Urinary Tract Infections And Dementia Urinary Tract Infections And Dementia
Urinary tract infections are a type of infection common among older people. If a person with a memory impairment or dementia has a UTI, this can cause sudden and severe confusion known as delirium.
Urinary tract infections and dementiaUrinary tract infections and dementia .
Who Is Affected By Utis And How Are They Treated
Women are more commonly affected by them than men. Around half of women will need treatment for at least one UTI during their lifetime.
If treated with the right antibiotics, UTIs normally cause no further problems and the infection soon passes. Though complications are uncommon, they can be serious and include kidney damage and blood poisoning, which can be fatal.
Older Adults Should Have Other Symptoms Too
When your loved ones doctor suspects a UTI, be sure to mention whether these symptoms are also present:
- Fever over 100.5 °F
- Worsening urinary frequency or urgency
- Sudden pain with urination
- Tenderness in the lower abdomen, above the pubic bone
Having at least two of the symptoms above, along with a positive urine culture, will confirm a UTI.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection Urinating After Sexual Intercourse
How The Urinary Tract Works
Urine is made by your two kidneys, one on each side of the tummy . Urine drains down tubes called ureters into the bladder. There it is stored and passed out through a tube called the urethra, when you go to the toilet.
In the average adult patient there should be a urine output of: 0.5-1 ml/kg/hr. This means that an average 70 kg man should produce 35-70 mls an hour. However urine output decreases in older patients and the target urine output should be 0.25-0.5 ml/kg/hr. This means that a 70 kg man who is aged over 65 years should produce 17.5-35 mls per hour.
Antibiotics Can Cause Serious Problems
Antibiotics can cause side effects, especially in older adults. Side effects include fever, rash, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, ruptured tendons, nerve damage, and kidney failure.
Using antibiotics can lead to vaginal yeast infections and other infections, including one that can cause severe diarrhea, a hospital stay, and even death in older people.
Also, older adults often take other medicines that can interact dangerously with antibiotics.
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection And Period
Utis In Institutionalized Elderly Patients
The diagnostic dilemma in this population is the paucity or absence of symptoms. Urinary frequency, urgency, or dysuria may or may not occur or may not be reported because of the underlying functional status of the patient. Geriatric patients with bacteriuria and bacteremia may not have fever or exhibit other signs of general infection. It is important to compare minor changes in the individual patients baseline and then begin the workup to rule out common causes of these alterations.31
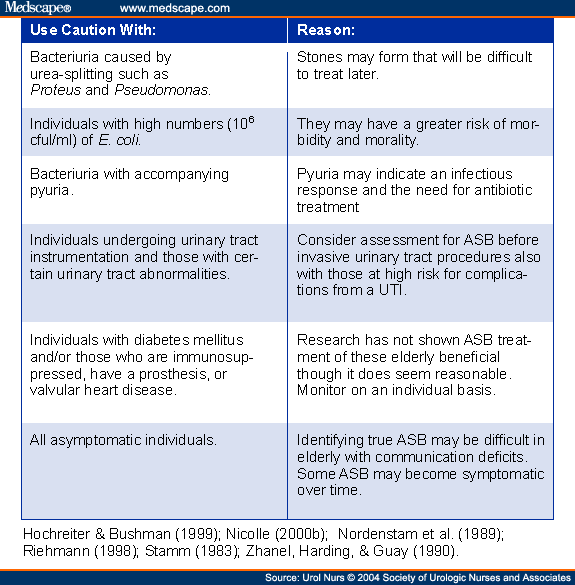
One of the most challenging problems in the clinical management of this population is asymptomatic bacteriuria, which is defined as the presence of more than 100,000 colony-forming units of bacteria without symptoms or signs. This condition may be present in up to 30% of ambulatory elderly and up to 50% of institutionalized elderly.32 It also is found in nearly all catheterized patients.
Because the presence of bacteriuria does not predict mortality in the aged, screening for asymptomatic bacteriuria is not recommended unless the patient is scheduled to undergo a genitourinary procedure. Treatment does not prevent recolonization in these patients and does not reduce the risk of development of a clinically significant UTI. In fact, aggressive treatment of this condition may contribute to unnecessary antimicrobial use, with its risks of adverse events, superinfection, and development of bacterial resistance.33
Prevention Of Catheter Associated Uti
Catheter associated UTI is the most common health care associated infection throughout the world and is common in long-term care facilities. Urinary catheterization should be avoided unless there is a clear clinical indication. Catheters should be avoided where possible for the management of incontinence. Staff should also be trained on indications for catheterization and written protocols should be put in place.26,27 Catheters should also be removed the moment that they are no longer required.
Alternatives to indwelling urethral catheters should be considered. Condom catheters are associated with a lower incidence of bacteriuria, however their use is sometimes difficult in confused patients.27 A Cochrane review on short-term urinary catheterization in adults found that suprapubic catheterization was associated with less bacteriuria than urethral catheterization.43 Suprapubic catheterization does carry a small risk of visceral injury on insertion through the abdominal wall. Intermittent catheterization was also associated with a lower risk of bacteriuria when compared to indwelling catheterization in this review, however studies included were mainly in an elective orthopedic setting.43
Guidelines suggest that antibiotic prophylaxis should not be used to prevent catheter associated UTI in catheterized patients.10 Although prophylaxis may decrease the incidence of asymptomatic bacteriuria in catheterized patients, it increases the risk of antimicrobial resistance.
Also Check: Royal Canin Urinary S O Moderate
Factors Associated With The Treatment Outcomes Of Utis Among The Elderly Population
The different associated factors involved in the treatment outcomes of UTIs among the elderly population have been predicted by using binary logistic regression analysis. Gender, marital status, age, race, smoking status, alcohol consumption, home, polypharmacy, and presence of co-morbidities are the factors that are analyzed to predict their association with the treatment outcomes of UTIs among the study population. Out of these nine independent variables, only four of them show statistically significant association with the treatment outcomes in binary logistic regression. These associated variables are then tested in multiple logistic regression, all of them show significant association except the age factor . Table 5 shows the detailed presentation of binary and multiple logistic regression analysis.
Table 5. Predictors affecting the treatment outcomes of UTIs among the study population.
Ways To Prevent A Uti
Antibiotics and natural medicines are available to help clear up UTIs, but there are preventative measures you can take to help ensure your body is able to stave off infections that tend to occur through the normal course of life. Read on to see three ways weve discovered through careful research to help prevent urinary tract infections in older women.
You May Like: Can You Cure A Urinary Tract Infection Without Antibiotics
Things You Can Do Yourself
To help ease symptoms of a urinary tract infection :
- takeparacetamolup to 4 times a day to reduce pain and a high temperature for people with a UTI, paracetamol is usually recommended over NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or aspirin
- you can give childrenliquid paracetamol
- rest and drink enough fluids so you pass pale urine regularly during the day
- avoid having sex
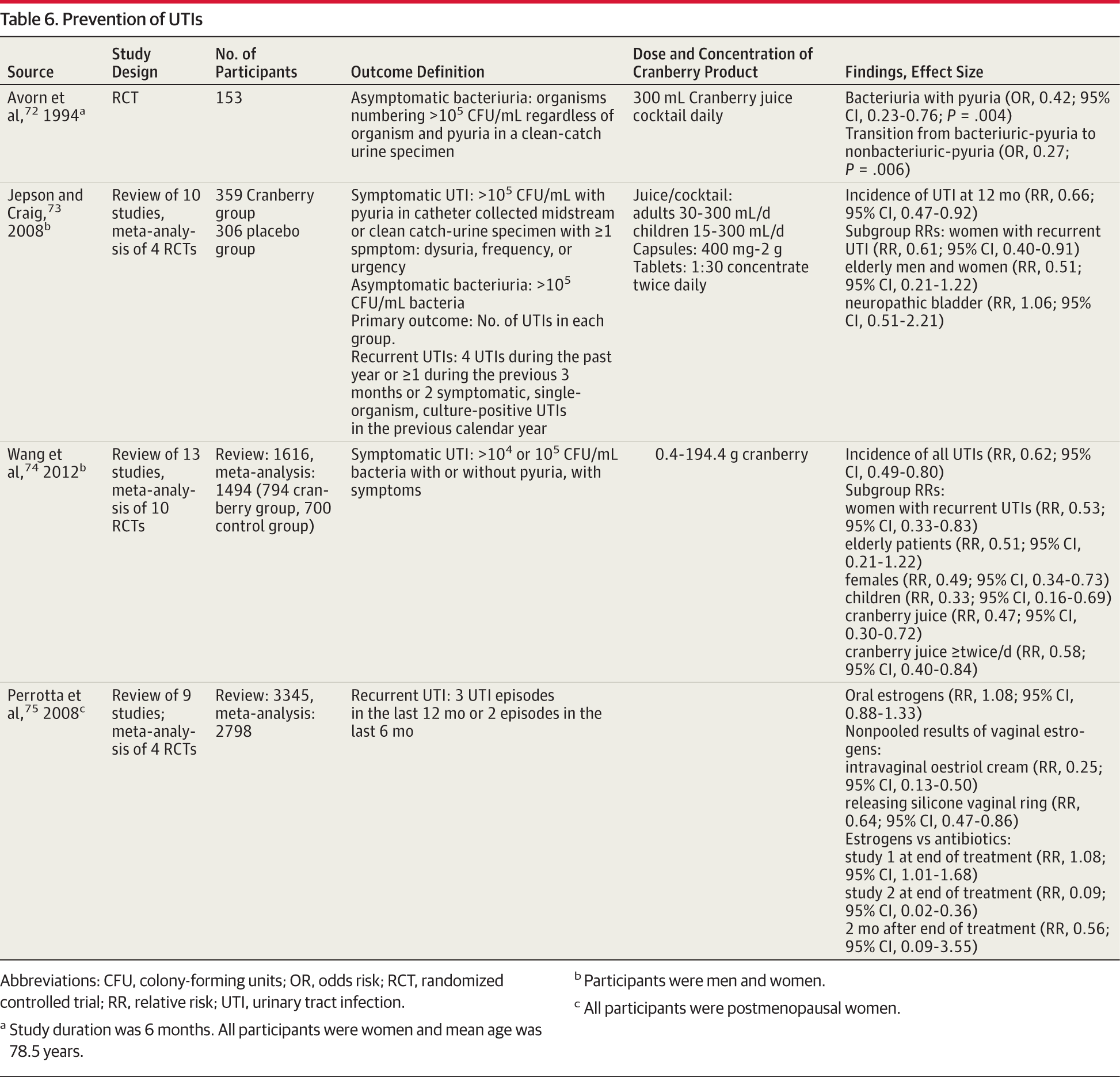
Some people take cystitis sachets or cranberry drinks and products every day to prevent UTIs from happening, which may help. But there’s no evidence they help ease symptoms or treat a UTI if the infection has already started.
How Are Utis Treated In Seniors
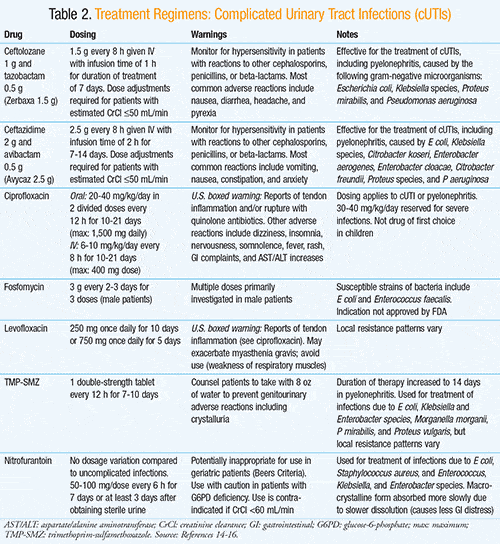
Fortunately, most seniors can recover from a urinary tract infection at home with an antibiotic. Older women who frequently develop UTIs may be given an estrogen cream to apply regularly to lower the likelihood of repeat infections. If a UTI turns into a kidney infection, hospitalization may be necessary.
Recommended Reading: Physical Therapy Exercises For Urinary Incontinence
Why Are Urinary Tract Infections Common In Older Adults
Seniors are more vulnerable for many reasons, including their overall susceptibility to infections due to a weakened immune system.
As you get older, your immune response changes its part of normal aging, explains Anna Dowd, APN, a gerontological nurse practitioner in the greater Chicago area.
According to the National Institutes of Health , the following conditions make older individuals more susceptible to UTIs:
- Urine retention
- Use of a urinary catheter
- Bowel incontinence
- Urinary incontinence
- Surgery of any area around the bladder
People with incontinence are at an increased risk for UTIs because of the close contact that adult briefs and other incontinence products have with their skin. While these products can help contain messes and prevent embarrassment associated with accidents, they can also introduce bacteria into the urethra. Women are more prone to UTIs because the female urethra is much shorter, allowing bacteria to travel to the bladder more easily.
Institutionalized Older Adults & Catheterized Patients
Similar to other populations, the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI in nursing home residents requires the presence of genitourinary symptoms in the setting of a positive urine culture. In older adults who are cognitively intact, the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI is relatively straightforward. However, nursing home residents often suffer from significant cognitive deficits, impairing their ability to communicate, and chronic genitourinary symptoms , which make the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI in this group particularly challenging. Furthermore, when infected, nursing home residents are more likely to present with nonspecific symptoms, such as anorexia, confusion and a decline in functional status fever may be absent or diminished . In the setting of atypical symptoms, providers are often faced with the challenge of differentiating a symptomatic UTI from other infections or medical conditions. The high prevalence of bacteriuria plus pyuria in this population often leads to the diagnosis of UTI. Although bacteriuria plus pyuria is necessary for diagnosis of a laboratory-confirmed UTI, alone it is not sufficient for making the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI. To date, universally accepted criteria for diagnosing UTI in this population do not exist, making it difficult for providers to distinguish a symptomatic UTI from other conditions in the presence of new nonspecific symptoms.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Urinary Incontinence
Recommended Reading: How Does A Man Get A Urinary Tract Infection
Are There Any Effective Homeopathic At
No. If your child has a diagnosed UTI, he or she should be treated with antibiotics. However, there are things to do at home that can help reduce pain and foster healing. These include:
- Drink plenty of water. This may help flush bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Use the bathroom frequently. Teach your child to urinate often and when he or she first feels the urge.
- Use a heating pad. If your childs back or abdomen hurts, the warmth may help ease some pain.
- Skip the bubble bath. Sitting in bathwater brimming with bubble bath can cause irritation.
- Avoid irritants. Spicy food, raw onions, citrus fruits, carbonated and caffeinated beverages, and artificial sweeteners can further irritate your child’s bladder, making it more difficult for your childs UTI to heal.
Its fairly common for parents to offer their children cranberry juice to treat urinary tract infections, but this method has not been proven effective. While cranberries do contain an active ingredient that can prevent the adherence of bacteria to the urinary tract, theres no evidence that your typical grocery store cranberry products can treat a UTI.
Utis In The Geriatric Population: Challenges For Clinicians
Kenneth R. Cohen, PharmD, PhDAssociate Professor of Pharmacy and Health OutcomesTouro College of Pharmacy
Jerry Frank, MD, Fellow, AAFPClinical Assistant ProfessorSUNY Stony Brook School of MedicineDepartment of Family Medicine
Parker Jewish Institute of Health Care and RehabilitationNew Hyde Park, New York
US Pharm. 2011 36:46-54.
The challenge of developing guidelines for the diagnosis, management, treatment, and prevention of urinary tract infections is a daunting one. The condition runs through diverse populations of the elderly, from the walking well to the chronically ill. Each population has unique characteristics and requires a tailored approach to diagnosis and treatment.
In this article, the discussion of UTIs has been structured according to walking-well, chronically ill, and institutionalized elderly patients in order to better elucidate the issues associated with each population.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Incontinence In Females Treatment
Urinary Tract Infections In Elderly Patients: How Best To Diagnose And Treat
DALE P. MURPHY, MDSeries Editorand MARYJO CLEVELAND, MD
How is urinary tract infection best managed in elderly persons?
Genitourinary infection is the second most common type of infection in community-dwelling adults older than 65 years it occurs only slightly less frequently than upper respiratory tract infection. 1 The presentation of UTI in elderly patients may differ significantly from that in younger ones. Chronic urinary symptoms are common in elderly persons, and the classic triad of UTI-frequency, urgency, and dysuria-occurs routinely in older persons without infection.2 As many as one third of community- dwelling elderly women are incontinent, which can further confuse the presentation. A high index of suspicion is needed first to entertain the diagnosis and then to pursue a thorough evaluation.A variety of risk factors predispose older persons to UTIs . In those between ages 50 and 70 years, the most common are urinary tract surgery, incontinence, cystocele, high postvoid residual volume, and low estrogen levels. Neurogenic conditions of the bladderparticularly those associated with diabetes and with anticholinergic medicationalsopredispose to UTI.3 In patients older than 70 years, risk factors include the use of multiple antibiotics, the presence of an indwelling catheter, and a history of UTI.
Clinical Policy And Research Implications
Our findings suggest that GPs consider early prescription of antibiotics for this vulnerable group of older adults in view of their increased susceptibility to sepsis after UTI and despite a growing pressure to reduce inappropriate antibiotic use. Particular care is needed for the management of older men and those in deprived communities. For researchers, there is a need to improve the understanding of the effects of deferred antibiotic prescribing in routine practice. New medical record or retrievable codes should therefore be in place to record when primary care clinicians advise patients to delay antibiotic consumption.
You May Like: How Can A Male Get A Urinary Tract Infection
Urine Infection In Older People
If you have a urine infection, you have germs in your bladder, kidneys or the tubes of your urinary system. Urine infections are more common in older people, and there is more likely to be an underlying cause.
In this article
Urine Infection in Older People
In this article
Urine Tests Usually Dont Help If You Dont Have Uti Symptoms
Older people often have bacteria in their urine, even if they have no urinary symptoms. This is true for nearly half of all nursing home residents.
Doctors will often order a urine test if an older adult has vague symptoms, such as increased confusion, irritability, or falling. The test will probably show some bacteria. This may lead the doctor to order an antibiotic.
But if the bacteria is in the urine and not causing a real infection, the antibiotic wont help the vague symptoms. There are many other reasons why an older adult might be confused or irritable, or fall.
Read Also: Can Green Tea Cause Urinary Tract Infection
Causes Of Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are usually caused by bacteria from poo entering the urinary tract.
The bacteria enter through the tube that carries pee out of the body .
Women have a shorter urethra than men. This means bacteria are more likely to reach the bladder or kidneys and cause an infection.
Things that increase the risk of bacteria getting into the bladder include:
-
do not use scented soap
-
do not hold your pee in if you feel the urge to go
-
do not rush when going for a pee try to fully empty your bladder
-
do not wear tight synthetic underwear, such as nylon
-
do not drink lots of alcoholic drinks, as they may irritate your bladder
-
do not have lots of sugary food or drinks, as they may encourage bacteria to grow
-
do not use condoms or a diaphragm or cap with spermicidal lube on them try non-spermicidal lube or a different type of contraception
Characteristics Of The Study Population
In the current 5 year retrospective cross-sectional study, 460 participants were included in which women 279 were in majority as compared with men 181 with a mean age of 72 ± 4 years. Most of the study participants 342 were in the age range of 6575 years of age and 118 were above 75 years. Majority of the included population was married 256 , Chinese 271 , non-smokers 312 , and non-alcoholic 318 . Detailed association between the sociodemographic variables with the treatment outcome parameters among the study population infected with UTIs is presented in Table 1.
You May Like: How To Deal With Urinary Incontinence
Signs And Symptoms Of Uti In The Elderly
Interestingly enough, the elderly with a UTI are often misdiagnosed with senior dementia or Alzheimer’s disease, because a UTI can mimic symptoms of such conditions. Also, according to Nursing magazine between 30% and 40% of elderly patients with serious infection don’t exhibit the hallmark sign of fever due to the inability of the immune system to mount a response to infection due to the effects of aging. As the bacteria in the urine spread to the bloodstream and cross the blood-brain barrier, confusion and other cognitive difficulties can be the result. Sudden onset of these symptoms should lead one to investigate possible UTI. An elderly person who is experiencing signs of mental difficulties should also be closely monitored for other signs of a UTI such as:
- Urine that appears cloudy
Are Frequent Utis A Sign Of Diabetes Or Is A Uti A Symptom Of Diabetes
A review from 2005 found that an astounding 50% of people with diabetes have some type of dysfunction of their bladder- thats half of every man and woman with diabetes. There are quite a few theories which we have already discussed, but again, most of the newer theories and research have only been conducted on rats.
Another fact this review highlights is that women who have Type 1 diabetes have a higher risk for kidney infections , which can potentially damage the kidneys function long term. This may lead to the need for a kidney transplant as the damage becomes severe.
You May Like:Azo Urinary Pain Relief Walgreens
Don’t Miss: To Avoid Pulling The Urinary Catheter