When Should I See A Healthcare Provider About An E Coli Infection
See your healthcare provider about an E. coli infection if:
You have diarrhea for more than three days and:
- You cant keep any fluids down.
- You have blood in your poop.
- You are feeling very tired.
- You have many bouts of vomiting.
- You have a fever higher than 102 °F.
- You are not peeing a lot.
- You are losing pink color in cheeks and inside your lower eyelids.
Vaccines Targeting Bacterial Adhesion
As adherence has a key role at nearly every step of UTI pathogenesis, one attractive strategy for the development of antivirulence therapies, including vaccines, has been to target CUP pili. As a general rule, vaccination with whole pili has been ineffective at generating an antibody response that can protect against UTIs. However, adhesin-based vaccines have been shown to be effective at blocking hostpathogen interactions, thus preventing the establishment of disease108112. Experiments using mouse and cynomolgus monkey models of UTIs determined that immunization with PapDPapG or FimCFimH chaperoneadhesin complexes protected against UTIs108112. The effectiveness of the FimCFimH vaccine was shown to be due, in large part, to antibodies that block the function of FimH in bladder colonization110. Furthermore, the anti-FimH antibodies did not seem to alter the E. coli niche in the gut microbiota109. Modifications of this vaccine are currently under development, with the aim of inducing greater immune stimulation108,112. For example, one approach has been to fuse FimH to the flagellin FliC in order to induce a more substantial acute inflammatory response, which functions through TLR4 signalling via the MYD88 pathway112. A Phase I clinical trial began in January 2014 to evaluate the efficacy of a FimCFimH vaccine using a synthetic analogue of monophosphoryl lipid A as the adjuvant.
Epidemiology And Risk Factors For E Coli Uti
Among bacterial infections in children, UTI ranks highly, even outnumbering bacterial meningitis, pneumonia, and bacteremia . About 1% of infants < 3 months old develop UTI, with more males affected than females. Proper and urgent UTI management is crucial in children as an estimated 1015% of children with UTI will develop permanent kidney damage, leading to other chronic diseases such as hypertension and renal insufficiency .
The propensity of UTIs to recur, often within a few weeks or months after an initial acute infection, is a problem in UTI management. Approximately 2030% of women will have a recurrent bladder infection within 6 months after an initial episode, and an additional 3% will experience a third infection .
Also Check: What Will Cure A Urinary Tract Infection
E Coli Sequence Type 131
Determining the clonal types of UPEC is crucial for understanding the role of clonal spread to emerging antimicrobial resistance, which is important for defining and interrupting transmission pathways. Multidrug-resistant E. coli sequence type 131 has emerged over the past decade as a globally disseminated cause of extraintestinal infections in humans and animals . The recent emergence of this clone has coincided with an increase in antibiotic resistance among E. coli generally, suggesting a contributing role for ST131 in resistance.
In contrast to traditional antimicrobial resistant E. coli , which mostly derive from low virulence phylogenetic groups A and B1, ST131 derives exclusively from phylogenetic group B2, which is traditionally known to be enriched for VF genes. This, plus limited experimental evidence of virulence and several case reports of unusually severe or fatal extraintestinal infections due to ST131, suggests that the emergence of ST131 may be due to a high virulence potential compared with other E. coli types. However, despite this, some studies have reported absence of traits commonly associated with B2 phylogeny, particularly adhesins and toxins .
Four VF genes are associated with ST131 isolates, and so could represent potential targets for vaccines or other interventions, particularly if a functional role in virulence or dissemination can be demonstrated for them. Most of the ST131 isolates are of the O25b variant, and the remainder are type O16 .
What Fruit Juice Is Good For Uti
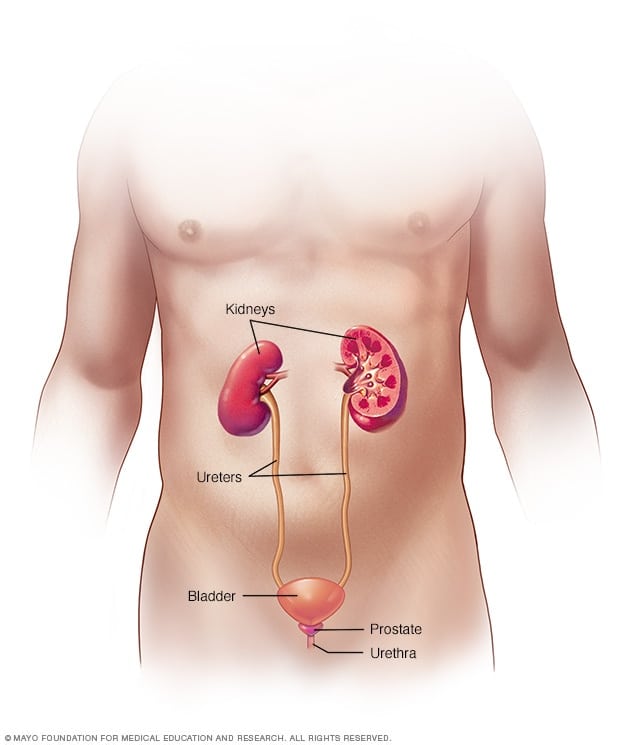
Image credit: https://pinimg.com
There are many different types of fruit juice that can be good for a urinary tract infection . Cranberry juice is one of the most popular options because it contains compounds that can help to prevent bacteria from sticking to the walls of the urinary tract. Other juices that may be beneficial include blueberry juice, pineapple juice, and watermelon juice. Drinking plenty of fluids is also important for a UTI, so juice can help to keep the urinary tract flushed and prevent bacteria from growing.
Bananas, as well as other high-fiber foods, may help with urinary tract health and infection prevention. In addition to supporting urinary tract health, drinking plenty of water aids in the digestive systems well-being by flushng bacteria from the urinary tract. Berries offer protection against infection thanks to a compound that fights bacteria. Yogurt is an excellent way to keep your digestive system running smoothly. A yogurt ice cream is both healthy and enjoyable to consume. When fiber-rich foods are combined with enough water, the bodys digestive system can function normally and bowel movements can be maintained. When you eat oranges, lemons, strawberries, or green leafy vegetables high in vitamin C, your urine becomes more acidic, preventing bacteria from growing.
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection And Bleeding
How Is Uti Treated In Males
Urinary tract infections are usually treated with oral antibiotics. In severe cases, antibiotics may be administered intravenously in a hospital setting. The choice of antibiotic depends on the type of bacteria and location of the infection.
- Upper UTI: Antibiotics course may last for 2 weeks
- Lower UTI: Antibiotics course may last for 3-7 days
Donât Miss: Myasthenia Gravis And Urinary Incontinence
How To Treat Intestinal E Coli Infections
For intestinal E. coli infections, what a person doesnt do to treat symptoms is as important as what that person does do. For instance, intestinal E. coli infections caused by Shiga toxinproducing E. coli, or STEC which spurs an estimated 265,000 foodborne infections each year in the United States does not require antibiotic treatment.
In fact, treating these cases with antibiotics can triple your risk of developing hemolytic uremic syndrome , a complication in which toxins destroy red blood cells, disrupting the kidneys filtering system and possibly causing kidney failure, according to a report published in the journal Toxins.
Its also important not to treat STEC infections with over-the-counter antidiarrheal medication. These, too, can increase your risk of developing HUS, according to a study published in Clinical Infectious Diseases. Antidiarrheal medication slows down the digestive system, which prevents the body from getting rid of the toxins swiftly.
But that doesnt mean theres nothing a person can do to help ease symptoms and feel better. Experts recommend the following supportive therapies that can be done at home to aid recovery from a STEC infection:
Read Also: How Serious Is A Urinary Tract Infection
Foods And Drinks That Boost Brainpower And Mental Health
Grape juice and cranberry juice are two excellent beverages that help to improve your brains health. These health benefits are primarily due to their high antioxidant levels. Antioxidants, in addition to protecting the body from free radicals, are also important in slowing the progression of cellular aging. Which drinks are safe for UTI? Cranberries, blueberries, oranges, dark chocolate, unsweetened probiotic yogurt, tomatoes, broccoli, spinach, and broccoli are examples of these foods. Decaffeinated coffee, cranberry, blueberry, or pomegranate juice, and black or green tea are the smart drinks to sip. A UTI can also be prevented by drinking a lot of water.
Who Is Prone To Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections may affect anybody, although they are more frequent in women. UTIs are the most common bacterial infection encountered in the outpatient setting: by the age of 24, one in every three women will have a UTI that requires antibiotic therapy, and half of all women will have at least one UTI in their lifetime.
Read Also: Why Am I Prone To Urinary Tract Infections
Impact Of A Primary Care Antimicrobial Stewardship Program On Bacterial Resistance Control And Ecological Imprint In Urinary Tract Infections
Antibiotics202211Reviewer 3:Antibiotics202211
Round 1
Reviewer 1 Report
This article describes the impact and feasibility of an antimicrobial stewardship program at the outpatient/ambulatory level. This is not a novel concept per say but it implies proof of feasibility in an real world setting.
The abstract is unclear it needs to be more succinct — in a few statements summarize the intervention and the major outcome findings. You do not need confidence intervals in the abstract. Your abstract distills to 1. AMSP have been a central component in reducing over prescription of unnecessary antibiotics with multiple studies showing a corresponding benefit in reduction of bacterial resistance. 2. Little data/less commonly AMSP have been studied in outpatient ambulatory settings. 3. Your group implemented an AMSP in a large regional outpatient setting to assess feasibility and effectiveness. 4. Over a 5-year post-implementation period, compared to the pre-intervention period, a significant reduction in antibiotic prescription occurred with a corresponding reduction in resistance in E. coli urinary isolates. 5. AMSP activities also was found to be cost effective with a reduction in attributable medication expenditure.
Lines 120 125: anomalous context
— Intervention this is part of design
Treatments For Specific Populations
Treating Pregnant Women
Pregnant women should be screened for UTIs, since they are at high risk for UTIs and their complications. Antibiotics used for treating pregnant women with UTIs include amoxicillin, ampicillin, nitrofurantoin, and cephalosporins . Fosfomycin is not as effective as other antibiotics but is sometimes prescribed for pregnant women. In general, there is no consensus on which antibiotic is best for pregnant women although some types of antibiotics, such as fluoroquinolones and tetracyclines, should not be taken as they can cause harm to the fetus.
Pregnant women with asymptomatic bacteriuria have an increased risk for acute pyelonephritis in their second or third trimester. They need screening and treatment for this condition. In such cases, they should be treated with a short course of antibiotics . For an uncomplicated UTI, pregnant women may need longer-term antibiotics .
Treating Children with UTIs
Children with UTIs are generally treated with TMP-SMX, cephalexin and other cephalosporins, or amoxicillin/clavulanic acid . These drugs are usually taken by mouth in either liquid or pill form. Doctors sometimes give them as a shot or IV. Children usually respond to treatment within a few days. Prompt treatment with antibiotics may help prevent renal scarring.
Children with acute kidney infection are treated with various antibiotics including oral cefixime or a short course of an intravenous antibiotic . An oral antibiotic then follows the IV.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Medication For Urinary Incontinence
Treatment Of Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs result in considerable economic and public health burdens and substantially affect the life quality of afflicted individuals. Currently, antibiotics such as trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole, ciprofloxacin and ampicillin are the most commonly recommended therapeutics for UTIs. However, increasing rates of antibiotic resistance and high recurrence rates threaten to greatly enhance the burden that these common infections place on society. Ideally, alternative therapies will be established that will be recalcitrant to the development of resistance. Many promising approaches are being developed, from leveraging what we have learned about the basic biology of UTI pathogenesis to specifically target virulence pathways. These antivirulence therapeutics should theoretically allow us to effectively neutralize, or disarm, the capacity of UTI pathogens to cause disease, without altering the gut commensal microbiota, because antivirulence therapeutics target processes that are critical for UTI pathogenesis but that are not required for the essential processes of growth and cell division .
Asymptomatic Urinary Tract Infection

An asymptomatic UTI is when a person has no symptoms of infection but has a significant number of bacteria that have colonized the urinary tract. The condition is harmless in most people and rarely persists, although it does increase the risk for developing symptomatic UTIs.
Screening and treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria is not usually necessary except for the following people:
- Pregnant women. Pregnant women with asymptomatic bacteriuria have an increased risk of acute pyelonephritis in their second or third trimester. Therefore, they need screening and treatment for this condition. Guidelines recommend that pregnant women be screened for asymptomatic bacteriuria at 12 to 16 weeks gestation or at the first prenatal visit, if later.
- People undergoing urologic surgery . The presence of an infection during surgery can lead to serious consequences.
You May Like: How Does Urinary Tract Infection Affect The Body
Treating E Coli Infections That Cause Neonatal Meningitis
While its true that E. coli causes about 20 percent of all neonatal meningitis cases, bacterial meningitis is still considered very rare in developed countries thanks to the success of vaccines.
If neonatal meningitis is suspected, a healthcare professional will draw blood and perform a spinal tap in order to test spinal fluid for the E. coli bacteria. If bacterial meningitis is confirmed, treatment would consist of IV antibiotics and fluids.
With early diagnosis and proper treatment, a child with bacterial meningitis has a reasonable chance of a good recovery.
Additional reporting by Joseph Bennington-Castro.
Urinary Tract Infections And Antibiotic
The standard treatment for most urinary tract infections is antibiotics. However, some E. coli strains are resistant to most antibiotic drugs. These strains are called extended-spectrum beta-lactamase -producing E. coli. Researchers found that UTIs caused by E. coli, which are resistant to ciprofloxacin, increased from 3-17 percent in 2000 up to 2010. Moreover, E. coli strains that are resistant to trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole also increased from 18-24 percent.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Medication For Cats
Small Molecules Targeting Bacterial Adhesion
Our detailed understanding of pilus assembly and pilusreceptor binding has opened the door to the development of two classes of small, rationally designed synthetic compounds to inhibit pili: mannosides, which inhibit pilus function and pilicides, which inhibit pilus assembly. Targeting CUP pilus function or assembly has therapeutic potential, as it should block UPEC colonization, invasion and biofilm formation, thus preventing disease30,31,120,121.
Mannosides, which are FimH receptor analogues, have been developed to bind FimH with high affinity and block FimH binding to mannosylated receptors35,121,123125. Mannosides are potent FimH antagonists that offer a promising therapeutic opportunity for the treatment and prevention of UTIs by interrupting key hostpathogen interactions123125. Studies in mouse models have demonstrated the potential of mannosides as novel therapeutic strategies against UTIs: mannosides are orally bioavailable they are potent and fast-acting therapeutics in treating and preventing UTIs they function by preventing bladder colonization and invasion they are effective against multidrug-resistant UPEC they potentiate antibiotic efficacy and they are effective against established UTIs and CAUTIs35,121,124,125.
Treatments For Urinary And Kidney Infections
Kidney infections always require antibiotics. Dont rely on home remedies alone to take care of kidney infections.
Usually, doctors will prescribe empiric antibiotics to cover all the potential bacteria that could have caused the infection until they can target the specific bacteria based on test results. Antibiotics are usually prescribed for at least a full week.
Normally, you wont require a stay at a hospital for a kidney infection as long as you can move around and consistently keep down oral antibiotics.
However, if you exhibit severe symptoms or cannot keep down the medication due to nausea and vomiting, you may be hospitalized so that your doctor may administer antibiotics and fluids intravenously.
If the kidney infection progresses enough to create an abscess in the kidney, you may require more serious treatment. Abscesses cannot be cured with antibiotics alone. In order to drain them, doctors will perform a nephrostomy, which involves placing a tube through your back, into the kidney.
Don’t Miss: What Vitamins Are Good For Urinary Tract Infections
What Is Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary Tract Infection means that there is an infection in your urinary system including
- Bladder- an organ that collects and stores urine.
- Urethra- a tube that takes urine from your bladder out of the body.
It is an infection in the urinary tract that begins at the urethra on the bottom, but if it is not treated, it moves up toward the kidneys. This is why it’s important to deal with this problem immediately.
When Urinary Tract Infections Keep Coming Back
|
Image: Thinkstock |
If you are prone to recurrent UTIs, you can head them off before they take hold.
Unless youâre in the fortunate minority of women who have never had a urinary tract infection , you know the symptoms well. You might feel a frequent urgency to urinate yet pass little urine when you go. Your urine might be cloudy, blood-tinged, and strong-smelling. For 25% to 30% of women whoâve had a urinary tract infection, the infection returns within six months.
If you have repeated UTIs, youâve experienced the toll they take on your life. However, you may take some comfort in knowing that they arenât likely to be the result of anything youâve done. âRecurrent UTIs arenât due to poor hygiene or something else that women have brought on themselves. Some women are just prone to UTIs,â says infectious diseases specialist Dr. Kalpana Gupta, a lecturer in medicine at Harvard Medical School.
You May Like: Do Urinary Tract Infection Go Away On Their Own
Antimicrobial Drugs And Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli
Managing UTI caused by UPEC has become challenging over the years due to increasing resistance to the commonly used antibiotics , which poses a great threat to future capacity to treat UTI caused by UPEC. Although TMP-SMX has traditionally been used as a first-line treatment for UTI , there are reports of increased resistance to this antibiotic, which in some countries is in the range 1520% . Many UPEC strains resistant to TMP-SMZ are also resistant to amoxicillin and cephalexin. Nitrofurantoin remains highly effective against UPEC, but is mainly used for cystitis treatment due to its inability to attain sufficient serum levels to treat invasive or systemic infections , and all have excellent bioavailability and achieve high urinary concentrations. However, increased FQ use has resulted in a rise in the prevalence of resistance, and FQ-resistant E. coli has become a major problem in several countries .