Symptoms Of Kidney Disease
Kidney disease is called a silent disease as there are often no warning signs. People may lose up to 90 per cent of their kidney function before getting any symptoms. The first signs of kidney disease may be general and can include:
- high blood pressure
- changes in the amount and number of times urine is passed
- changes in the appearance of urine
- blood in the urine
- puffiness of the legs and ankles
- pain in the kidney area
- tiredness
- have a family history of kidney failure
- have a history of acute kidney injury
- are of Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander origin.
How Are Kidney Infections Treated
A physician will treat the disease based on his or her examination. He or she may start the patient on the standard treatment of a course of antibiotics before the lab tests results are available. The medication may change once the exact strain of bacteria is revealed by the lab tests.
If the treatment is effective, the patient should feel better in two to three days. If not, your healthcare provider will start looking for additional problems. Most antibiotic treatments last for 14 days and it is essential that patients take the pills as recommended for the full 14 days even though symptoms may disappear after a few days. The disappearance of symptoms does not mean all bacteria are killed. Some may remain and the infection may reappear.
There is also a concern that those bacteria that remain may develop resistance to the medication. For some reason the disease is more difficult to treat in men and they may have to take medication for up to six weeks. Patients with severe illness, those that have significant nausea and vomiting, high fevers, significant pain and signs of dehydration may be hospitalized for a few days while the antibiotics are administered intravenously. Urine samples are taken after about six weeks of treatment and examined to insure the bacterial infection is eradicated.
Risks Of Uti And Comorbidities
Apart from the impaired immune defence associated with CKD, the risk for developing UTI also depends on the underlying kidney disease. High-risk groups are patients suffering from diabetic nephropathy, nephrotic syndrome, and hypoproteinaemia, patients with analgesic nephropathy, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, Randall plaques , and renal stone formers. Among them, one may also find those with congenital errors of the metabolism: cystinosis, oxalosis, chloride channel mutations, Fabrys disease, Dents disease, Bartter syndromes , renal tubular acidosis, idiopathic hypercalciuria, hypocitraturia, familiar hypomagnesiaemia, nephrolithiasis, genetic defects of the calcium-sensing receptor, etc. Obstructive nephropathy associated with an increased risk for UTI may arise from papillary necrosis and/or exfoliation of tissue debris into the tubular lumen, most commonly in ischaemia as well as diabetic and analgesic nephropathy. A variety of primary kidney diseases , membranous GN, focal sclerosing glomerulopathy) are treated with immunosuppressive agents. Early diagnosis of UTI may be missed easily in those patients with no or only minor clinical symptoms. In a similar manner, CKD patients suffering from systemic vasculitis, autoimmune disease, and renal allograft dysfunction should be closely monitored for UTI. Typical signs of an infection are often completely missing in these cases.
Read Also: Can Smoking Weed Cause Urinary Problems
How Are Kidney Infections Diagnosed
Two common laboratory tests are performed to diagnose kidney infections . A urine sample is examined under a microscope to determine if white and/or red blood cells are present. The urine is also sent to the lab to see if bacteria grow in a urine culture. If a person is very sick, blood cultures may also be sent. The strain of bacteria that are cultured will determine the type of therapy used in your treatment.
Pyelonephritis can often be treated without X-ray studies, unless your doctor suspects there may be an addition problem. CT scans produce images of structures and organs and these scans are usually done without contrast . A renal ultrasound may sometimes suffice for evaluation.
What Conditions Are Related To Recurrent Utis
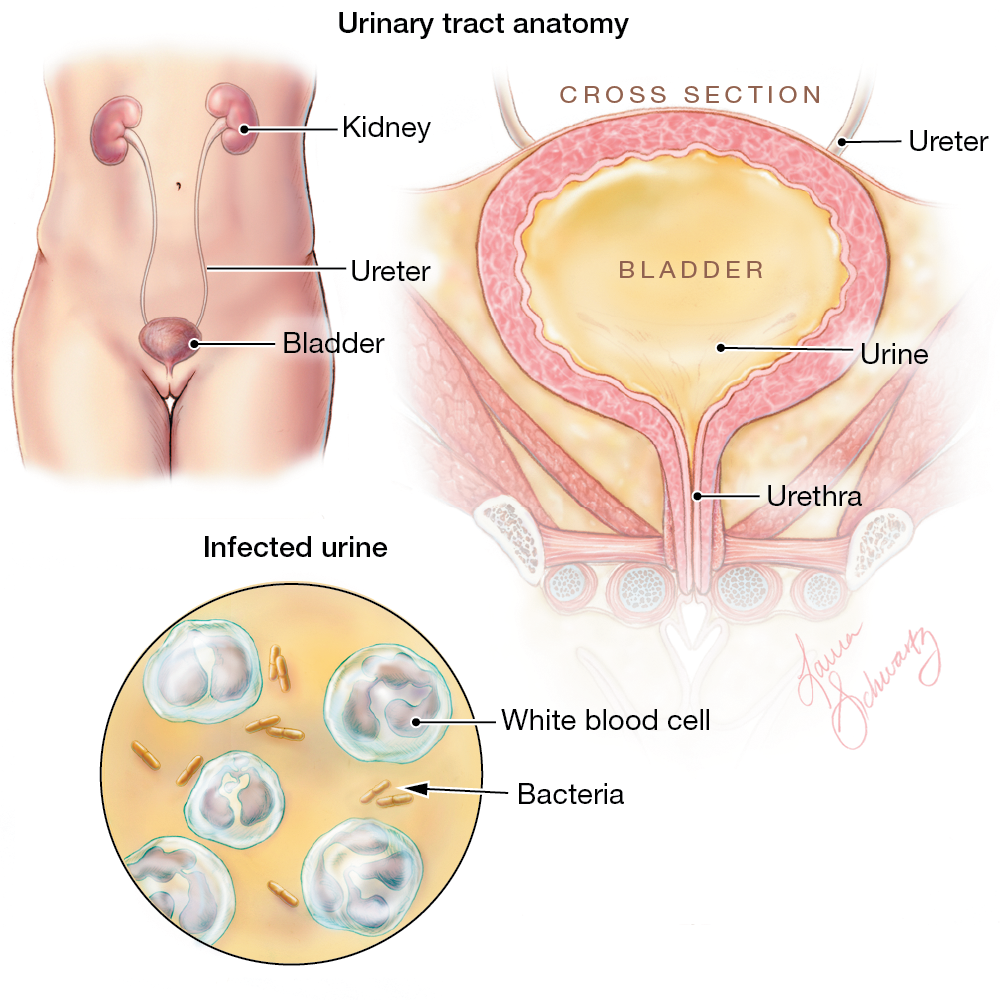
Recurrent UTIs sometimes happen along with other conditions, such as:
- vesicoureteral reflux , which is found in 30%50% of kids diagnosed with a UTI. In this congenital condition, pee flows backward from the bladder to the ureters. Ureters are thin, tube-like structures that carry pee from the kidney to the bladder. Sometimes the pee backs up to the kidneys. If it’s infected with bacteria, it can lead to pyelonephritis.
- hydronephrosis, which is an enlargement of one or both kidneys due to backup or blockage of urine flow. It’s usually caused by severe VUR or a blocked ureter. Some kids with hydronephrosis might need to take daily low doses of antibiotics to prevent UTIs until the condition producing hydronephrosis gets better or is fixed through surgery.
But not all cases of recurrent UTIs can be traced back to these body structure-related problems. For example, dysfunctional voiding when a child doesn’t relax the muscles properly while peeing is a common cause of UTIs. Not peeing often enough also can also increase a child’s risk for recurrent infections. Both dysfunctional voiding and infrequent urination can be associated with constipation.
Rarely, unrelated conditions that harm the body’s natural defenses, such as diseases of the immune system, also can lead to recurrent UTIs. Use of a nonsterile urinary catheter can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract and also cause an infection.
Recommended Reading: Physical Therapy For Urinary Incontinence
How Is Pyelonephritis Treated
Dogs with pyelonephritis are usually treated as outpatients unless they have bacteria circulating in their blood causing , or they have clinical signs of kidney failure. The specific treatment of pyelonephritis depends on the underlying cause. If dogs with pyelonephritis also have kidney disease, part of their treatment will include a kidney support nutritional profile .
Ectopic ureters are repositioned surgically to properly drain urine into the bladder. Blockage of the upper urinary tract by a urinary tract stone in a dog with bacterial infection/inflammation of the kidneys may rapidly progress to generalized disease and septicemia. This is a medical emergency and is most often treated with surgery.
Antibiotics to treat pyelonephritis are chosen based on testing the urine for bacteria and antibiotic sensitivity. The chosen antibiotic should kill bacteria, be present at appropriate levels in the blood and in the urine, and should not be toxic to the kidneys. Antibiotics are generally given for 4-6 weeks to treat pyelonephritis.
What Is The Outlook For Kidney Infections
With treatment, the outlook for kidney infections is very positive. It is vital that you take all of any prescribed medications for the infection. You may begin feeling better shortly after beginning a treatment, but still need to take the entire prescribed treatment.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 05/22/2019.
References
- National Kidney Foundation. Urinary Tract Infections Accessed 5/23/19.
- National Institute of Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases . Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection Accessed 5/23/19.
Don’t Miss: What Can Cause Urinary Frequency
Duration Of Antimicrobial Therapy
There are no valid published data from randomized trials determining the optimal duration of treatment of UTI in patients with CKD and in dialysis patients. It is customary to treat even uncomplicated cystitis for at least 7 days and to continue for 21 days or more, depending on clinical severity , . However, the response to even longer courses of antibiotics in higher dosage may only be transitory. Even if the urinary concentration of the antibiotic is adequate, the underlying infection may not be eradicated, thus leading to a relapse after the end of antimicrobial treatment.
Recurrent UTI presumably occur due to bacterial regrowth from colonies of non-planktonic bacteria residing in a protected biofilm environment. Persistent microbial niches may develop and colonize deeply within damaged renal parenchymal or urothelial tissue. Furthermore, antibiotic therapy may select highly resistant intracellular, ecologically stable bacterial communities living temporarily as commensals, so-called small colony variants .
Importantly, recent studies have confirmed again that any infection irrespective of severity is an independent risk factor for increased adverse events in the CKD population .
Complications Related To Kidney Infection:
Most cases of kidney infections come to a complete cure. However, if left untreated, it can lead to life-threatening complications that include:
- Permanent kidney damage which lead to chronic kidney disease and kidney failure.
- Spread of infection through the blood stream which leads to life threatening condition called sepsis.
Recommended Reading: Hill’s Urinary Hairball Control
Kidney Infection Risk Factors
Anyone can get a kidney infection. But just as women get more bladder infections than men, they also get more kidney infections.
A womanâs urethra is shorter than a manâs, and itâs closer to their vagina and anus. That means itâs easier for bacteria or viruses to get into a womanâs urethra, and once they do, itâs a shorter trip to the bladder. From there, they can spread to the kidneys.
Pregnant women are even more likely to get bladder infections. This is because of hormone changes and because a baby puts pressure on the motherâs bladder and ureters and slows the flow of urine.
Any problem in your urinary tract that keeps pee from flowing as it should can raise your chances of a kidney infection, such as:
- A blockage in your urinary tract, like a kidney stone or enlarged prostate
- Conditions that keep your bladder from completely emptying
- A problem in the structure of your urinary tract, like a pinched urethra
- Vesicoureteral reflux , which is when pee flows backward from your bladder toward your kidneys
Youâre also more likely to get an infection if you have:
- A weakened immune system, as with type 2 diabetes
What Are The Symptoms Of A Kidney Infection
First, kidney infection starts with symptoms of lower urinary tract infection such as discomfort with urination and frequent urination. However, once the infection has travelled up to the kidneys, you will start to experience more severe symptoms such as:
- Fever and chills
- Frequent urination and pain during urination
- Blood or pus with urine
- Children younger than 2 years old may only have a high fever without other symptoms
- Older people may not have any symptoms related to the kidneys instead, they may exhibit confusion, disordered speech, or hallucinations.
Also Check: Mckesson Disposable Urinary Leg Bag
How Is A Kidney Infection Diagnosed
If your physician suspect kidney infection based upon medical history and physical examination, you may be asked to do the following tests:
- General urine test and urine culture to identify the bacteria in the urine
- Blood culture
- Imaging, such as Ultrasound and CT scan, may be necessary to diagnose any blockage or birth defects in the urinary tract thats leading to repeated kidney infection.
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Utis
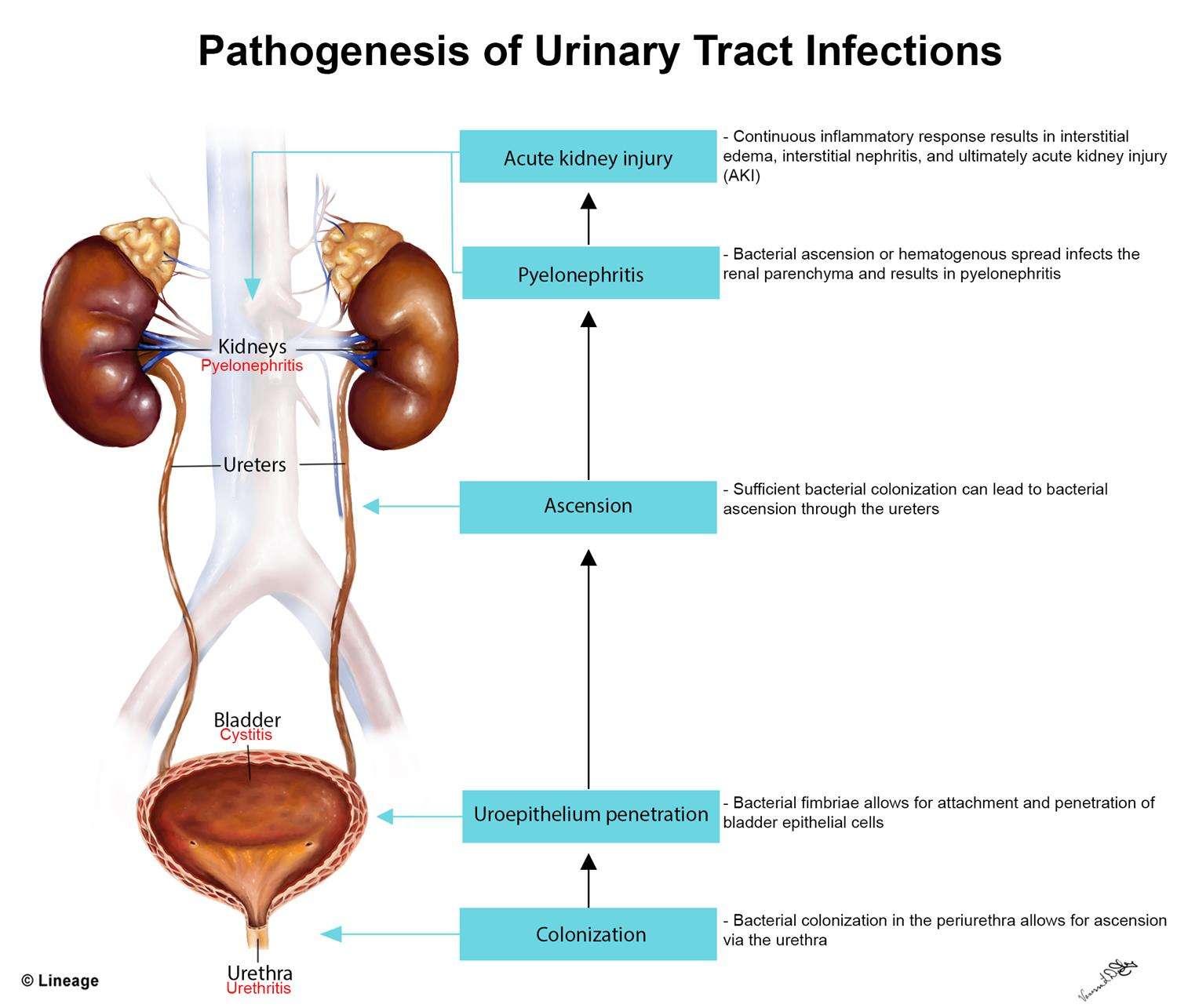
Symptoms of a UTI can include:
- pain when peeing
- changes in how often a child needs to pee
- changes in the look or smell of pee
- fever
- lower belly pain
- lower back pain or discomfort
UTIs also can cause kids to wet their pants or the bed, even if they haven’t had these problems before. Infants and very young children may only show nonspecific signs, such as fever, vomiting, or decreased appetite or activity.
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Urinary Retention Naturally
Kidney Infection Home Remedies
You can do some things at home to feel better while you have an infection:
- Drink plenty of fluids to flush out germs.
- Get extra rest.
- When you go to the bathroom, sit on the toilet instead of squatting over it, which can keep your bladder from completely emptying.
- Take a pain reliever with acetaminophen. Donât use aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen because these can raise your risk of kidney problems.
- Use a heating pad on your belly, back, or side.
Prevention And Treatment Of Kidney Infection
-
Antibiotics
-
Occasionally surgery
Antibiotics are started as soon as the doctor suspects pyelonephritis and samples have been taken for laboratory tests. The choice of drug or its dosage may be modified based on the laboratory test results , how sick the person is, and whether the infection started in the hospital, where bacteria tend to be more resistant to antibiotics. Other factors that can alter the choice or dosage of drug include whether the person’s immune system is impaired and whether the person has a urinary tract abnormality , including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Blockage can be complete… read more ).
Outpatient treatment with antibiotics given by mouth is usually successful if the person has:
-
No nausea or vomiting
-
No signs of dehydration
You May Like: Purina Pro Plan Urinary Ox St
When Should I Call The Doctor
As soon as you think that your child has a UTI, call your doctor. The doctor may recommend another urine test after treatment to be sure that the infection has cleared.
If your child has from recurrent UTIs, consult a pediatric urologist, who can do a thorough evaluation and order tests for urinary system abnormalities. In the meantime, follow your doctor’s instructions for treating a UTI.
What If The Infection Does Not Clear Up With Treatment
Most infections clear up with treatment. However, if an infection does not clear up, or if you have repeated infections, you may be given some special tests such as:
-
a type of x-ray called an intravenous pyleogram , which involves injecting a dye into a vein and taking pictures of your kidney and bladder
-
an ultrasound exam, which gives a picture of your kidneys and bladder using sound waves
-
a cytoscopic exam, which uses a hollow tube with special lenses to look inside the bladder.
Also Check: Homeopathic Medicine For Urinary Tract Infection
Diagnosis Of Kidney Infection
Imaging tests Imaging Tests of the Urinary Tract There are a variety of tests that can be used in the evaluation of a suspected kidney or urinary tract disorder. X-rays are usually not helpful in evaluating… read more are done in people who have intense back pain typical of renal colic, in those who do not respond to antibiotic treatment within 72 hours, in those whose symptoms return shortly after antibiotic treatment is finished, in those with long-standing or recurring pyelonephritis, in those whose blood test results indicate kidney damage, and in men . Ultrasonography or helical computed tomography studies done in these situations may reveal kidney stones, Stones in the Urinary Tract Stones are hard masses that form in the urinary tract and may cause pain, bleeding, or an infection or block of the flow of urine. Tiny stones may cause no symptoms, but larger stones… read more structural abnormalities, or other causes of urinary obstruction.
Tips To Reduce Your Risk For Utis With Adpkd
If you have kidney disease, a UTI can cause a bladder or kidney infection. Find out how to prevent UTIs from occurring.
Theres nothing that unusual about a urinary tract infection : Theyre responsible for more than 8 million doctor visits per year, according to the Urology Care Foundation. But for people with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease , UTIs carry some potentially elevated risks.
UTIs occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . The bacteria usually travel from the skin or rectum into the urethra, the tube that connects the bladder to the outside of the body so you can urinate. Symptoms can include needing to urinate a lot, a feeling of urgency, pain when urinating, or feeling the need to urinate even when your bladder is empty.
While UTIs are often easily treated with antibiotics, people with ADPKD may need to avoid taking certain medications since they can potentially damage the kidneys. Left untreated, though, a UTI can cause a kidney infection, the CDC says.
Heres what to know about preventing and treating UTIs if you have ADPKD.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get A Urinary Tract Infection From Intercourse
Keeping Your Kidneys Healthy
There are a number of things you can do to keep your kidneys healthy, including:
- If you have diabetes, make sure that your blood sugar control is excellent. Follow your doctors advice about insulin injections, medicines, diet, physical activity and monitoring your blood sugar.
- Control high blood pressure. Have your blood pressure checked regularly. Medications used to lower blood pressure , such as ACE inhibitors or angiotensin blockers, can slow the development of kidney disease.
- If you have one of the risk factors for kidney disease, have a kidney health check at least every two years .
- Treat urinary tract infections immediately.
- Control blood cholesterol levels with diet and medications if necessary.
- Drink plenty of water and choose foods that are low in sugar, fat and salt, but high in fibre. Stick to moderate serving sizes.
- Do not smoke.
- Drink alcohol in moderation only.
- Stay at a healthy weight for your height and age.
- Try to exercise moderately for at least 30 minutes a day.
Are There Risk Factors For Pyelonephritis
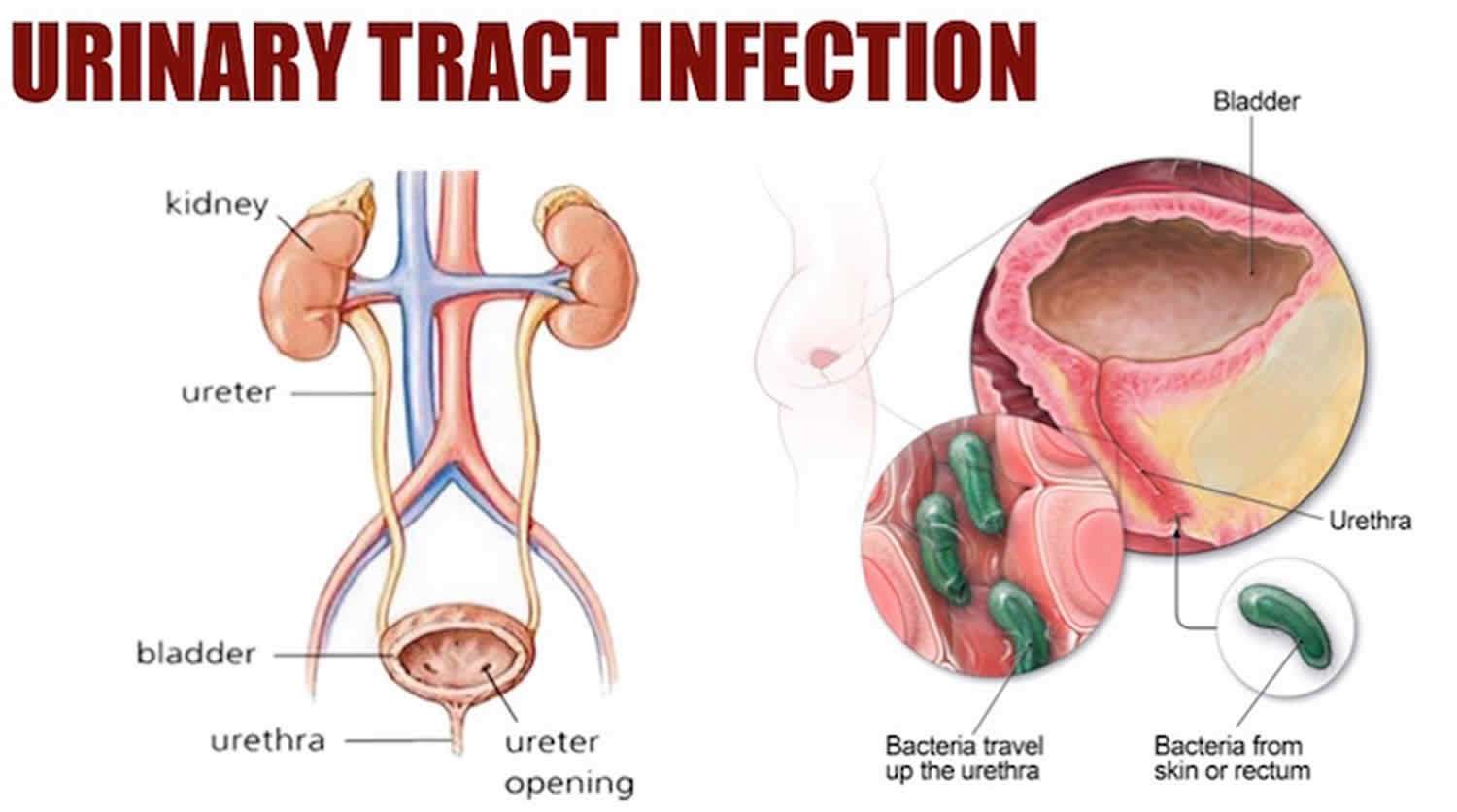
There are several developmental conditions that increase the risk for pyelonephritis.
- Ectopic ureters describe a condition in which the ureters do not attach to the bladder properly or may attach to reproductive organs instead of the bladder.
- Vesicoureteral reflux describes backflow of urine from the bladder back into the ureters.
- Renal dysplasia describes abnormal development of the kidneys from birth.
There are several medical and procedural conditions that increase the likelihood of urinary tract infection including:
- Diabetes mellitus, causing glucose in the urine, making the urine very attractive to bacteria.
- Cushing’s disease , or overactive adrenal glands, causing increased levels of steroids in the body and decreasing the body’s resistance to infection.
- Administration of medications containing steroids.
- Kidney failure.
- Urine retention.
- Bladder or kidney stones.
- Surgical removal of the penis with creation of a new opening into the urethra .
Read Also: How Does Sickle Cell Affect The Urinary System