What Are Urinary Antispasmodics
Urinary antispasmodics are the name given to a group of medicines that block the effects of acetylcholine and inhibit involuntary detrusor muscle contractions. The detrusor muscle is found in the wall of the bladder. Urinary antispasmodics are used to treat symptoms of urge incontinence and overactive bladder.
Acetylcholine is the main neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system . The parasympathetic nervous system regulates various organ and gland functions at rest, including digestion, defecation, lacrimation, salivation, and urination.
Acetylcholine acts on two types of receptors nicotinic and muscarinic cholinergic receptors. Some urinary antispasmodics are non-selective, which means they bind to both nicotinic and muscarinic receptors. Others selectively block M3 . Selective antispasmodics cause less drowsiness than non-selective antispasmodics but may cause more constipation, dry mouth, and blurred vision.
Current Therapies For Stress Urinary Incontinence
There are a variety of therapies for SUI, including conservative measures involving physical therapy , bladder retraining, anti-incontinence devices , and a combination of these strategies. These conservative therapies often fail or are unsatisfactory options for patients with more severe SUI. Periurethral bulking agents, retropubic suspension procedures, and various transvaginal anti-incontinence procedures are more invasive options.
The one type of treatment of SUI that has been sufficiently devoid of novel strategies is pharmacologic therapies that increase urethral resistance. Although several medications have been used to treat SUI, none is FDA-approved and none is very successful. Once patients have completed a full evaluation, initial treatment often consists of behavioral modification, followed by surgical therapies. The concept of pharmacologic therapy as a first-line therapy for SUI is presented in this paper, along with the possibility of synergy between pharmacologic therapy and current conservative measures to help improve our current treatment strategies for SUI.
Incontinence And Alzheimers Disease
People in the later stages of Alzheimers disease often have problems with urinary incontinence. This can be a result of not realizing they need to urinate, forgetting to go to the bathroom, or not being able to find the toilet. To minimize the chance of accidents, the caregiver can:
- Avoid giving drinks like caffeinated coffee, tea, and sodas, which may increase urination. But dont limit water.
- Keep pathways clear and the bathroom clutter-free, with a light on at all times.
- Make sure you provide regular bathroom breaks.
- Supply underwear that is easy to get on and off.
- Use absorbent underclothes for trips away from home.
For more ways to deal with incontinence and other common medical problems in someone with Alzheimers, visit Alzheimers Disease: Common Medical Problems.
You May Like: Magnetic Therapy For Urinary Incontinence
Drug Increasing Bladder Capacity To Hold Urine
Two medications, in the beta-three adrenergic agonist class of drugs, have been studied in women with urgency incontinence. These medications work by improving the bladder’s capacity to hold urine and therefore increase the time between “urgent” trips to the toilet.
Mirabegron and solabegron are newer drugs and have been designed to resolve urgency urinary incontinence without causing bothersome harms. However, fewer clinical studies have examined these drugs. Future research will help us to know more about the long-term safety of mirabegron and solabegron.
Medicine For Stress Incontinence

If stress incontinence does not significantly improve with lifestyle changes or exercises, surgery will usually be recommended as the next step.
However, if you’re unsuitable for surgery or want to avoid an operation, you may benefit from an antidepressant medicine called duloxetine. This can help increase the muscle tone of the urethra, to help keep it closed.
You’ll need to take duloxetine tablets twice a day and will be assessed after 2 to 4 weeks to see if the medicine is beneficial or causing any side effects.
Possible side effects of duloxetine can include:
- nausea
- constipation
Do not suddenly stop taking duloxetine, as this can also cause unpleasant side effects. A GP will reduce your dose gradually.
Duloxetine is not suitable for everyone, however, so a GP will discuss any other medical conditions you have to determine if you can take it.
You May Like: Help For Female Urinary Incontinence
What The Experts Say
Incontinence is never normal at any age. Women especially should not accept this as part of their lives. We dont want people to miss the opportunity to get this addressed. There are some very good non-medication, non-surgical approaches to incontinence,Catherine DuBeau, M.D., a specialist in general internal medicine at the Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center
Beta Agonists For Bladder Problems
This class of medication, mirabegron , works by relaxing the bladder muscle during the storage phase, thus increasing the capacity of bladder to hold more urine. They can be used for the treatment of overactive bladder . Mirabegron is the first drug in this category.
- How beta-agonist drugs work: They work by relaxing the bladder muscles and reducing bladder overactivity.
- Who should not use this medication: Individuals with the following conditions should not use mirabegron or a similar class of drugs:
- Allergy to this drug
- Advanced kidney disease
Also Check: Azo Urinary Pain Relief Maximum Strength Tablets
Who Cannot Take Medicines For Urinary Urgency And Incontinence
In general, most people are able to take these medicines however, there are some people who are unable to take these medicines.
Duloxetine should not be taken by people who have severe kidney or liver problems, uncontrolled high blood pressure, or are taking certain medicines – for example, antidepressants called monoamine-oxidase inhibitors.
Antimuscarinics should not be taken by people with:
- Myasthenia gravis. This is a condition where muscles become easily tired and weak.
- Severe bladder problems or urinary retention .
- Severe inflammation of the gut .
- Blockage of the gut.
- A condition of the eye, known as uncontrolled angle-closure glaucoma.
For a full list of people who cannot take these medicines, see the leaflet that came with your medicines.
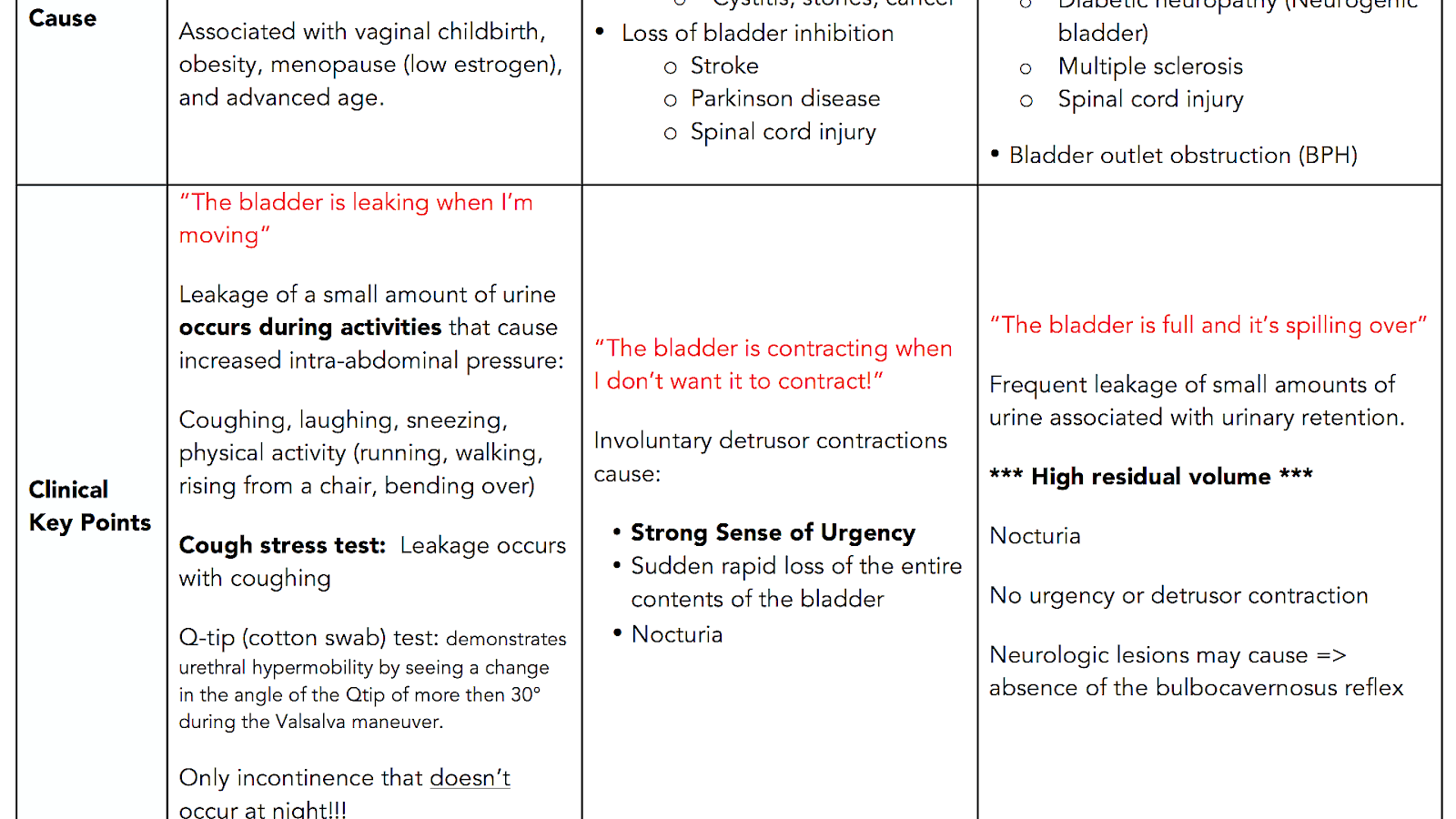
What Is Urinary Incontinence
Many people experience involuntary leakage of urine from the bladder. This condition is called urinary incontinence. It affects nearly a quarter to a third of men and women in the United States. That is millions of Americans.
Urinary incontinence is the leaking of urine from the bladder that you cant control. There are different kinds of urinary incontinence, and not all types are permanent. An experienced doctor can help you find the best treatment for your urinary incontinence.
Stress urinary incontinence is when the muscles arent strong enough to hold urine in the body. SUI shows itself through physical symptoms, including involuntary leaking of urine through the bladder when active.
Overactive bladder is a strong sudden urge to urinate, which may or may not cause urine to leak from the bladder.
In some cases, people experience a combination of both SUI and OAB. This shows itself through physical symptoms. If this is the case for you, you will find involuntary leaking of urine through the bladder and strong sudden urges to urinate that you cant control.
Overflow incontinence is when the bladder isnt able to empty itself completely. Overflow incontinence shows itself through physical symptoms, including constant dribbling of small amounts of urine when the bladder is full.
These symptoms are not just physical. Urinary incontinence has emotional and psychological effects, too.
Don’t Miss: Burning Sensation In Urinary Tract
Drugs Stopping Sudden Bladder Muscle Contractions
Six approved antimuscarinic drugs work because they block nerve signals regulating bladder muscle contractions the drugs help to relax the bladder muscle and to decrease urges to void. Several studies have shown that these drugs resolve urinary incontinence in one woman among every eight or nine treated . These drugs include:
- Darifenacin ,
However, these drugs, especially oxybutynin, may cause adverse effects which may include:
For oxybutynin, one out of every 16 women stopped using it because of intolerable side effects.
When researchers compared the benefits and harms across these six different antimuscarinic drugs, they found that although these drugs demonstrate similar benefits, the potential for adverse effects was not the same . Women should discuss with their doctor what adverse effects are the most troubling for them. They can then choose the medication with the least risk for those specific side effects.
Unfortunately, none of the clinical studies evaluated the long-term safety of these antimuscarinic drugs. All drugs were tested in older women . However, we do not know long-term safety of these drugs in real-life geriatric settings. Future research should look at long-term safety in older women who are also taking several medications because of other chronic diseases.
Who Suffers From Stress Incontinence
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases , women are twice as likely as men to suffer from involuntary leakage. The most common causes of stress incontinence among women are pregnancy and childbirth, especially having multiple vaginal deliveries. During pregnancy and childbirth, the sphincter and pelvic muscles stretch out and are weakened.
Older age and conditions that cause a chronic cough can also cause stress incontinence. This condition can also be a side effect of pelvic surgery.
Some women only suffer from stress incontinence during the week before they get their period. The NIDDK explains that estrogen drops during this phase of the menstrual cycle, which can weaken the urethra. This is not common though.
Among men, prostate surgery is a common cause of stress incontinence. The prostate gland surrounds the male urethra, and its removal can result in the loss of support of the urethra.
Other risk factors for stress incontinence include:
- smoking due to chronic cough
- any other condition associated with chronic cough
- excessive caffeine and alcohol use
- obesity
Treatment for stress incontinence varies according to the underlying cause of your problem. Your doctor will help you come up with a treatment plan using a combination of medications and lifestyle adjustments.
Recommended Reading: Purina One Urinary Tract Reviews
Disposable Absorbent Underwear Are The Best Products For Heavy Leaks
Adult diapers, in the form of open briefs with tabs or underwear-like pull-up pants, are an excellent solution if you need more absorbency. There are products made to fit any body size and type of incontinence level and can be worn under clothes with minimal bulging.
They use the same technology as baby diapers, including superabsorbent polymers that can absorb liquid many times their weight. They also have an absorbent core along with an acquisition and distribution layer, which immediately absorbs urine and locks it away from your skin.
Made for Living is a premium brand of disposable pull-up style absorbent underwear available in four sizes and two absorbency levels:
- Maximum: These are thinner disposable underwear and are made for active users and have an extra soft cloth-like cover
- Ultimate: This is an overnight urinary incontinence product made with extra absorption, a soft, cloth-like cover, and can also be used during the daytime.
Botox Injection For Bladder Problems
Botox injection has recently been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of overactive bladder for patients who have failed to respond to standard therapy with anticholinergic medications.
Overactive bladder is a type of urinary incontinence caused by overactivity of the muscles in the bladder, causing frequent squeezing of the bladder and, thus, frequent urge to urinate. Botox can be injected into the bladder directly through a cystoscope .
Common side effects of Botox injection may include incomplete emptying, urinary tract infection, and painful urination.
Don’t Miss: What Meds Treat Urinary Tract Infection
What Is The Evidence For Effective Treatments For Urinary Incontinence
Women have several options to manage their urinary incontinence and these primarily include either drug or non-drug treatments. Many studies have shown that the majority of women improve their symptoms using non-drug conservative interventions and these include:
Intra-vaginal electrical or magnetic stimulation may help some women with incontinence . However, some women do not benefit from these non-drug treatments, or they are unable to access these treatments, or make the necessary lifestyle changes. In this case, doctors may suggest the use of drugs to help with incontinence problems. We review the current scientific evidence about the effectiveness of these drugs to help manage incontinence.
How Is The Sling Procedure Performed
Before the procedure begins, you are placed under either general or spinal anesthesia. With general anesthesia, you will remain asleep throughout the procedure and will feel no pain. With spinal anesthesia, you are completely awake except that the area of your body from the waist down is numb and you dont feel pain as the procedure is performed. Following application of anesthesia, the urologist places a tube into your bladder to drain any urine already inside it.
The surgeon then proceeds to place the sling in any of the following ways:
1. Retropubic Method : The surgeon makes a tiny incision inside your vagina, just under the urethra. Two other cuts are then made above your pubic bone large enough to allow needles through. The surgeon uses a needle to place the sling beneath the urethra and behind the pubic bone. Using stitches or skin glue that is easily absorbed by the body, the surgeon closes off the cuts.
2. Single-Incision Mini Method: The surgeon makes a single tiny incision in the vagina, then passes the sling through it. No stitches are used to attach the sling, but over time the scar tissue grows and forms around it, keeping it in place.
3. Transobturator Method: The surgeon makes a tiny cut inside the vagina, just under the urethra. Two more cuts are made, one on each side of the labia . Using the incisions, the surgeon inserts the sling under the urethra.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get An E Coli Urinary Tract Infection
Targeting Both The 1 Receptors And The 5
There are several possible methods of increasing the effects of serotonin and norepinephrine on the storage mechanisms of the lower urinary tract. One method is to block the reuptake of these neurotransmitters at the nerve terminals, thereby increasing receptor stimulation . Duloxetine and venlafaxine are two such drugs that block both serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake.
Monoaminergic synapse, illustrating monoamine reuptake from the synaptic cleft and monamine reuptake inhibition.
Read Also: Urinary Tract Infection What Is It
Where To Go For Urinary Incontinence Treatment
For urinary incontinence treatment, start with your primary care doctor. Tell them you are having problems with bladder control. If your primary care doctor is unable to help, ask for a referral to a specialist. Doctors who specialize in treating urinary incontinence include urogynecologists, gynecologists with extra training in urinary incontinence, or urologists, doctors who specialize in problems of the urinary tract system in men and women.
Also Check: What Can You Do For Urinary Incontinence
What To Expect At Your Doctor’s Office
Your doctor will give you a physical examination and ask questions about:
- Any past prostate problems
- When your urine leakage occurs
- Whether you strain or have discomfort when urinating
You may be asked to cough vigorously to see if it causes urine loss. This is a sign of stress incontinence.
Your doctor may suggest urine tests to find:
- Infection
Your doctor may order a pelvic ultrasound to look at your bladder, kidneys, and urethra.
Medications For Overactive Bladder
Drugs used to treat OAB block the abnormal contractions of the bladder muscle and can therefore also help ease the symptoms of urge urinary incontinence in both men and women. Youll find a list of OAB medications available in Canada on page 20. Generally speaking, these drugs fall into three categories:
Anticholinergics
Anticholinergic medications block the action of acetylcholine, a chemical messenger that tells the muscles of the bladder wall to contract. Unfortunately, acetylcholine acts in other parts of the body as well, so medications that block it can cause unwanted side effects like dry mouth, blurred vision, impaired cognition and constipation. New extended or prolonged release versions of anticholinergic medications reduce the incidence of side effects and improve compliance because they only need to be taken once a day to produce a steady absorption rate and constant blood levels of the drug.
Read Also: Hill’s Urinary Hairball Control
Why Is Urinary Incontinence A Health Issue
Urinary incontinence is a very common problem in aging women . When women leak urine during exercise, sneezing, or coughing, doctors call this type of incontinence stress-related . When women have strong urges to urinate and have trouble holding urine until getting to the bathroom, they may have what is known as urgency incontinence . Although most women have one or the other type of incontinence, older women often have both types. Incontinence hurts women’s self-confidence, interferes with their ability to enjoy their favorite activities, and decreases the quality of their lives .
What Are The Types Of Urinary Incontinence

More than half of people with stress incontinence also have urge incontinence. Having both stress and urge incontinence is known as mixed incontinence. An overactive bladder causes urge incontinence. This type of urinary incontinence causes you to leak urine when you feel an urgent need to pee.
Overflow incontinence is a different type of urinary incontinence. It causes you to leak urine because your bladder is too full or you cant completely empty it.
You May Like: Is Azithromycin Good For Urinary Tract Infection
Don’t Miss: How To Improve Urinary Health