Vaccines Targeting Bacterial Adhesion
As adherence has a key role at nearly every step of UTI pathogenesis, one attractive strategy for the development of antivirulence therapies, including vaccines, has been to target CUP pili. As a general rule, vaccination with whole pili has been ineffective at generating an antibody response that can protect against UTIs. However, adhesin-based vaccines have been shown to be effective at blocking hostpathogen interactions, thus preventing the establishment of disease. Experiments using mouse and cynomolgus monkey models of UTIs determined that immunization with PapDPapG or FimCFimH chaperoneadhesin complexes protected against UTIs. The effectiveness of the FimCFimH vaccine was shown to be due, in large part, to antibodies that block the function of FimH in bladder colonization. Furthermore, the anti-FimH antibodies did not seem to alter the E. coli niche in the gut microbiota. Modifications of this vaccine are currently under development, with the aim of inducing greater immune stimulation,. For example, one approach has been to fuse FimH to the flagellin FliC in order to induce a more substantial acute inflammatory response, which functions through TLR4 signalling via the MYD88 pathway. A Phase I clinical trial began in January 2014 to evaluate the efficacy of a FimCFimH vaccine using a synthetic analogue of monophosphoryl lipid A as the adjuvant.
Small Molecules Targeting Bacterial Adhesion
Our detailed understanding of pilus assembly and pilusreceptor binding has opened the door to the development of two classes of small, rationally designed synthetic compounds to inhibit pili: mannosides, which inhibit pilus function and pilicides, which inhibit pilus assembly. Targeting CUP pilus function or assembly has therapeutic potential, as it should block UPEC colonization, invasion and biofilm formation, thus preventing disease,,,.
Mannosides, which are FimH receptor analogues, have been developed to bind FimH with high affinity and block FimH binding to mannosylated receptors,,. Mannosides are potent FimH antagonists that offer a promising therapeutic opportunity for the treatment and prevention of UTIs by interrupting key hostpathogen interactions. Studies in mouse models have demonstrated the potential of mannosides as novel therapeutic strategies against UTIs: mannosides are orally bioavailable they are potent and fast-acting therapeutics in treating and preventing UTIs they function by preventing bladder colonization and invasion they are effective against multidrug-resistant UPEC they potentiate antibiotic efficacy and they are effective against established UTIs and CAUTIs,,,.
Treatment Of Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs result in considerable economic and public health burdens and substantially affect the life quality of afflicted individuals. Currently, antibiotics such as trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole, ciprofloxacin and ampicillin are the most commonly recommended therapeutics for UTIs. However, increasing rates of antibiotic resistance and high recurrence rates threaten to greatly enhance the burden that these common infections place on society. Ideally, alternative therapies will be established that will be recalcitrant to the development of resistance. Many promising approaches are being developed, from leveraging what we have learned about the basic biology of UTI pathogenesis to specifically target virulence pathways. These antivirulence therapeutics should theoretically allow us to effectively neutralize, or disarm, the capacity of UTI pathogens to cause disease, without altering the gut commensal microbiota, because antivirulence therapeutics target processes that are critical for UTI pathogenesis but that are not required for the essential processes of growth and cell division .
Recommended Reading: Ways To Get Rid Of Urinary Tract Infection
How Are Recurrent Utis Treated
Treatment for recurrent UTIs depends on what’s causing them. Sometimes the answer is as simple as teaching a child to empty their bladder as soon as they have the urge to go.
If a condition like VUR is causing the infections, the solution is a bit more complicated. Kids with VUR must be watched closely, because it can lead to kidney infection and kidney damage. Most kids outgrow the condition. Some might need surgery to correct the reflux.
Some kids with VUR benefit from daily treatment with a small amount of antibiotics, which can also make surgery unnecessary. Kids with VUR should see a pediatric urologist, who can decide if antibiotic treatment is the best option.
In some cases, surgery is needed to correct VUR. The most common procedure is ureteral reimplantation, in which one or both of the ureters are repositioned to correct the backflow of urine from the bladder. This procedure requires only a small incision and, in some children, can be done using robotic-assisted laparoscopy. When surgery is necessary, the success rate is high, but not everyone is a good candidate for it.
Kids may be candidates for ureteral reimplantation if they:
- have an intolerance to antibiotics
- get recurrent infections while on antibiotic treatment
- have severe, or “high-grade,” reflux
- are older kids and teens with reflux
What Are Possible Complications Of A Urinary Tract Infection
Most UTIs cause no complications if they spontaneously resolve quickly or if treated early in the infection with appropriate medications. However, there are a number of complications that can occur if the UTI becomes chronic or rapidly advances. Chronic infections may result in urinary strictures, abscesses, fistulas, kidney stones, and, rarely, kidney damage or bladder cancer. Rapid advancement of UTIs can lead to dehydration, kidney failure, sepsis, and death. Pregnant females with untreated UTIs may develop premature delivery and a low birth weight for the infant and run the risks of rapid advancement of the infection.
Read Also: Z Pack Urinary Tract Infection
What Is The Prognosis For A Urinary Tract Infection
A good prognosis is usual for spontaneously resolved and quickly treated UTIs. Even patients that have rapidly developing symptoms and early pyelonephritis can have a good prognosis if quickly and adequately treated. The prognosis begins to decline if the UTI is not quickly recognized or treated. Elderly and immunosuppressed patients may not have the UTI recognized early their prognosis may range from fair to poor, depending on how much damage is done to the urinary tract or if complications like sepsis occur. Like adults, most adequately treated children will have a good prognosis. Children and adults with recurrent UTIs may develop complications and a worse prognosis recurrent UTIs may be a symptom of an underlying problem with the urinary tract structure. These patients should be referred to a specialist for further evaluation.
Living With Urinary Tract Infections
If you have 3 or more urinary tract infections each year, your doctor may want you to begin a preventive antibiotic program. A small dose of an antibiotic taken every day helps to reduce the number of infections. If sexual intercourse seems to cause infections for you, your doctor many suggest taking the antibiotic after intercourse.
Also Check: What Home Remedy Is Good For Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary Infections In Children
A urinary infection in a child needs to be investigated as it may indicate a more serious condition.
The most common urinary system condition is urinary reflux. With this condition, the bladder valve isnt working properly and allows urine to flow back to the kidneys, increasing the risk of a kidney infection.
Urinary reflux and the associated infections can scar or permanently damage the kidney, and can also lead to:
- high blood pressure
- toxaemia in pregnancy
- kidney failure.
Urinary reflux tends to run in families, so its important to screen children as early as possible if a close relative is known to have the problem.
Acute And Chronic Prostatitis
In the 1800s, prostatitis was thought to be secondary to excessive alcohol consumption or physical or sexual activity. It was often associated with gonorrhea and could be fatal or lead to abscess formation. By the 1920s, most cases were attributed to microorganisms, and antibiotics combined with prostate massage were standard therapy after World War II. Although the role of bacteria was questioned in the 1950s, it was reemphasized in 1968 when Meares and Stamey described their “4-glass test.”
Acute prostatitis is caused by an acute infection of the entire prostate gland, resulting in fever and localized pain. Microscopically, neutrophilic infiltrates, diffuse edema, and microabscesses may be seen, which may coalesce into larger collections.
Chronic prostatitis may be caused by inflammatory or noninflammatory diseases. This condition may arise via dysfunctional voiding, intraprostatic reflux, chronic exposure to microorganisms, autoimmune mechanisms, irritative urinary metabolites, and as a variant of neuropathic pain. Chronic bacterial prostatitis often produces few or no symptoms related to the prostate, but it is probably the most common cause of relapsing UTI in men.
Chronic prostatitis has been subdivided by the National Institutes of Health into the following categories:
Also Check: Urinary Infection Blood In Urine
Uti Tests And Diagnosis
If you suspect that you have a urinary tract infection, go to the doctor. You’ll give a urine sample to test for UTI-causing bacteria.
If you get frequent UTIs and your doctor suspects a problem in your urinary tract, they might take a closer look with an ultrasound, a CT scan, or an MRI scan. They might also use a long, flexible tube called a cystoscope to look inside your urethra and bladder.
How To Prevent Uti Re
Following some tips can help you avoid getting another UTI:
- Empty your bladder often as soon as you feel the need to pee don’t rush, and be sure you’ve emptied your bladder completely.
- Wipe from front to back after you use the toilet.
- Drink lots of water.
- Choose showers over baths.
- Stay away from feminine hygiene sprays, scented douches, and scented bath products they’ll only increase irritation.
- Cleanse your genital area before sex.
- Pee after sex to flush out any bacteria that may have entered your urethra.
- If you use a diaphragm, unlubricated condoms, or spermicidal jelly for birth control, you may want to switch to another method. Diaphragms can increase bacteria growth, while unlubricated condoms and spermicides can irritate your urinary tract. All can make UTI symptoms more likely.
- Keep your genital area dry by wearing cotton underwear and loose-fitting clothes. Donââ¬â¢t wear tight jeans and nylon underwear they can trap moisture, creating the perfect environment for bacteria growth.
Show Sources
Read Also: How Urinary Tract Infection Is Transmitted
How Do You Prevent Urinary Tract Infections In Dogs
Do I Need To See A Doctor
Yes. Painful urination can be a symptom of a more serious problem. You should tell your doctor about your symptoms and how long youve had them. Tell your doctor about any medical conditions you have, such as diabetes mellitus or AIDS, because these could affect your bodys response to infection. Tell your doctor about any known abnormality in your urinary tract, and if you are or might be pregnant. Tell your doctor if youve had any procedures or surgeries on your urinary tract. He or she also need to know if you were recently hospitalized or stayed in a nursing home.
If your doctor thinks your pain may be from vaginal inflammation, he or she may wipe the lining of your vagina with a swab to collect mucus. The mucus will be looked at under a microscope to see if it has yeast or other organisms. If your pain is from an infection in your urethra , your doctor may swab it to test for bacteria. If an infection cant be found, your doctor may suggest other tests.
Read Also: Why Do Elderly Get Urinary Tract Infections
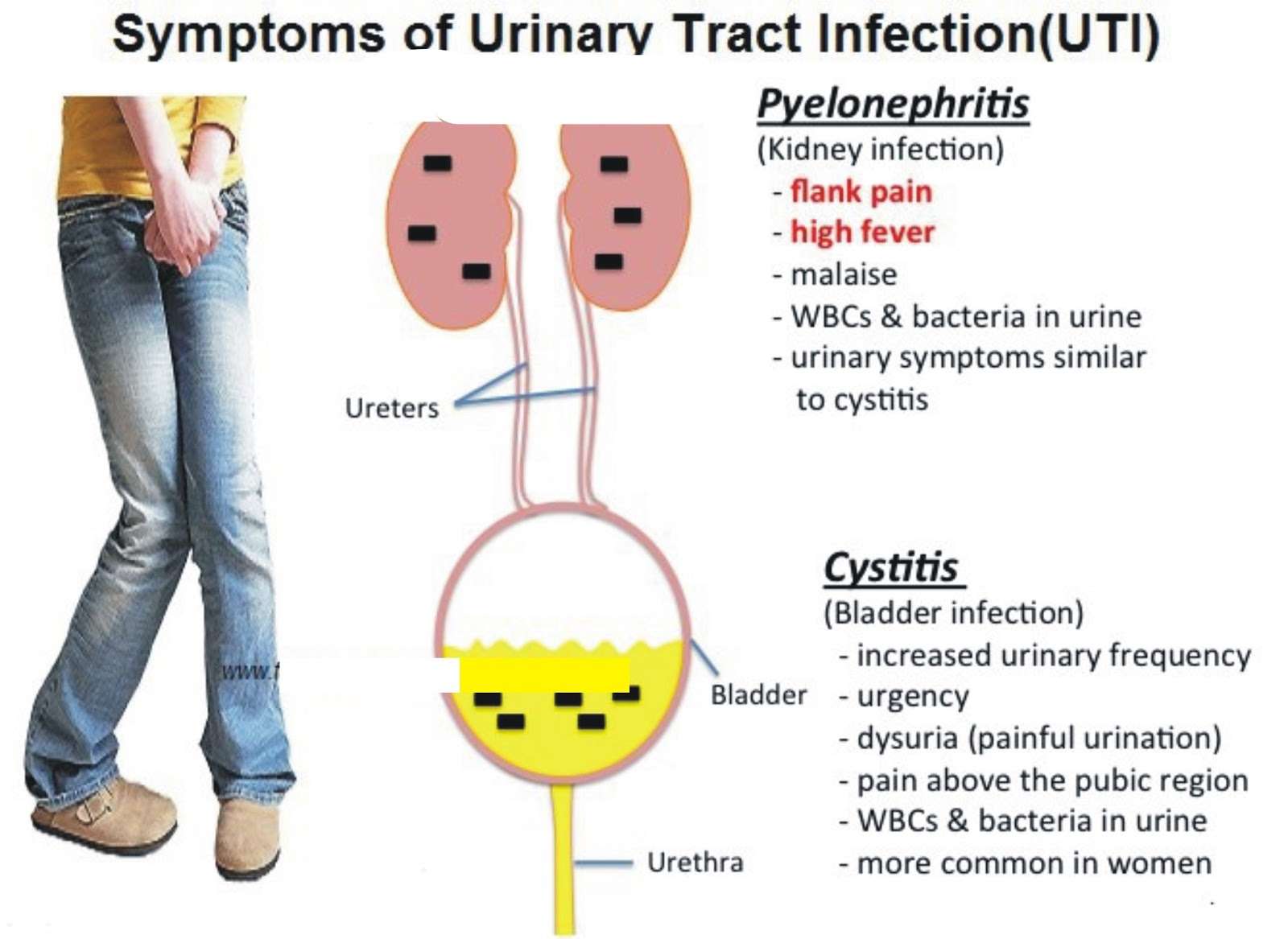
Common Uti Symptoms And Signs
The urine of most healthy, properly hydrated people appears light yellow or clear and is nearly free of odor. It also causes zero pain or discomfort to pass.
But for the majority of people who experience a urinary tract infection, thats not the case. Instead, they will likely encounter at least one of the following indicators:
When the kidneys are infected, other noticeable symptoms may include:
- Fever, shaking, and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Upper back, side, or groin pain
While its been long noted that confusion in the elderly is a sign of UTI, a 2019 report in BMC Geriatrics concludes that theres insufficient evidence connecting the symptom to that diagnosis.
RELATED: Causes and Risk Factors of Urinary Tract Infections
Organs Of The Urinary Tract
|
The urinary tract consists of the kidneys, ureters , bladder, and urethra. These organs may be injured by blunt force or by penetrating force . Injuries may also occur unintentionally during surgery. |
UTIs are usually classified as upper or lower according to where they occur along the urinary tract, although it is sometimes difficult or impossible for doctors to make such a determination:
Some doctors also consider infections of the urethra and prostate to be lower UTIs. In paired organs , infection can occur in one or both organs. UTIs can occur in children Urinary Tract Infection in Children A urinary tract infection is a bacterial infection of the urinary bladder , the kidneys , or both. Urinary tract infections are caused by bacteria. Infants and younger… read more as well as in adults.
Also Check: Urinary Tract Infection Men Home Treatment
Urinary Catheter Care: What Does The Evidence Say
Sweating due to fever can also result from catheter insertion: almost all catheter users develop bacteriuria within four weeks of catheter insertion people with indwelling catheters are up to 6.5 times more likely to develop a urinary tract infection .The patients own colonic and perineal flora, and the hands of health care professionals, act as …
You Wipe From Back To Front
Wiping from back to front can transport E. coli, the bacteria thats behind most UTIs, from the rectal region to the urethra. Moral of the story: Always wipe from front to back. Al-Badr A, et al. . Recurrent urinary tract infections management in women: A review.
You May Like: Tips For Urinary Tract Infection
Treatment From A Gp For Utis That Keep Coming Back
If your UTI comes back after treatment, you may have a urine test and be prescribed different antibiotics.
Your doctor or nurse will also offer advice on how to prevent UTIs.
If you keep getting UTIs and regularly need treatment, a GP may give you a repeat prescription for antibiotics.
If you have been through the menopause, you may be offered a vaginal cream containing oestrogen.
In Men Over : Bph May Be The Cause Of High Psa
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is an enlargement of the prostate. But its not prostate cancer. BPH means more cells, so more cells that make PSA. BPH is the most common prostate problem in men over 50. It is not necessarily necessary to treat it, unless it causes frequent or difficult urination. Your GP may be able to tell the difference between BPH and prostate cancer by performing a digital rectal exam. But this usually requires evaluation by a urologist and additional tests, such as a biopsy or imaging tests.
Recommended Reading: Where Does A Urinary Tract Infection Hurt
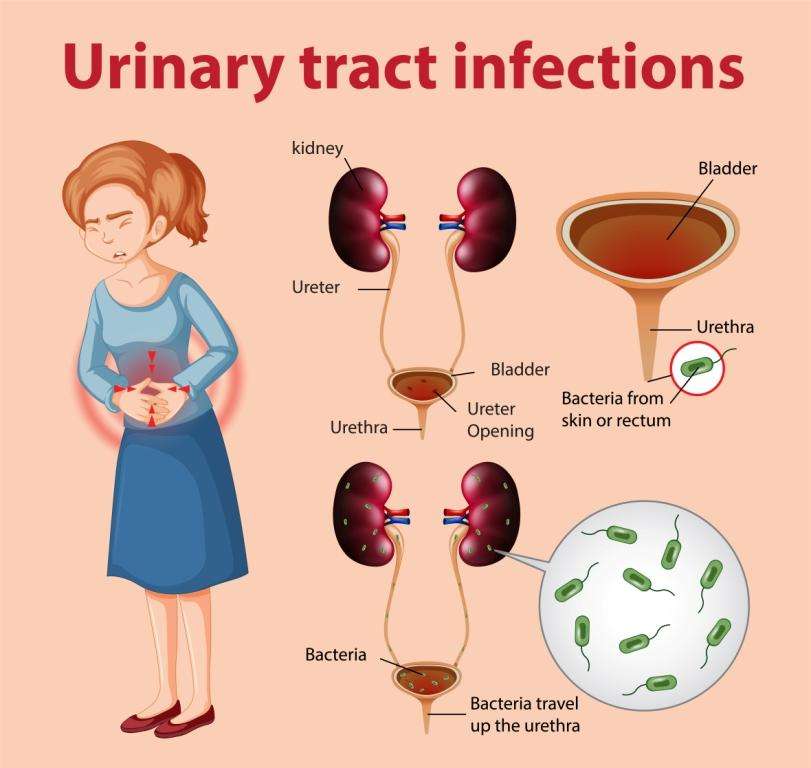
What Causes Urinary Tract Infection
Microorganisms typically bacteria that enter the urethra and bladder, producing Inflammation and infection, are responsible for urinary tract infections.
Some common causes of a UTI include:
- A new sexual partner or multiple sex partners
- Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during the menstrual cycle
- Wiping from back to front after a bowel movement rather than front to back
- Using an intrauterine device for birth control
- Not enough intake of fluids and dehydrated state
- Diabetes
- Kidney stones that block the flow of urine or keep the bladder from emptying
- A weakened immune system due to certain disorders, such as diabetes or cancer
- Menopause, which can cause changes in the urinary tract
- Pregnancy, which can cause hormonal changes that promote infection
- Narrowing of the urethra in males due to prostate enlargement, which blocks the flow of urine
You Dont Pee After Sex
The threat of getting a UTI shouldnt stop you from getting it on. But that doesnt mean resigning yourself to the afterburn.
One simple way to cut your risk: Head to the potty after youve finished your romp. Youll possibly flush out the bacteria that may have made their way into your urinary tract. Urinary Tract Infection. .
You May Like: What Can I Do To Prevent Urinary Tract Infections
Causative Organisms Of Catheter Associated Urinary Tract
Background: Catheter associated urinary tract infection is a urinary tract infection where an indwelling catheter was in for more than two calendar days on the date of event . It is one of the most common hospital acquired infection and causes problems in hospitalized patients. Objectives: To review the overall occurrence of CAUTI,
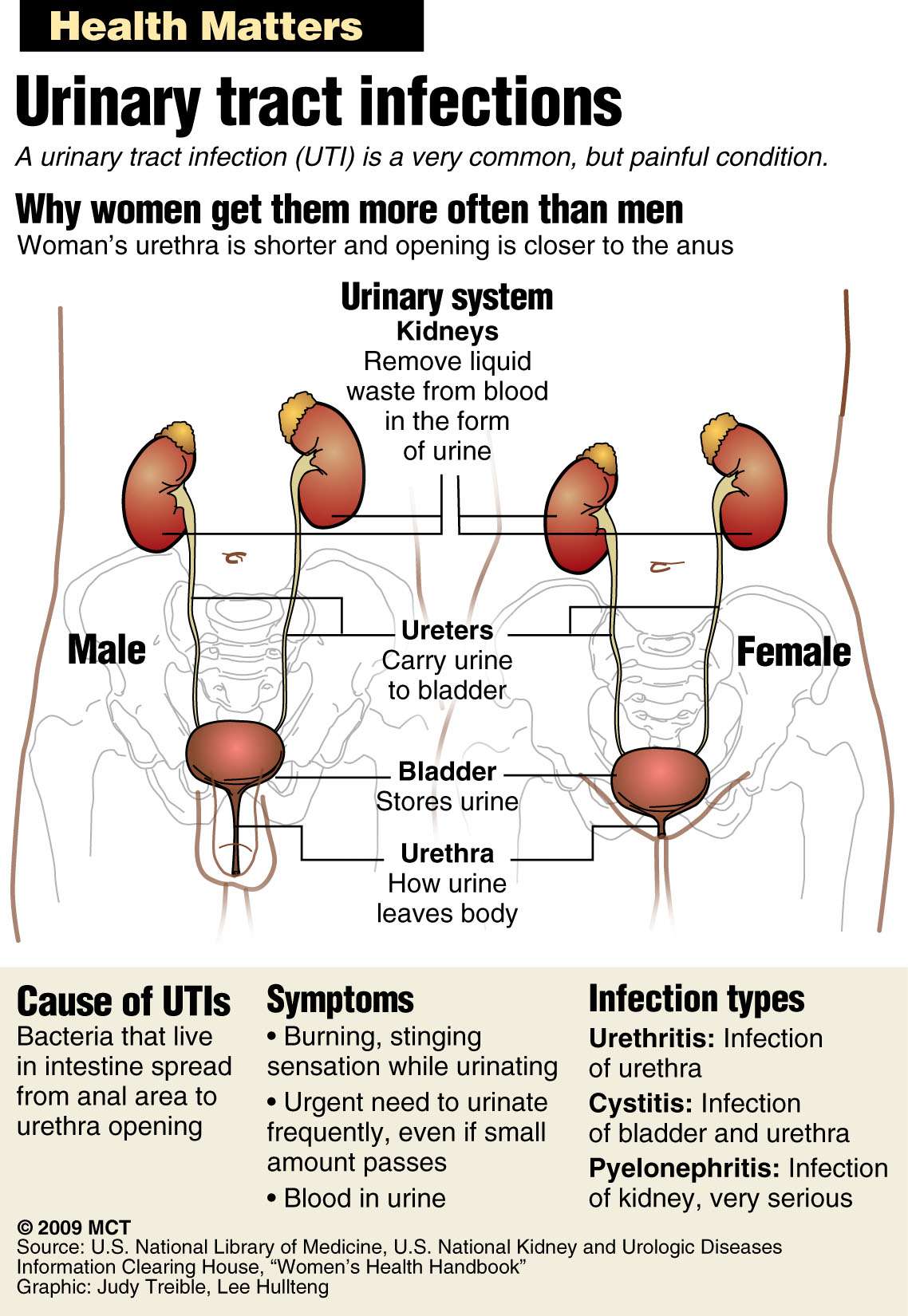
What Are The Types Of Utis
Common types of UTIs include:
- cystitis: this bladder infection is the most common type of UTI. It happens when bacteria move up the urethra and into the bladder.
- urethritis: when bacteria infect the urethra
- pyelonephritis: a kidney infection caused by infected urine flowing backward from the bladder into the kidneys or an infection in the bloodstream reaching the kidneys
Read Also: All Natural Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
How Do I Know If Dog Has Uti
U.S. dogs suffering from urinary tract infections are generally unable to urinate very frequently outdoors in part because they often experience pain as they urinate. Many times, you will also detect urinating in their urine with dripping saliva or frequent licking of the genital area. There is also the possibility that they may also suffer from UTIs.
When Should I Call My Healthcare Provider
- Fever.
- Back pain.
- Vomiting.
If you have any of these symptoms, or your other symptoms continue after treatment, call your healthcare provider. A UTI can spread throughout your urinary tract and into other parts of your body. However, treatment is very effective and can quickly relieve your symptoms.
Also Check: D Mannose For Urinary Tract Health