Treatment For Recurrent Utis
You can typically get rid of a simple UTI with antibiotics, the Mayo Clinic explains. But, when you have chronic UTIs, your doctor may recommend the following, per the Mayo Clinic:
Low-dose antibiotics, for six months but maybe longer
Self-diagnosis and treatment, if you stay in touch with your doctor
A single dose of an antibiotic after sex, if your recurrent UTIs are related to sex
Vaginal estrogen therapy, if youre postmenopausal
Took Antibiotics Some Uti Symptoms Resolved Other Symptoms Still Linger
So why if it wasnt a UTI, the prescribed antibiotics worked and you did feel a relief? Well, there could be at least three reasons:
Dr. Hawes hypothesizes that it could be due to some sort of a side-effect from Cipro: perhaps, the medicine does something else to the body besides killing bacteria that could indeed reduce UTI-like symptoms.
When Treatment Doesnt Work
UTI is a fairly common illness, accounting for around 8.3 million doctor visits yearly in the United States alone. This is probably why most people just shrug it off as another harmless condition, and most of the time, theyre right not to worry. Generally, this genitourinary infection is non-complex and thus fairly easy to manage.
There are cases, however, when patients dont respond to the treatment. According to Erik Castle, MD, from Mayo Clinic, there are several factors that may predispose you to UTI, particularly if youre a woman. These are:
- kidney or bladder stones
- bacteria entering the urethra during intercourse
- changes in estrogen levels
- previous surgery on the urinary tract
- diabetes and other associated complications
- bladder cancer
In men, however, having an enlarged or infected prostate can exacerbate their UTI symptoms or predispose them to a chronic infection. Also, if you have other conditions requiring you to use a catheter, the chances of getting your urinary tract infected also increase.
Also Check: Urinary Tract Probiotics Garden Of Life
How Are Urinary Abnormalities Diagnosed
It’s important for a doctor to rule out any underlying problems in the urinary system when a child gets UTIs repeatedly. Kids with recurrent infections should see a pediatric urologist to see what is causing the infections.
Some problems can be found before birth. Hydronephrosis that develops before birth can be seen in an ultrasound as early as 16 weeks. In rare cases, doctors may consider neonatal surgery if hydronephrosis affects both kidneys and is a risk to the fetus. Most of the time, though, doctors wait until after birth to treat the condition, because almost half of all cases seen prenatally disappear by the time a baby is born.
Doctors will closely watch the blood pressure of a newborn thought to have hydronephrosis or another urinary system abnormality, because some kidney problems can cause high blood pressure. Another ultrasound may be done to get a closer look at the bladder and kidneys. If the condition appears to be affecting both kidneys, doctors usually will order blood tests to check kidney function.
Clinical Presentation And Diagnosis
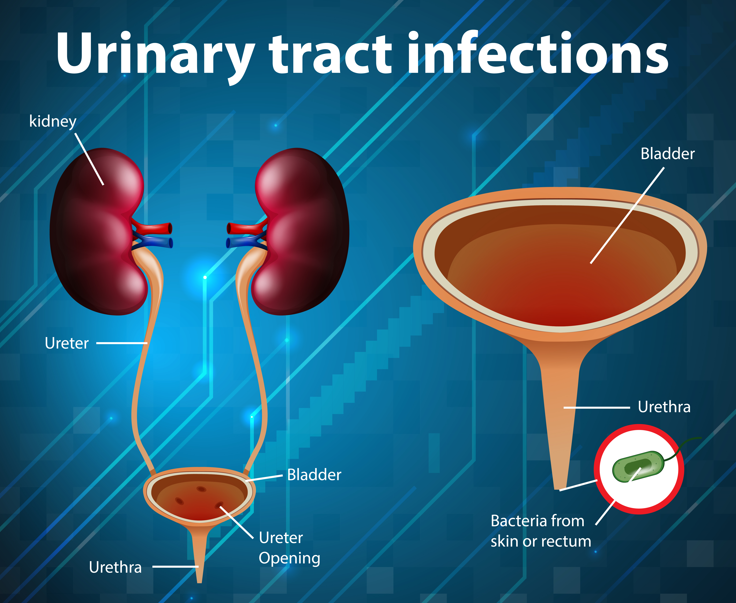
Common symptoms of a UTI are dysuria, urinary frequency, urgency, suprapubic pain and possible haematuria. Systemic symptoms are usually slight or absent. The urine may have an unpleasant odour and appear cloudy.23 Diagnosis of RUTI depends on the characteristic of clinical features, past history, three positive urinary cultures within the previous 12-month period in symptomatic patients and the presence of neutrophils in the urine .7,8,21 Irritative voiding symptoms are present in 2530 % of women with RUTIs.25 The probability of finding a positive culture in the presence of the above symptoms and the absence of vaginal discharge is around 81%.26 In a complicated UTI, such as pyelonephritis, the symptoms of a lower UTI will persist for more than a week with systemic symptoms of persistent fever, chills, nausea and vomiting.25
Women with RUTIs should have an initial evaluation including a history-taking and a physical and pelvic examination the latter is important to detect pelvic organ prolapse and to assess the status of the vaginal epithelium.28 Urinalysis and urine culture with sensitivity are also valuable investigations. Women with a positive family history of DM, obesity or RUTI must be screened for DM.28,29 Women with suspected urine retention need to be evaluated for high post-void residual urine volume.
Also Check: To Treat Urinary Tract Infection
What Can I Do To Prevent Recurrent Utis
The majority of UTIs, about 90%, are caused by E. coli, a bacteria that naturally occurs in your intestines where its helpful. When this bacteria comes in contact with your urinary tract system, however, it can be harmful and lead to a UTI.
For most people, simple hygiene and lifestyle changes can help prevent recurrent UTIs. To help stop a UTI before it starts, try implementing these tips:
- Avoid spreading E. coli by washing your genitals with warm water and mild soap before and after sex.
- Drink plenty of fluids to flush out any wandering bacteria from the urinary system.
- Be sure to urinate after having sex to keep bacteria from lingering in the urethra.
- When you feel the urge to urinate, go postponing urination increases your risk of developing a UTI.
- Be sure to wipe from front to back to avoid spreading E. coli to the vagina.
Ready to learn more about UTIs and how they affect older women? Experiencing symptoms of a UTI? Contact our Littleton office or book an appointment online now and the help you need!
Things You Can Do Yourself
To help ease symptoms of a urinary tract infection :
- takeparacetamolup to 4 times a day to reduce pain and a high temperature for people with a UTI, paracetamol is usually recommended over NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or aspirin
- you can give childrenliquid paracetamol
- rest and drink enough fluids so you pass pale urine regularly during the day
- avoid having sex
Some people take cystitis sachets or cranberry drinks and products every day to prevent UTIs from happening, which may help. However, there’s no evidence they help ease symptoms or treat a UTI if the infection has already started.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Urinary Incontinence After Prostate Surgery
Ideas To Talk To Your Doctor About
If you get a lot of UTIs, your doctor may consider:
- A daily low dose of antibiotics, taken for 6 months or longer
- Having you test yourself for a UTI at home when you have symptoms
- Taking a single dose of antibiotics after having sex
If youâve gone through menopause, you could ask about estrogen vaginal cream. After menopause, women have less estrogen in their bodies, which can cause vaginal dryness and make the urinary tract more vulnerable to infection. The treatment can help balance the areaâs pH factor and allow âgoodâ bacteria to flourish again.
How Is A Recurrent Uti Diagnosed
According to Dr. Stewart, the criteria for diagnosing recurrent UTIs was recently re-evaluated by the American Urological Association . Recurrent UTIs are defined as two UTIs in six months or three UTIs within one year, she says, but they need to be cases of culture-proven, bacterial cystitis with symptoms.
In other words, youll need to have confirmed cases of bacteria from a urine sample and noticeable UTI symptoms to qualify. Dr. Stewart explains that some people regularly test positive for bacteria without symptoms and others have symptoms without a positive culture . Those scenarios should be treated differently than a patient who presents with both.
A urine culture includes a check of sensitivities, meaning that we can tell which antibiotics will kill that infection and which will not, explains Dr. Cadish, adding that a diagnosis of UTI really means that the specific bacteria causing the infection has been identified in a culture. From there, a healthcare provider can prescribe an appropriate course ofantibiotics for that particular infection.
Its important not to neglect symptoms of UTIs if left untreated, your UTI can become a kidney infection, a serious and potentially life-threatening problem known as pyelonephritis.
Also Check: How To Clean My Urinary Tract
How Can I Help Prevent Recurrent Utis
You can help your child reduce their risk of developing another UTI. Dr. Kronborg shares these suggestions to help prevent infections down the road.
Why Do Older Women Get Recurrent Utis
Urinary tract infections are most common in older women for two reasons. First, women are generally more likely to get a UTI because of the physical structure of their urinary tract. The female anatomy includes a shorter urethra than men. This means bacteria only needs to travel a short distance to reach deeper into the urinary tract. It is also easier for bacteria from the rectum or from intercourse to travel to the vagina and urethra.
Second, as womens bodies go through menopause, the major hormonal shifts lead to changes in the urinary tract. Post-menopausal women may not have the right pH balance in their vagina. When your system is out of balance, it makes you more susceptible to infections in your urinary tract.
Also Check: What Causes Urinary Urgency Incontinence
What If They Keep Coming Back
Recurrent UTIs are defined as having two infections in a period of six months or three infections in a year. Most recurrences are due to a new infection as opposed to the old infection lingering. There are a few reasons why these recurrences might happen, including having cell receptors that bacteria is more prone to affecting. Those who are sexually active are also more prone to infections, due to the fact that bacteria is more likely to spread during sex, which is why proper hygiene and urinating after sex is very important. Your diet can also contribute. If youre not well hydrated, your body may have difficulty flushing out bacteria effectively. Additionally, a balanced diet can keep your bowels running properly, meaning theres less pressure on your bladder from your bowels. Diarrhea can also more easily spread bacteria. If you feel like you might have a urinary tract infection, especially if you suffer from recurrent UTis, its important to book an appointment with Mississippi Urology Clinic for an official diagnosis. A simple UTI can develop into a more complex infection if untreated. On the other hand, the symptoms could also come from a different type of infection that may require a different type of treatment. Most importantly, dont suffer these symptoms without reaching out for help. We can diagnose a UTI and have you feeling better soon with the proper medication and treatment.
How Is A Recurrent Uti Treated
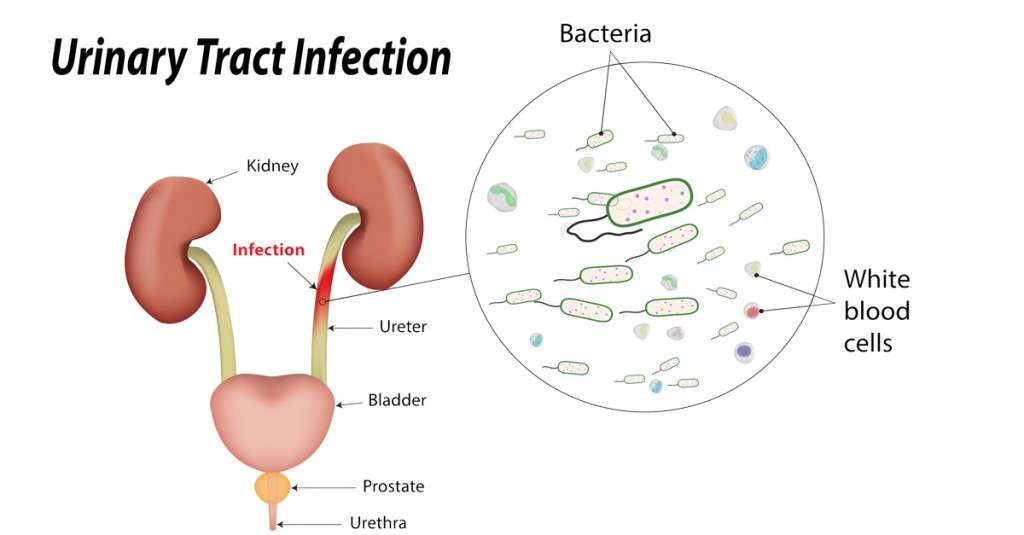
A UTI is diagnosed with a urine test. The test is sent to a lab to determine which bacteria are causing the infection.
UTIs are treated with antibiotics. If you have an active UTI, your doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotics to take over several days.
If UTIs are recurrent, your doctor might prescribe lower dose antibiotics to take for several months. This keeps bacteria from invading the bladder, and allows the bladder to heal from the chronic inflammation of repeated infections.
Long-term use of antibiotics may cause some side effects, such as yeast infections or diarrhea.
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection Pills Over The Counter
Can Utis Increase The Risk Of Bladder Cancer
Several studies have investigated whether UTIs may be a risk factor for bladder cancer.
- Epidemiological studies that have examined evidence of an association between UTIs and urothelial carcinoma have to date produced varying results.3,13,14 Some data indicates there may be increased risk in individuals who experience previous UTIs,3,14 whereas other findings suggest that previous UTIs could have a protective effect against bladder cancer, possibly due to an anti-cancer effect of the antibiotics used in their treatment.3,13,14
- Colibactin, a bacterial toxin that can damage DNA, is suspected to play a role in some types of cancer. Researchers have recently detected colibactin production in E. coli isolated from the urine of patients with UTIs.15 Furthermore, in the urinary tracts of mice infected with colibactin-producing E. coli, DNA damage in bladder cells was observed .
- Preliminary data appears to support a link between recurrent UTIs and increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the bladder.16 However, as squamous cell carcinoma is a rare type of bladder cancer , the overall impact of this potential association would be relatively minor.
It may be concluded that the extent of any direct relationship between UTIs and bladder cancer is yet to be fully determined. However, it is clear that a major bladder cancer risk associated with recurrent UTIs in women is that of delayed diagnosis, caused by the extensive overlap in symptoms between the two conditions.
What Causes Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer occurs when cells making up the bladder begin to grow and spread in an uncontrolled way, leading to the formation of a malignant tumor. This abnormal cell growth is caused by mutations in the genes that control cell replication, repair, and programmed death: genes that help cells to grow and divide may be switched on, whereas genes that regulate cell division, repair, and programmed death may be switched off.
Most of the gene mutations associated with bladder cancer are acquired, meaning that they develop during a persons life rather than being present at birth . Some of the acquired gene mutations are caused by exposure to toxins or chemicals that are recognised risk factors for developing bladder cancer, such as tobacco smoke.
You May Like: Can Iud Cause Urinary Incontinence
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection In Pregnancy
UTI is the most frequent medical complication of pregnancy. The risk factors of preterm delivery, low infant birth weight and abortions are most commonly associated with symptomatic and asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy.77 In pregnancy, factors that contribute to UTI risk are ureteric and renal pelvis dilation increased urinary pH decreased muscle tone of the ureters, and glycosuria, which promotes bacterial growth. Treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy reduces the risk of pyelonephritis. As RUTIs are common in pregnancy, they need prophylactic treatment if they occur. Screening for bacteriuria is recommended in all pregnant women at their first prenatal visit and then in the third trimester.82,83 They should subsequently be treated with antibiotics such as nitrofurantoin, sulfisoxazole or cephalexin.21,24,8284 Antibiotic prophylaxis for RUTI in pregnant women is effective using continuous or post-coital regimens. The causative organisms of UTI in pregnancy are similar to those found in non-pregnant patients, with E. coli accounting for 8090% of infections.85,86 Urinary group B streptococcal infections in pregnant women need to be treated and followed by intrapartum prophylaxis.21
Why Does My Uti Keep Coming Back
Chronic or recurring UTIs may keep coming back due to one of the risk factors listed above. Use of spermicides for birth control, for instance, may kill off beneficial bacteria in and around the vagina, making it easier for harmful bacteria to enter the urinary tract.
In some cases, what seem like recurrent UTIs may actually be another condition, such as kidney stones or interstitial cystitis, a painful bladder condition with no infection. If you think youre getting recurrent UTIs, see your provider, who can help rule out another condition, notes ACOG.
Read Also: What Can Cause Urinary Retention
How Are Utis Treated
UTIs are usually treated with antibiotics. To help avoid the recurrence of a UTI, it is important to ensure that the full antibiotic course is completed.
Can UTI symptoms linger after antibiotic treatment?
If antibiotic treatment has been effective, UTI symptoms should be fully resolved. When symptoms persist at completion of the prescribed antibiotic course, further tests and treatment will be necessary. This may involve culturing a urine sample to determine which antibiotic types are effective against the infecting bacteria, and the use of diagnostic imaging to check the urinary tract.
How long can a UTI go untreated?
If you ever see blood in your urine or are concerned about other UTI signs and symptoms, contact your doctor. Seeking treatment promptly not only decreases the chance of UTI-related complications, but also helps to avoid extended periods of misdiagnosis if your symptoms are not being caused by a UTI.
If symptoms such as back pain, fever, and nausea/vomiting are present always seek urgent treatment, because of the risk of permanent kidney damage and/or life-threatening complications.