Do You Need To See A Doctor To Get Antibiotics For A Uti
You need to speak with your doctor or a licensed medical professional to be prescribed antibiotics for a UTI. This can usually be done in person, at the doctor, or over the phone.
If this is your first UTI or your symptoms are severe it may be helpful to get treated in person to rule out the possibility of sexually transmitted infections.
How Long Should I Take Antibiotics
Your doctor will let you know. Typically, for an uncomplicated infection, you’ll take antibiotics for 2 to 3 days. Some people will need to take these medicines for up to 7 to 10 days.
For a complicated infection, you might need to take antibiotics for 14 days or more.
If you still have symptoms after completing antibiotics, a follow-up urine test can show whether the germs are gone. If you still have an infection, you’ll need to take antibiotics for a longer period of time.
If you get UTIs often, you may need a prolonged course of antibiotics. And if sex causes your UTIs, you’ll take a dose of the medicine right before you have sex. You can also take antibiotics whenever you get a new UTI if youâre having symptoms and a positive urine culture.
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Urinary Tract Infections In Children
BRETT WHITE, MD, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, Oregon
Am Fam Physician. 2011 Feb 15 83:409-415.
Acute urinary tract infections are relatively common in children, with 8 percent of girls and 2 percent of boys having at least one episode by seven years of age. The most common pathogen is Escherichia coli, accounting for approximately 85 percent of urinary tract infections in children. Renal parenchymal defects are present in 3 to 15 percent of children within one to two years of their first diagnosed urinary tract infection. Clinical signs and symptoms of a urinary tract infection depend on the age of the child, but all febrile children two to 24 months of age with no obvious cause of infection should be evaluated for urinary tract infection . Evaluation of older children may depend on the clinical presentation and symptoms that point toward a urinary source . Increased rates of E. coli resistance have made amoxicillin a less acceptable choice for treatment, and studies have found higher cure rates with trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole. Other treatment options include amoxicillin/clavulanate and cephalosporins. Prophylactic antibiotics do not reduce the risk of subsequent urinary tract infections, even in children with mild to moderate vesicoureteral reflux. Constipation should be avoided to help prevent urinary tract infections. Ultrasonography, cystography, and a renal cortical scan should be considered in children with urinary tract infections.
You May Like: Best Probiotic For Urinary Tract Infection
Does Cranberry Juice Prevent A Uti
Some patients may want to use cranberry or cranberry juice as a home remedy to treat a UTI. Cranberry juice has not been shown to cure an ongoing bacterial infection in the bladder or kidney.
Cranberry has been studied as a preventive maintenance agent for UTIs. Studies are mixed on whether cranberry can really prevent a UTI. Cranberry may work by preventing bacteria from sticking to the inside of the bladder however, it would take a large amount of cranberry juice to prevent bacterial adhesion. More recent research suggests cranberries may have no effect on preventing a UTI
- According to one expert, the active ingredient in cranberries — A-type proanthocyanidins — are effective against UTI-causing bacteria, but is only in highly concentrated cranberry capsules, not in cranberry juice.
- However, cranberry was not proven to prevent recurrent UTIs in several well-controlled studies, as seen in a 2012 meta-analysis of 24 trials published by the Cochrane group.
- While studies are not conclusive, there is no harm in drinking cranberry juice. However, if you develop symptoms, see your doctor. Some people find large quantities of cranberry juice upsetting to the stomach.
Increasing fluid intake like water, avoiding use of spermicides, and urinating after intercourse may be helpful in preventing UTIs, although limited data is available.
Why Antibiotics Sometimes Dont Work
Most UTIs arent serious. But if left untreated, the infection can spread up to the kidneys and bloodstream and become life threatening. Kidney infections can lead to kidney damage and kidney scarring.
Symptoms of a UTI usually improve within 2 to 3 days after starting antibiotic therapy. Many doctors prescribe an antibiotic for at least 3 days.
While this type of medication is the standard treatment, researchers are noticing that antibiotic-resistant bacteria are reducing the effectiveness of some antibiotics in treating UTIs.
Some UTIs dont clear up after antibiotic therapy. When an antibiotic medication doesnt stop the bacteria from causing an infection, the bacteria continue to multiply.
The overuse or misuse of antibiotics is often the reason for antibiotic resistance. This can happen when the same antibiotic is prescribed over and over again for recurrent UTIs. Because of this risk, experts have been looking for ways to treat UTIs without antibiotics.
Some research has shown that UTIs can be treated without traditional antibiotics by targeting E. colis surface component for adhesion, FimH.
Typically, the urinary tract flushes away bacteria when you urinate. But according to researchers, FimH can cause E. coli to firmly attach to the cells in the urinary tract. And because of this tight grip, its hard for the body to naturally flush the bacteria from the urinary tract.
Recommended Reading: How Can I Cure A Urinary Tract Infection
Antibiotics For Urinary Tract Infections
26 December, 2019
Urinary tract infections are relatively common. Women are more affected by them due to the shorter length of their urogenital tract. In fact, its estimated that at least one in five women will suffer from some form of urinary tract infection throughout her life. UTIs occur in any part of the urinary system. This means that they can be located in the bladder, kidneys, ureters, or urethra. However, its estimated that 80% of cases are of infections in the lower urinary tract, or the bladder and urethra.
The most common form of urinary tract infection is cystitis in women and prostatitis in men. In older adults, the incidence of the condition is similar in both sexes. Seasonal or geographical factors dont seem to have any influence on these cases. In this article, well take a closer look at what causes these infections and how antibiotics help treat them.
Causes Of Urinary Tract Infection
There are uncomplicated and complicated UTIs. Uncomplicated is usually caused by the E. coli strain, affecting women more often than men, but are quite easily treated. Cystitis is the alternative name for a bladder infection, which is more often associated with an uncomplicated UTI. Pyelonephritis is when the infection runs through the bloodstream and into kidneys.
A complicated UTI is much more severe and difficult to treat, generally taking several high-dose antibiotics. These complicated infections are often caused by anatomical blockages that prevent the clearing of the infection, catheter usage, dysfunction of the bladder or kidney transplant. Complicated infections can very easily become recurrent because of their difficulty in treatment.
The strains that are most commonly responsible for uncomplicated UTI are E. coli, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Klebsiella, Enterococci, Proteus mirabilis, Ureaplasma urealyticum and Mycoplasma hominis . Organisms responsible for the more severe complicated infections include a severe form of E. coli that spreads to the bloodstream Klebsiella, Proteus mirabilis, and Citrobacter species in patients with anatomical or structural abnormalities in these systems Candida albicans Pseudomonas aeruginosa Enterobacter and Serratia.
Don’t Miss: How To Cure Urinary Retention
Side Effects In Children
Children who take Augmentin can experience the same side effects as adults.
In addition to those side effects, children can experience tooth discoloration. Augmentin use can cause a brown, gray, or yellow staining of childrens teeth. In most cases, brushing or dental cleaning can reduce or remove the discoloration.
The following information describes some of the common uses of Augmentin and Augmentin XR.
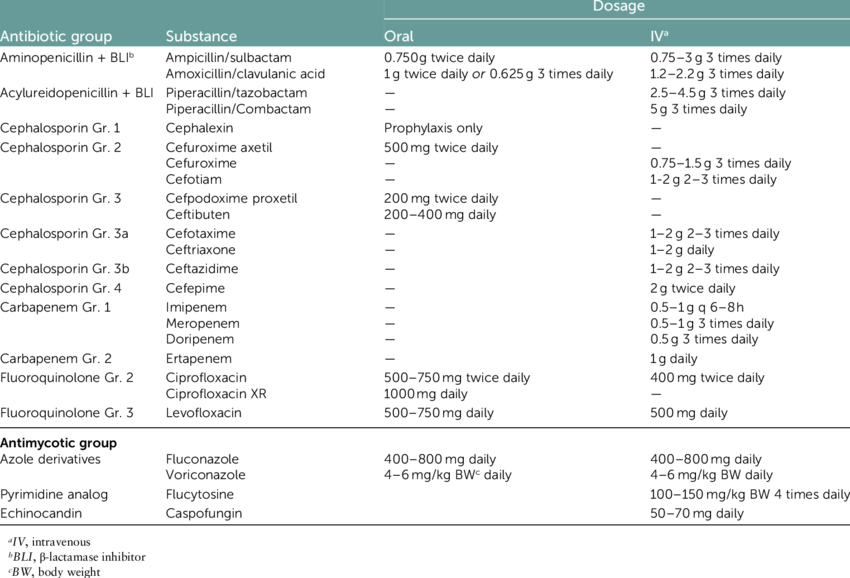
Will I Need An Intravenous Antibiotic For A Uti
If you are pregnant, have a high fever, or cannot keep food and fluids down, your doctor may admit you to the hospital so you can have treatment with intravenous antibiotics for a complicated UTI. You may return home and continue with oral antibiotics when your infection starts to improve.
In areas with fluoroquinolone resistance exceeding 10%, in patients with more severe pyelonephritis, those with a complicated UTI who have allergies to fluoroquinolones, or are unable to tolerate the drug class, intravenous therapy with an agent such as ceftriaxone, or an aminoglycoside, such as gentamicin or tobramycin, may be appropriate. Your ongoing treatment should be based on susceptibility data received from the laboratory.
Read Also: How To Get Rid Of Urinary Incontinence
Search Strategy And Selection Criteria
The study was approved by the ethics institutional review board of the People’s Hospital of Hechi. PubMed, Embase, Medline , and Cochrane library databases up to November 2018 were systematically searched. The following search terms were used: complicated urinary tract infection, cUTI, carbapenem, imipenem, meropenem, biapenem, ertapenem, doripenem, faropenem, panipenem, razupenem, tebipenem, tomopenem, and sanfetrinem. No language restriction was imposed. We included articles regardless of the language of publication and conference abstracts. The reference lists of all retrieved articles were also reviewed to identify additional articles missed by using these search terms. The authors approved all enrolment studies.
What To Expect At Home
UTIs can lead to infection. Most often the infection occurs in the bladder itself. At times, the infection can spread to the kidneys.
Common symptoms include:
- Pain or burning when you urinate
- Needing to urinate more often
- Hard to empty your bladder all the way
- Strong need to empty your bladder
These symptoms should improve soon after you begin taking antibiotics.
If you are feeling ill, have a low-grade fever, or some pain in your lower back, these symptoms will take 1 to 2 days to improve, and up to 1 week to go away completely.
Recommended Reading: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Urinary
Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
If you are a healthy adult man or a woman who is not pregnant, a few days of antibiotic pills will usually cure your urinary tract infection. If you are pregnant, your doctor will prescribe a medicine that is safe for you and the baby. Usually, symptoms of the infection go away 1 to 2 days after you start taking the medicine. Its important that you follow your doctors instructions for taking the medicine, even if you start to feel better. Skipping pills could make the treatment less effective.
Your doctor may also suggest a medicine to numb your urinary tract and make you feel better while the antibiotic starts to work. The medicine makes your urine turn bright orange, so dont be alarmed by the color when you urinate.
Also Check: Natural Remedy For Wisdom Tooth Infection
Are There Natural At
Yes. While taking antibiotics is still considered the gold standard of UTI treatments, there are some things you can do at home that help relieve symptoms, as well. These include:
- Drink plenty of water. Consuming at least six to eight 8-ounce glasses of water daily can help flush away UTI-causing bacteria, setting you up for a quicker recovery. Plus, the more you drink, the more youll have to urinate.
- Urinate often. Each time you empty your bladder, youre helping to flush bacteria out of your system.
- Try heat. Applying a heating pad to your pubic area for 15 minutes at a time can help soothe the pressure and pain caused by UTI-related inflammation and irritation.
- Tweak your wardrobe. Wearing loose cotton clothing and underwear can help you recover from a UTI.
- Go fragrance-free. Make sure your personal hygiene products are fragrance-free to sidestep further irritation, notes the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
- Cut out certain irritants. Caffeine, alcohol, spicy food, raw onions, citrus fruits, carbonated drinks, artificial sweeteners, and nicotine can further irritate your bladder, making it more difficult for your body to heal, per the Cleveland Clinic.
RELATED: 8 Home Remedies for Urinary Tract Infections Symptoms
Don’t Miss: Why Do Men Get Urinary Tract Infections
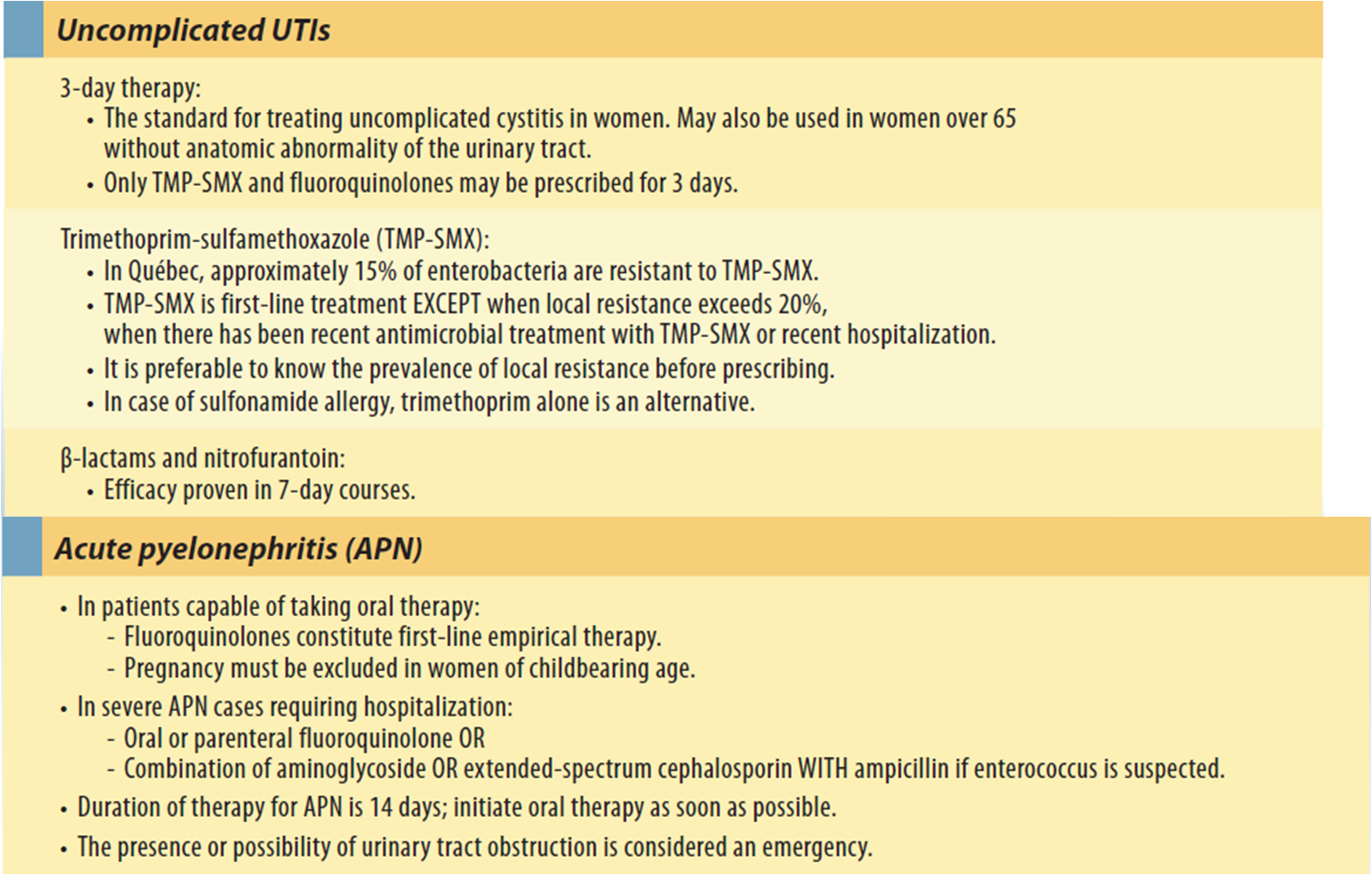
First Line Antibiotics For A Uti
- Ampicillin
- Nitrofurantoin
- Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
Notably absent from the list of antibiotics prescribed for the treatment of UTIs is Amoxicillin. While very popular and useful in treating numerous other bacterial infections, urinary tract infections are not amongst the infections Amoxicillin is used for.
Risk Of Bias Assessment
Three reviewers independently evaluated the methodological quality of identified studies. The risk of bias tool referred to the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.3.0 was used to assess methodological quality. In terms of the assessment criteria, each study was rated and assigned one of the 3 following risk of bias: low: if all quality criteria were adequately met, the study was deemed to have a low risk of bias unclear: if one or more of the quality criteria was only partially met or was unclear, the study was deemed to have a moderate risk of bias or high: if one or more of the criteria was not met, or not included, the study was deemed to have a high risk of bias.
Recommended Reading: Urinary Tract Infection Pills Cvs
Treating Uti With Antibiotics
1. Beta-Lactams
The antibiotics that belong to the beta-lactam group are very similar to penicillins and cephalosporins in their chemical composition. In fact, they also share some chemical features with other recently introduced antibiotics as well. Hence, they are a popular choice for treating urinary tract infection. Another beta lactam antibiotic is pivmecillinam that is very similar to mecillinam. This antibiotic is very commonly used in European countries for the treatment of UTI.
2. Penicillin
A very popular antibiotic belonging to the penicillin group is Amoxicillin. This antibiotic is widely used in the treatment of bacterial skin infections such as acne. However, amoxicillin was also prescribed for the treatment of UTI until a few years ago. The standard procedure of treating UTI was taking amoxicillin for 10 days. But now the E. coli have become resistant to the medication and in almost 25% cases the antibiotic doesnt work.
Another form of penicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate or Augmentin is being used these days for treating urinary tract infection in adults as well as in children. Augmentin is generally given for treating bacterial infections that have do not respond to other antibiotic treatments. However, this medication only works if the urinary tract infection is the result of rapid multiplication of Gram-positive bacteria such as those belonging to the Enterococcus and S. saprophyticus classes.
3. Cephalosporins
4. TMP-SMX
5. Fluoroquinolones
What Oral Antibiotics Are Used To Treat An Uncomplicated Uti In Women
The following oral antibiotics are commonly used to treat most uncomplicated UTI infections :
Your doctor will choose your antibiotic based on your history, type of UTI, local resistance patterns, and cost considerations. First-line options are usually selected from nitrofurantoin, fosfomycin and sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim. Amoxicillin/clavulanate and certain cephalosporins, for example cefpodoxime, cefdinir, or cefaclor may be appropriate options when first-line options cannot be used.
Length of treatment for cystitis can range from a single, one-time dose, to a course of medication over 5 to 7 days. Kidney infections may require injectable treatment, hospitalization, as well as a longer course of antibiotic, depending upon severity of the infection.
Sometimes a UTI can be self-limiting in women, meaning that the body can fight the infection without antibiotics however, most uncomplicated UTI cases can be treated quickly with a short course of oral antibiotics. Never use an antibiotic that has been prescribed for someone else.
In men with symptoms that do not suggest a complicated UTI, treatment can be the same as women. In men with complicated UTIs and/or symptoms of prostatitis are not present, men can be treated for 7 days with a fluoroquinolone . Tailor therapy once urine cultures are available.
You May Like: How Does A Urinary Tract Infection Feel
Understanding Drug Pharmacokinetics And Pharmacodynamics Is Essential When Determining The Most Effective Antibiotic Therapy For Utis In Dogs And Cats
Dr. Foster is an internist and Director of the Extracorporeal Therapies Service at Friendship Hospital for Animals in Washington, D.C. He has lectured around the world on various renal and urinary diseases and authored numerous manuscripts and book chapters on these topics. He is the current president of the American Society of Veterinary Nephrology and Urology.
Urinary tract infections are common in small animal practice it has been reported that up to 27% of dogs will develop infection at some time in their lives.1
Most UTIs are successfully treated with commonly used drugs, dosages, and administration intervals. However, infections can be challenging to effectively treat when they involve the kidneys and prostate . In addition, it can be difficult to create an appropriate antibiotic prescription in patients with kidney disease due to reduced drug clearance.
Understanding drug pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics is essential when determining the most effective antibiotic therapy. In addition, successful antimicrobial therapy requires appropriate choice of antibiotic, including dose, frequency, and duration .
What Are Possible Side Effects Of Macrobid
Macrobid may cause serious side effects, including:
- skin rash, bruising, severe tingling, numbness, pain, muscle weakness
- agitation, confusion, unusual thoughts or behavior, seizures
- nausea, upper stomach pain, itching, loss of appetite, clay-colored stools, jaundice or
- severe skin reaction — fever, sore throat, swelling in your face or tongue, burning in your eyes, skin pain, followed by a red or purple skin rash that spreads and causes blistering and peeling.
Don’t Miss: Why Do I Have Urinary Incontinence
Monitoring Response To Therapy
Patients with a simple, uncomplicated UTI may not require rigorous monitoring. However, patients with complicated, relapsing, or recurrent infections should be monitored very closely. The following protocol is recommended to monitor response to therapy in patients with relapsing, recurrent, or refractory UTI.3