How Long Does A Uti Last Untreated
If an elderly woman has nonspecific symptoms, it is important for the clinicians to encourage such persons to drink more water until more tests are done for proper diagnosis. When a delay is made, usually the women dont need to use antibiotics in the long run.
Even with no antibiotics, some positive results can be witnessed if adequate amounts of fluids are taken in a weeks time. However, it is important to assess other criteria because UTIs can be deadly and can spread if not treated on time.
It is important to be very careful when you are administering antibiotics to seniors. The dose and the duration of use should also be carefully thought out. It is important to aim at the organism that is actually causing the infection so that the side effects can be minimized.
There are older adults in long-term facilities who may have renal insufficiency and this makes it necessary to make some adjustments to the most common dosages by using a glomerular filtration rate which is estimated.
Ask your doctor how to relieve UTI pain at night.
Also Check: Can Energy Drinks Cause Urinary Problems
Causes Of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections
The most common recurrent urinary tract infection causes in women are
- The female urethra is shorter than a mans, which means that bacteria has a shorter distance it needs to travel in order to get to the bladder, multiply, and cause infection.
- The proximity of the female urethra and rectum can result in a bacteria exchange from the rectum to the urethra, particularly if the patient wipes back to front instead of front to back after defecating.
They can be prevented by:
- Staying hydrated aka drinking plenty of water, ideally a gallon per day, to flush out bacteria.
- Being cautious when using a diaphragm during sex. Diaphragms can push up against the urethra, which makes it harder to fully empty the bladder during urination. The urine that doesnt empty is more likely to grow bacteria.
Why Are Women More Commonly Affected By Utis
Women are more commonly affected by UTIs because of:
- The female anatomy
- The female urethra is short which allows easier entry of skin and surface bacteria into the bladder.
Recommended Reading: Can Prostate Cancer Spread To The Bladder
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of A Urinary Tract Infection Male
Urinary Infections Predisposing To Bacterial Cystitis Can Be Divided Into 4 Categories :
- Isolated infections occur in 30 to 40% of women, between 27 and 42 years of age. They represent the first episode of urinary infection or infections that recur after an interval of at least 6 months
- unresolved infectionswhen drug treatment has failed to sterilise the urine
- re-infections are those that account for 90% of recurrent urinary infections
- persistent infections when there is a recurrence of the urinary infection, caused by the same infecting micro-organism, starting from an outbreak within the urinary tract.
This disease is also very common in pregnant women and the elderly.
Acute Bacterial Cystitis Is A Common Disease In Females
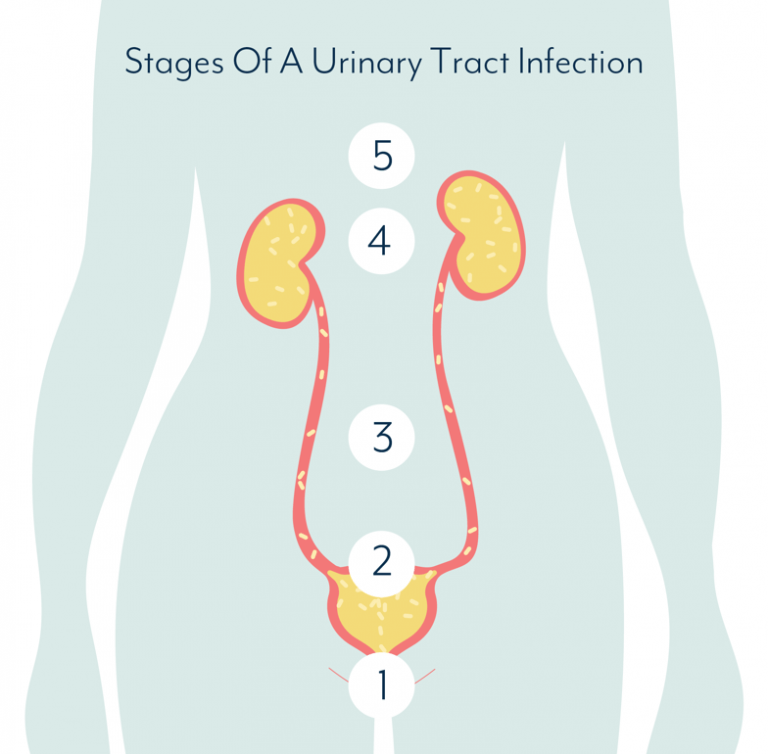
Approximately 25 30 % of women between 20 and 50 years of age report a history of urinary tract infection on examination.
People who have had an acute episode of cystitis are familiar with the painful symptoms and, above all, the consequences that such symptoms can have on their daily life and sex life.
We cannot consider it as a single disease but as a group of diseases.
In fact, on the one hand we find women with isolated or infrequent infections, and on the other, women with recurrent and intolerably recurrent infections.
This pathology can also cause serious infectious complications at the kidney level and not inconsiderable problems at the bladder level or present coexistence with Candida Albicans, which arises after antibiotic therapy as a demonstration of a drop in immune defences and metabolic alterations.
Chronic bladder infections can also be predisposing causes for bladder cancer, today the fourth leading cause of death worldwide.
Don’t Miss: How To Cure Urinary Retention
What Are The Types Of Utis
Common types of UTIs include:
- cystitis: this bladder infection is the most common type of UTI. It happens when bacteria move up the urethra and into the bladder.
- urethritis: when bacteria infect the urethra
- pyelonephritis: a kidney infection caused by infected urine flowing backward from the bladder into the kidneys or an infection in the bloodstream reaching the kidneys
Immunostimulants Studied In Humans
Strovac comprises ten strains of heat-killed uropathogens administered by intramuscular injection. This product was subsequently replaced by a vaginal preparation known as Urovac vaginal vaccine owing to considerable adverse reactions at the administration site. A meta-analysis of three randomized, placebo-controlled phase II studies consisting of 220 women demonstrated a modest effect that supports the need for further investigation of this immunostimulant . Benefits were highest in those patients receiving booster doses of the vaccine at monthly intervals,, but data are from small studies. Large, randomized phase III trials are required to establish the efficacy of this therapeutic option.
Don’t Miss: What Medications Treat Urinary Tract Infections
Pathogenesis And Risk Factors
Multiple potential mechanisms unique to diabetes may contribute to the increased risk of UTI in diabetic patients.38 Higher glucose concentrations in urine may promote the growth of pathogenic bacteria.8,39 However, several studies did not find an association between HbA1c level, which serves as a proxy for glycosuria, and risk of UTI among diabetic patients also, sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, which increase glycosuria, were not found to increase the rate of UTI.3,40 High renal parenchymal glucose levels create a favorable environment for the growth and multiplication of microorganisms, which might be one of the precipitating factors of pyelonephritis and renal complications such as emphysematous pyelonephritis.30,41 Various impairments in the immune system, including humoral, cellular, and innate immunity may contribute in the pathogenesis of UTI in diabetic patients.5,6,42 Lower urinary interleukin-6 and -8 levels were found in patients with diabetes with ASB, compared to those without diabetes with ASB.41 Autonomic neuropathy involving the genitourinary tract results in dysfunctional voiding and urinary retention, decreasing physical bacterial clearance through micturition, thereby facilitating bacterial growth.9,10,43 Bladder dysfunction occurs in 26%85% of diabetic women, depending on age extent of neuropathy and duration of diabetic disease,44 and thus should be considered in all diabetic patients with UTI.
How Is A Uti Diagnosed
To find out whether you have a UTI, your doctor or nurse will test a clean sample of your urine. This means you will first wipe your genital area with a special wipe. Then you will collect your urine in midstream in a cup. Your doctor or nurse may then test your urine for bacteria to see whether you have a UTI, which can take a few days.
If you have had a UTI before, your doctor may order more tests to rule out other problems. These tests may include:
- A cystogram. This is a special type of x-ray of your urinary tract. These x-rays can show any problems, including swelling or kidney stones.
- A cystoscopic exam. The cystoscope is a small tube the doctor puts into the urethra to see inside of the urethra and bladder for any problems.
Recommended Reading: Azo Urinary Tract Health Cranberry 50 Caplets
What Causes Urinary Tract Infections
Normal urine is sterile and contains fluids, salts, and waste products. It does not contain bacteria, viruses, or fungi. A UTI occurs when germs, most often bacteria from the digestive tract, get into the opening of the urethra and start to multiply.
Most UTIs are caused by E. coli bacteria, which normally live in the colon.
Dont Miss: How Do You Get E Coli Urinary Tract Infection
Is It Possible To Have A Uti Without Any Symptoms
Yes. Symptoms of a UTI can vary, and its not entirely uncommon for someone to experience no symptoms of a urinary tract infection. Its estimated that 1 to 5 percent of younger women experience asymptomatic bacteriuria , which is a UTI without the classic symptoms. While its unclear why the bacteria involved with urinary tract infections sometimes dont cause symptoms for these people, we do know that instances of symptom-free UTIs increase with age. Up to 16 percent of women older than 65 have been found to have ASB, and that number grows to almost 20 percent for women over 80. Other factors that increase your chances of an asymptomatic UTI are:
- Urinary catheter use
Dont Miss: Thin Pads For Urinary Incontinence
Also Check: Can A Urinary Tract Infection Heal On Its Own
Uti Causes And Risk Factors
The most common cause of a UTI in the urethra is a sexually transmitted disease. Chlamydia and gonorrhea are two STDs that can cause a UTI. STDs are also the most common cause of UTIs in younger men.
Prostate problems can also cause UTIs. An enlarged prostate is common in older men and can block the flow of urine. This can increase the odds that bacteria will build up and cause a UTI.
Prostatitis, which is an infection of the prostate, shares many of the same symptoms as UTIs.
Diabetes and other medical issues that affect your immune system can also make you more likely to get a UTI.
How Are Chronic Utis Treated
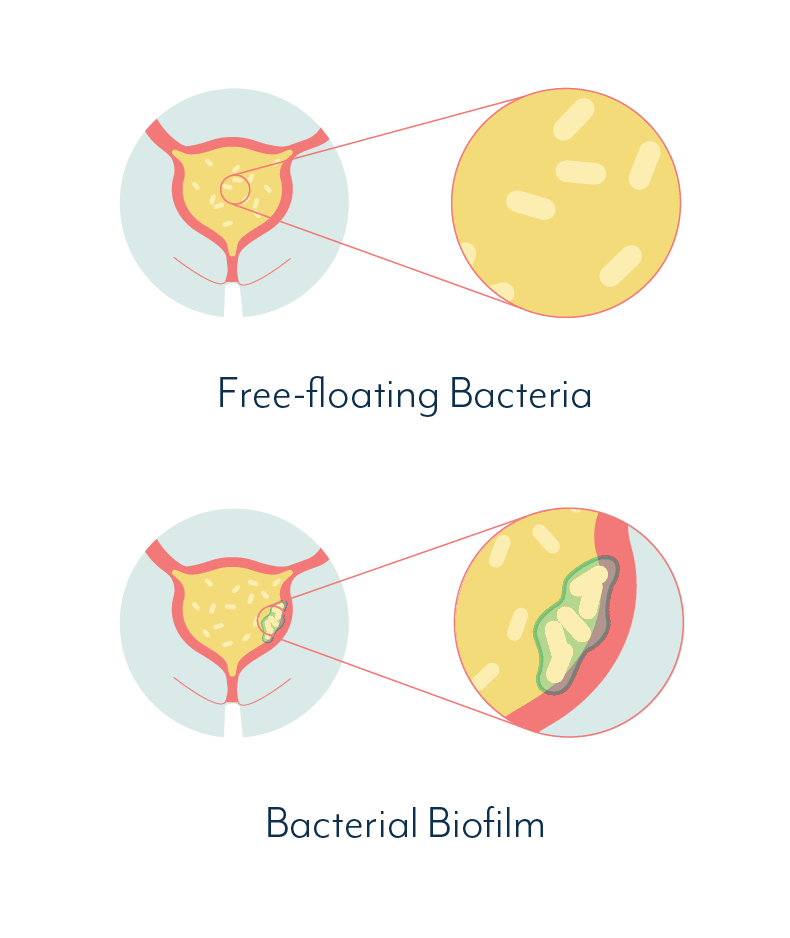
If you have recurrent or chronic UTIs, your doctor may send you to a urologist who specializes in diseases of the urinary system. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, some of the ways that recurrent UTIs are evaluated and treated include:
- Testing The doctor will want to take a urine sample to test for bacteria and white blood cells. It may be necessary to do special X-ray studies to see if there is an obstruction or stones in the urinary tract. A urologist may look into your bladder by passing a special scope through the opening into your bladder. This exam is called cystoscopy.
- Antibiotics for Treatment Normally, UTIs responds very well to antibiotics, and you may only need to take medication for a few days. For recurrent UTIs, antibiotics may be needed for 10 days or more.
- Surgery In some cases of prostate disease, stones, or other obstruction of the urinary system, surgery may be done to restore normal flow of urine and help clear up infections.
- Antibiotics for Prevention Some strategies to prevent recurrent UTIs with antibiotics include taking low-dose antibiotics for six months or taking antibiotics after sexual intercourse.
- Frequent Urine Testing Women who have recurrent UTIs may benefit from testing their urine frequently with a dipstick that warns of any bacteria in the urine.
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection Instant Relief
Read Also: Can Azo Urinary Tract Defense Get Rid Of Uti
What Can You Do To Prevent Recurrent Utis
If you are suffering from recurrent UTIs, you must get in touch with your primary care physician or a urologist. After carefully evaluating your condition, he/she will design an appropriate course of treatment.
Also, there are a lot of ways through which you can minimize your chances of getting UTIs. For this,
- Drink plenty of water It will help you get flush out all the bacteria through urine.
- Do not hold your pee If you feel the urge to urinate, find a bathroom and go.
- Maintain good sexual hygiene Do not indulge in unhealthy sexual activities. Also, urinate shortly after sex.
- Always use clean washrooms Make sure the washroom that you are using is clean and fresh.
- Use dermatologically tested products Always use sprays, deodorants and powders that are medically approved. And avoid using sprays close to your genitals.
- Keep your genitals clean Always wipe yourself from front to back after urinating.
- Wear cotton underwear Always prefer cotton panties to help keep your urethra dry.
Also Check: Will Overactive Bladder Go Away
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Utis
Symptoms of a UTI can include:
- pain when peeing
- changes in how often a child needs to pee
- changes in the look or smell of pee
- lower belly pain
- lower back pain or discomfort
UTIs also can cause kids to wet their pants or the bed, even if they havent had these problems before. Infants and very young children may only show nonspecific signs, such as fever, vomiting, or decreased appetite or activity.
Read Also: Prescription Drugs For Urinary Tract Infection
Do Cranberries Prevent Utis
Research on whether or not cranberries can prevent UTIs is inconsistent. Some studies show a benefit while others show very little or no benefit. Some researchers think that cranberries work because they have a component called proanthocyanidin that makes it hard for E. coli to move around and attach to the urinary tract.
There are no clinical recommendations for an exact dose or product to use. Small clinical studies suggest that 150 mL to 750 mL of cranberry juice every day might be helpful. Other small studies have shown that dried cranberries and cranberry tablets might work. The FDA also does not regulate cranberry products like they do medications.
Cranberries are generally considered to be safe. However, too much can cause stomach irritation and weight gain . Cranberries can also affect how medications behave, so be sure to consult your provider if you are considering taking them at the same time. Also keep in mind, cranberries are not as effective as antibiotics a 2011 clinical trial showed TMP/SMX led to fewer UTIs per year than cranberry capsules .
Read Also: Of A Urinary Tract Infection
Causes Of Recurrent Utis
Women who experience two or more UTIs in a six-month period, or those who have three or more UTIs in the course of a year are diagnosed with recurrent UTIs.
Sexual intercourse is a common cause of UTIs in women. People who use catheters are also at increased risk of developing recurrent UTIs.
After experiencing six or more UTIs a year, Marie knew there was a bigger problem. Learn how she finally found an answer at CU Urogynecology.
Dont Miss: How To Cure Urinary Retention Naturally
You May Like: Does Vitamin C Cause Urinary Tract Infections
Innate And Adaptive Immunity
The urothelium reacts to infection by undergoing apoptosis and exfoliation of infected cells from the urothelial host cells. Innate and adaptive immune system are not well understood in UTI, but the defense system against bacterial challenge may explain why the majority of women who experience initial and acute UTI do not show recurrent infection . Jaillon et al. demonstrated the important role of pentraxin 3 , a key player in the humoral and innate immunity against UTIs. PTX3-deficient animal model showed damaged response and exacerbated inflammation after UTI. Upregulation of PTX3 was induced in urothelial host cells by UPEC in a TLR4- and MyD88-dependent manner. The study also reported that increased level of PTX3 in the serum and urine of patients was associated with the severity of UTI. Moreover, they showed that polymorphisms of the PTX3 gene were correlated with susceptibility to infections. Based on these results, PTX3 could be involved in innate immunity against UTIs and have activity of ingestion of bacteria and phagosome maturation in neutrophils. In addition, PTX3-deficient neutrophils showed damaged ability of phagocytosis. The deficiency of PTX3 might show poor ability to control infection, resulting in spread of infection. Therefore, PTX3 deficiency could be associated with recurrent and chronic UTI .
Cystitis However Can Also Affect The Upper Urinary Tract Causing Pyelonephritis Caused By
The other routes of invasion of the parenchyma, lymphatic and haematogenous, are not common in normal subjects: in fact, lymphatic dissemination may occur only in cases of major intestinal infections, while haematogenous dissemination may occur in patients with bacteremia caused by Staf. Aureus or Candida fungemia.
Read Also: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Help With Urinary Tract Infections
Treatment Of Recurrent Utis
Most UTIs go away with a short course of antibiotics. UTIs may be treated with antibiotics in addition to home remedies such as drinking large amounts of water, frequent urination and completely emptying the bladder, and taking cranberry supplements.
However, women with recurrent UTIs often require preventive antibiotics, depending on the frequency or triggers of their infections.
Women who regularly develop UTIs following sexual intercourse may benefit from a dose of antibiotics that is taken after sex. For women who have less than three UTIs per year, a physician may provide a prescription for antibiotics that can be filled whenever symptoms start to appear.
For women whose recurrent UTIs occur more than three times per year, another treatment option is to take a regular, low dose of antibiotics to help prevent infections.
Other women with recurrent UTIs that may benefit from preventive antibiotics include women who have spinal cord injuries or other complex conditions involving the nervous system, such as multiple sclerosis or diabetes.
Recurring urinary tract infections may be a side effect of a more serious condition. If you are concerned, take our âDo I need a Urogynecologist?â self-assessment.
If youâre struggling with a pelvic floor disorder, we want to help. Contact us today to learn about our services and treatment options.
Skip call wait times by requesting an appointment online.
Dont Miss: How Long Is Bladder Surgery
Lipopolysaccharide A Virulence Factor In Upec
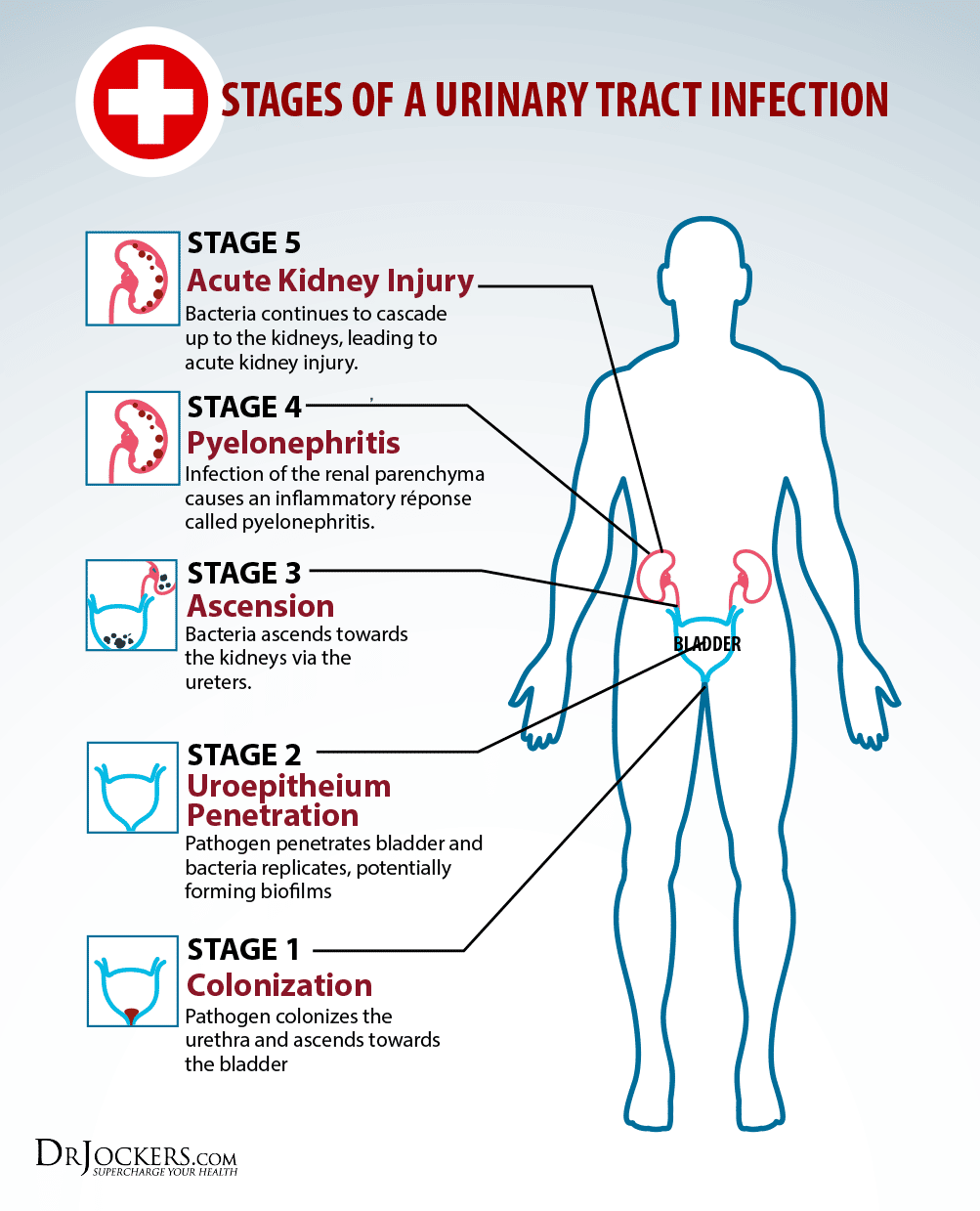
Lipopolysaccharide may induce cytokine release in cultured urothelial cells via inflammation signaling . LPS has amphipathic characteristics and it is bound to a O antigen which is a long polysaccharide chain . Structure of LPS modulates life cycle of UPEC and helps to form reservoirs of UPEC, and stimulate responses of innate and adaptive immune system .
Umbrella cells line the bladder lumen and perform a barrier function through tight-junction proteins. The umbrella cells show specialized functions for example, the cells represent the sentinel cells in defense against UPEC through rapid release of inflammatory cytokines and mediating of impermeability in bladder to provide barrier function. Receptors of LPS in the surface of urothelium may stimulate intracellular signaling pathways. The mechanism process of activated LPS might be through a Toll-like receptor 4-mediated increase in cytosolic calcium. This is atypical pathway to fast release mechanism of cytokines against UPEC. Interestingly, the cells shown in mouse to harbor IBCs of UPEC. The conventional antibiotics cannot eradicate LPS in IBC due to insufficient ability to penetrate urothelial cells. Due to the remnant LPS in the IBCs, symptom and pain in patients with UTI might be aggregated . Importantly, UPEC has been implicated in inhibiting cytokine production by LPS-TLR4 signaling. Hunstad et al. proposed that they isolated genes in UPEC that contributed to suppressing the cytokine responses.
Don’t Miss: Home Remedies To Get Rid Of A Urinary Tract Infection