on test results than on the symptoms their patients are describing and rule out infection as a cause.
No test is perfect, as they all have different sensitivity levels. A relatively low concentration of bacteria may fall below the sensitivity limit of a given test, but still be concentrated enough to have a profound effect on the patient. As a result, UTIs are best diagnosed with a combination of tests, physical examinations and symptom analysis.
Also Check: Z Pak For Urinary Tract Infection
How Can I Help Prevent The Spread Of Genital Warts
- Keep the genital area clean and dry. You can use a hair dryer to help dry the area.
- Wash your hands thoroughly after touching the area with warts.
- Do not scratch the warts.
- Avoid sexual activity until the warts have completely healed.
- Use latex condoms during intercourse. Condoms can reduce your risk of getting genital warts, but warts can spread from areas not covered by a condom.
- Avoid having intercourse with multiple partners.
A vaccine is available to prevent types of HPV infections that are high risk for genital warts and cancer of the cervix. If you already have HPV, the vaccine will not cure your infection, but it will prevent infections with several other types of HPV.
The HPV vaccine is approved for boys, girls, men and women 9 to 26 years old. It is recommended for all girls 11 to 12 years old as part of their routine immunization schedule. It is given in 3 shots. The vaccine may protect against HPV for 5 years. Researchers are doing studies to see if a booster shot is needed after 5 years.
The vaccine is usually not given to pregnant women.
Read Also: Cvs Urinary Tract Infection Medicine
Why Some Women Get Recurrent Utis
The infections are usually caused by Escherichia coli, a bacterium that lives in the intestinal system. If E. coli are carried from the rectum to the vagina, they can enter the urethra and infect the bladder.
Risk factors for UTI vary with age. Before menopause, the most common risk factors are sexual intercourse and use of spermicides. It’s thought that sex increases the number of bacteria in the bladder, and many experts advise women to urinate after sex to flush them out. Spermicides may kill off Lactobacilli, beneficial bacteria in the vagina, making it easier for E. coli to move in.
After menopause, certain physical changes help set the stage for UTIs. The numbers of Lactobacilli in the vagina naturally decline. The bladder also contracts less strongly than it once did, making it more difficult to empty it completely.
In both premenopausal and postmenopausal women, genes play a role as well. Having a mother or sister who has frequent UTIs is also a risk factor.
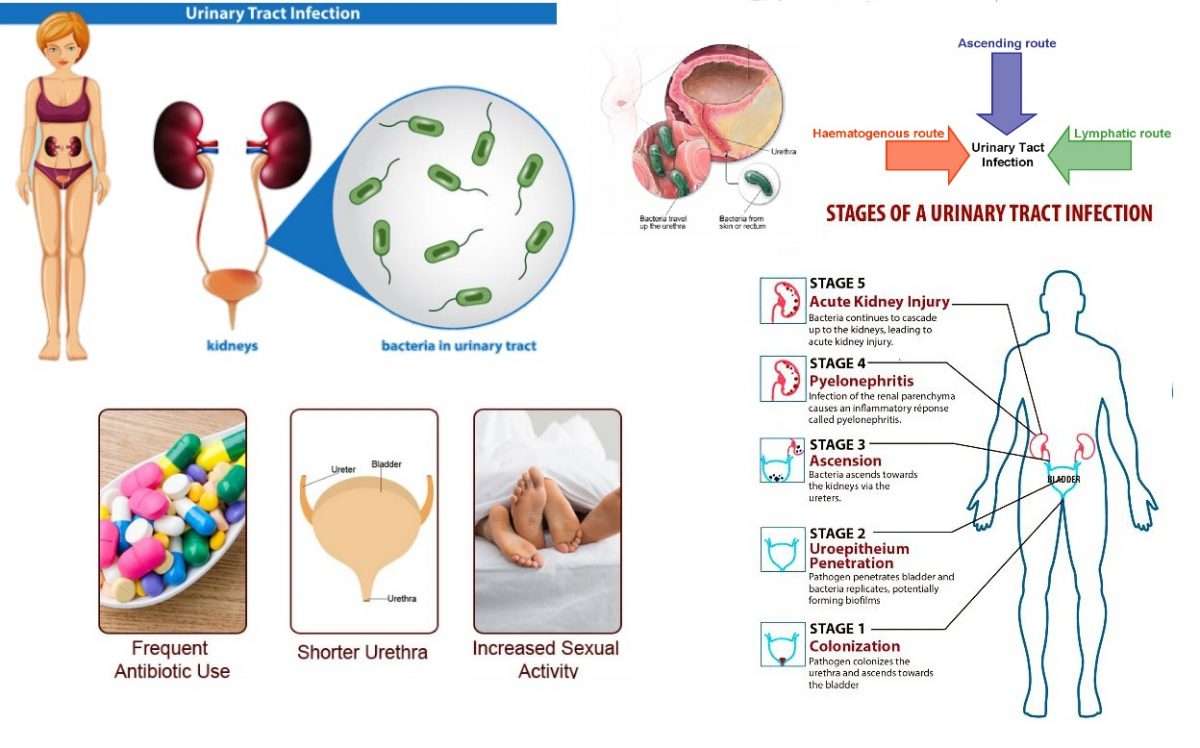
Urinary Tract Infection Causes
Urinary tract infections typically occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra, travel into the bladder and begin to multiply. Common bladder infection causes include:
- Infection of the bladder This type of infection is usually caused by Escherichia coli , a type of bacteria commonly found in the gastrointestinal tract. However, other bacteria are sometimes responsible. To reduce your risk of this type of infection, be sure to wipe front to back , drink plenty of fluids, avoid holding your urine, urinate before and after intercourse, avoid scented products and take probiotics that contain cranberry. Also, be sure to change your pad or panty liner every 3-5 hours.
- Infection of the urethra This type of infection occurs when GI bacteria spread from the anus to the urethra. Because the urethra is in close proximity to the vagina, sexually transmitted infections like herpes, gonorrhea, chlamydia and mycoplasma can also cause urethritis.
Donât Miss: Womenâs Bladder Leakage Protection
Read Also: Over The Counter Urinary Tract Infection Pain Relief
What Are The Symptoms Of A Urinary Tract Infection
These are the most common symptoms of a UTI:
- Frequent urination
- Pain or burning when passing urine
- Fever
- Urine looks dark, cloudy, or reddish in color
- Urine smells bad
- Feeling pain even when not urinating
- Tiredness
- Pain in the back or side, below the ribs
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Despite an strong urge to urinate, only a small amount of urine is passed
- Women may feel an uncomfortable pressure above the pubic bone
The symptoms of UTI may look like other conditions or medical problems. Always see a health care provider for a diagnosis.
Potential Complications Of A Bladder Infection
Without treatment, bacteria from the bladder can travel up to the kidneys and cause a . This can cause pain on the sides of the body . You may also experience fever and chills.
is another possible complication of infection. Although bladder infections can sometimes cause a , it is important to let your doctor know if you experience a high and shaking or chills.
When treating a bladder infection, take the full course of medication, even if you start feeling better. Completing the treatment reduces the risk of complications.
Donât Miss: Cysts On Bladder And Kidneys
Also Check: Tea For Urinary Tract Infection
What Causes A Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections are often caused when bacteria from the vagina or anus gets into and travels through the urinary system.
A common cause of a recurrent UTI is that some bacteria from a previous UTI may remain in the urinary tract system. In these cases, it may not have been completely eradicated the last time it was treated.
Another common cause of a recurring UTI could be related to your habits, such as:
- Not urinating frequently enough to flush your system
- Not urinating after sexual intercourse
- Wiping incorrectly
Are Some Women More At Risk For Utis
Yes. You may be at greater risk for a UTI if you:1,5
- Are sexually active. Sexual activity can move germs that cause UTIs from other areas, such as the vagina, to the urethra.
- Use a diaphragm for birth control or use spermicides with a diaphragm or with condoms. Spermicides can kill good bacteria that protect you from UTIs.
- Are pregnant. Pregnancy hormones can change the bacteria in the urinary tract, making UTIs more likely. Also, many pregnant women have trouble completely emptying the bladder, because the uterus with the developing baby sits on top of the bladder during pregnancy. Leftover urine with bacteria in it can cause a UTI.
- Have gone through menopause. After menopause, loss of the hormone estrogen causes vaginal tissue to become thin and dry. This can make it easier for harmful bacteria to grow and cause a UTI.
- Have diabetes, which can lower your immune system and cause nerve damage that makes it hard to completely empty your bladder
- Have any condition, like a kidney stone, that may block the flow of urine between your kidneys and bladder
- Have or recently had a catheter in place. A catheter is a thin tube put through the urethra into the bladder. Catheters drain urine when you cannot pass urine on your own, such as during surgery.
You May Like: Does Tylenol Help Urinary Tract Infections
When To See Your Healthcare Provider
If youre experiencing bladder pain or pelvic discomfort that wont go away or is getting worse, reach out to your healthcare provider. Your provider can properly diagnose whats going on UTI or not and come up with a treatment plan that helps you feel better ASAP.
In-person office visits can be booked using your app or the One Medical website. If youd like to consult with a provider urgently in real time to help you make a plan, on-demand video chats can be requested from your One Medical app.
Donât Miss: How To Cure Urinary Tract Infection
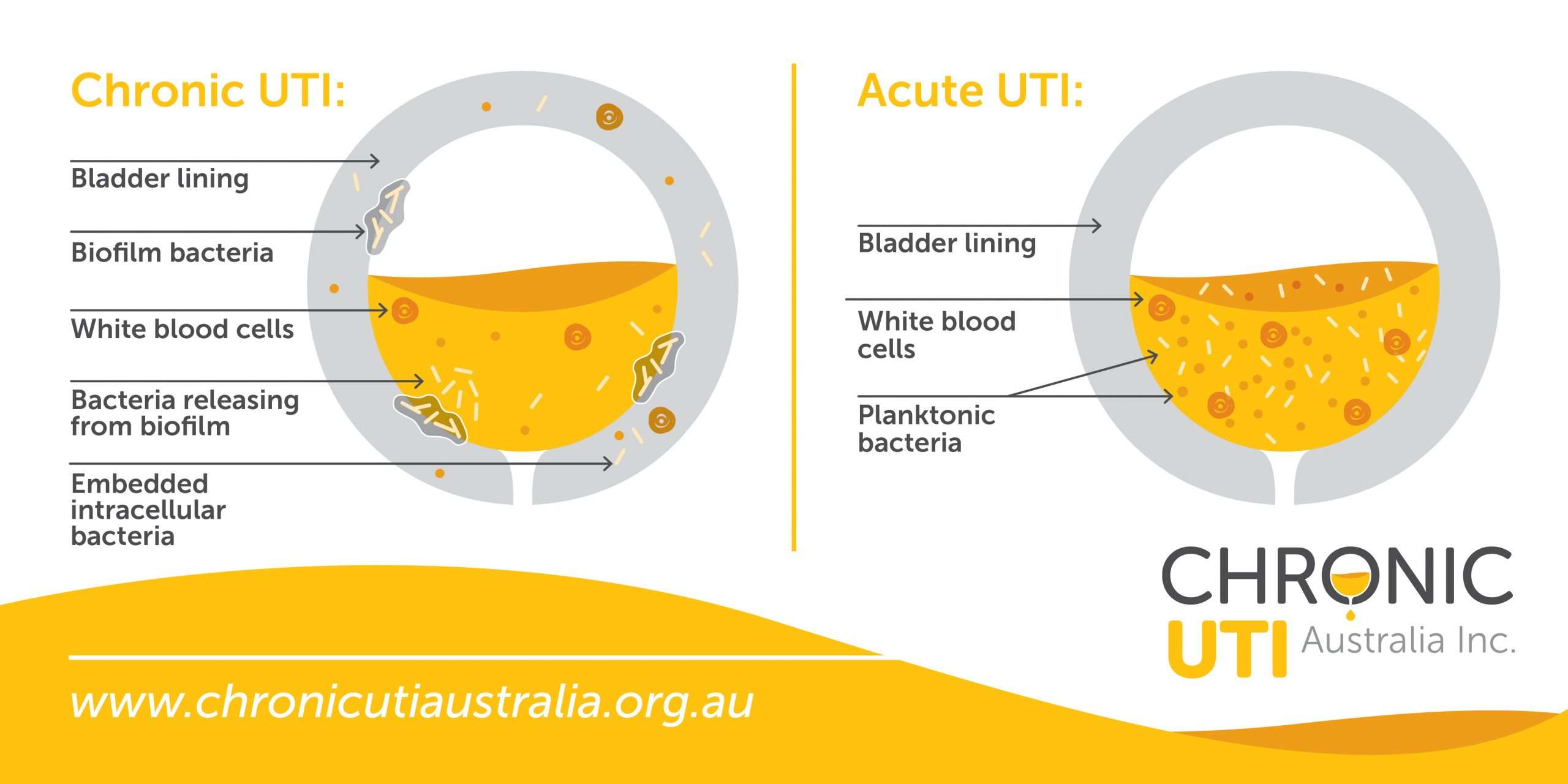
Is Interstitial Cystitis Linked To Frequent Utis
We mentioned a study above, that found that 74% of survey respondents diagnosed with Interstitial Cystitis, had previously been diagnosed with recurrent UTI.
Research has also shown that a high percentage of females with Interstitial Cystitis may in fact have biofilms, IBCs, or both within their bladder, and that this is the cause of their ongoing infection and recurrent or continuous symptoms.
Interstitial Cystitis and associated conditions are considered to be incurable, however
Interstitial Cystitis is a diagnosis of exclusion. This means IC is diagnosed in the absence of any other obvious cause. If a cause for your UTI symptoms is not identified by testing, a diagnosis of IC may be given.
Check out our expert video series to learn more about the chronic UTI and IC connection.
You May Like: Mckesson Disposable Urinary Leg Bag
Complications Of Utis In Seniors
A UTI that goes untreated in anyone can lead to complications. However, elderly individuals have a higher risk of complications from urinary tract infections than any other category of individual.
- Kidney damage. A typical UTI can become more difficult to treat and tolerate if it moves into the kidneys. In addition, it can cause scarring on the kidneys, which leads to potential for hypertension and kidney failure.
- . Because kidney function can be reduced, some of the waste the kidneys would normally filter out and push from the body with urination may flow back into the bloodstream, leading to illness, which is difficult on the seniors immune system.
- . In the same process, the infection may enter the bloodstream, leading to blood poisoning that is a life threatening issue.
- Worsening dementia. While the symptoms of confusion that a UTI causes in the elderly may not directly lead to dementia, if the condition develops in a patient who already has dementia, a urinary tract infection could cause a quicker progression of dementia, leading to worsening overall health for the elderly patient.
Institutionalized Older Adults & Catheterized Patients
Similar to other populations, the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI in nursing home residents requires the presence of genitourinary symptoms in the setting of a positive urine culture. In older adults who are cognitively intact, the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI is relatively straightforward. However, nursing home residents often suffer from significant cognitive deficits, impairing their ability to communicate, and chronic genitourinary symptoms , which make the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI in this group particularly challenging. Furthermore, when infected, nursing home residents are more likely to present with nonspecific symptoms, such as anorexia, confusion and a decline in functional status fever may be absent or diminished . In the setting of atypical symptoms, providers are often faced with the challenge of differentiating a symptomatic UTI from other infections or medical conditions. The high prevalence of bacteriuria plus pyuria in this population often leads to the diagnosis of UTI. Although bacteriuria plus pyuria is necessary for diagnosis of a laboratory-confirmed UTI, alone it is not sufficient for making the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI. To date, universally accepted criteria for diagnosing UTI in this population do not exist, making it difficult for providers to distinguish a symptomatic UTI from other conditions in the presence of new nonspecific symptoms.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Urinary Incontinence
Read Also: How Can A Woman Get A Urinary Tract Infection
What Causes Urinary Tract Infections
Normal urine is sterile and contains fluids, salts, and waste products. It does not contain bacteria, viruses, or fungi. A UTI occurs when germs, most often bacteria from the digestive tract, get into the opening of the urethra and start to multiply.
Most UTIs are caused by E. coli bacteria, which normally live in the colon.
Also Check: Frequent Bladder Infections In Females
Can I Prevent Recurrent Utis
There are steps you can take to help reduce UTIs. The most basic is to drink plenty of fluids. This encourages frequent urination and helps flush out bacteria.
For women, following good hygiene practices is especially important:
- After a bowel movement, wipe from front to back to reduce the chance of moving E. coli bacteria from the rectal area to the urethra.
- Pee immediately before and after sex.
- Dont douche or use feminine deodorants on your genitals.
- Wear cotton underwear.
For older adults, take care to deal with retention problems, which are especially an issue as you age.
I tell them to double-void urinate and then go back and urinate again, Dr. Vasavada says.
What about drinking cranberry juice to fight UTIs?
Thats one of the most commonly asked questions, Dr. Vasavada says. Theres conflicting data. Its not going to cure an infection, but it could help prevent one, so we dont discourage it.
You May Like: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Urinary S O Moderate Calorie
Check If Its A Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms of a UTI may include:
- pain or a burning sensation when peeing
- needing to pee more often than usual during the night
- pee that looks cloudy
- needing to pee suddenly or more urgently than usual
- needing to pee more often than usual
- lower tummy pain or pain in your back, just under the ribs
- a high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
Also Check: How Can I Strengthen My Bladder
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Utis

Symptoms of a UTI can include:
- pain when peeing
- changes in how often a child needs to pee
- changes in the look or smell of pee
- fever
- lower belly pain
- lower back pain or discomfort
UTIs also can cause kids to wet their pants or the bed, even if they haven’t had these problems before. Infants and very young children may only show nonspecific signs, such as fever, vomiting, or decreased appetite or activity.
Don’t Miss: Cure For Male Urinary Tract Infection