Prevention Of Catheter Associated Uti
Catheter associated UTI is the most common health care associated infection throughout the world and is common in long-term care facilities. Urinary catheterization should be avoided unless there is a clear clinical indication. Catheters should be avoided where possible for the management of incontinence. Staff should also be trained on indications for catheterization and written protocols should be put in place.26,27 Catheters should also be removed the moment that they are no longer required.
Alternatives to indwelling urethral catheters should be considered. Condom catheters are associated with a lower incidence of bacteriuria, however their use is sometimes difficult in confused patients.27 A Cochrane review on short-term urinary catheterization in adults found that suprapubic catheterization was associated with less bacteriuria than urethral catheterization.43 Suprapubic catheterization does carry a small risk of visceral injury on insertion through the abdominal wall. Intermittent catheterization was also associated with a lower risk of bacteriuria when compared to indwelling catheterization in this review, however studies included were mainly in an elective orthopedic setting.43
Guidelines suggest that antibiotic prophylaxis should not be used to prevent catheter associated UTI in catheterized patients.10 Although prophylaxis may decrease the incidence of asymptomatic bacteriuria in catheterized patients, it increases the risk of antimicrobial resistance.
The Evidence: Diagnosis Management And Prevention
We searched Ovid for English-language human studies conducted among adults aged 65 years and older and published in peer-reviewed journals from 1946 to November 20, 2013. We focused on community-dwelling older adults. Search terms included UTI, asymptomatic bacteriuria, risk factors and UTI, community-onset UTI, functional decline and UTI, delirium and UTI, dehydration and UTI, diagnosis and UTI, diet and drug therapy and UTI, prevention and UTI, and urine tests and UTI. We also searched for recently published Cochrane reviews regarding treatment and prevention of UTI in community-dwelling older adults. The recommendations that follow are based on evaluation of the existing evidence.
Control Of Urinary Tract Infections
For seniors that are immobile and can no longer take the best care of themselves, assisted living facilities may be a better option in ensuring that they are always dry and clean, and that proper preventive measures are followed. Senior caregivers at assisted living facilities are well trained about how to help elderly adults prevent and manage urinary tract infections. The senior caregivers will also accompany the elderly adults to visit their healthcare professionals.
The seniors may need to visit their healthcare provider to discuss the best care plan options. As urinary tract infection symptoms can present differently in each senior, the healthcare provider will be able to assess whether the older adult shows such a symptom.
Also Check: Home Remedies For Urinary Frequency
How To Prevent Utis In Seniors
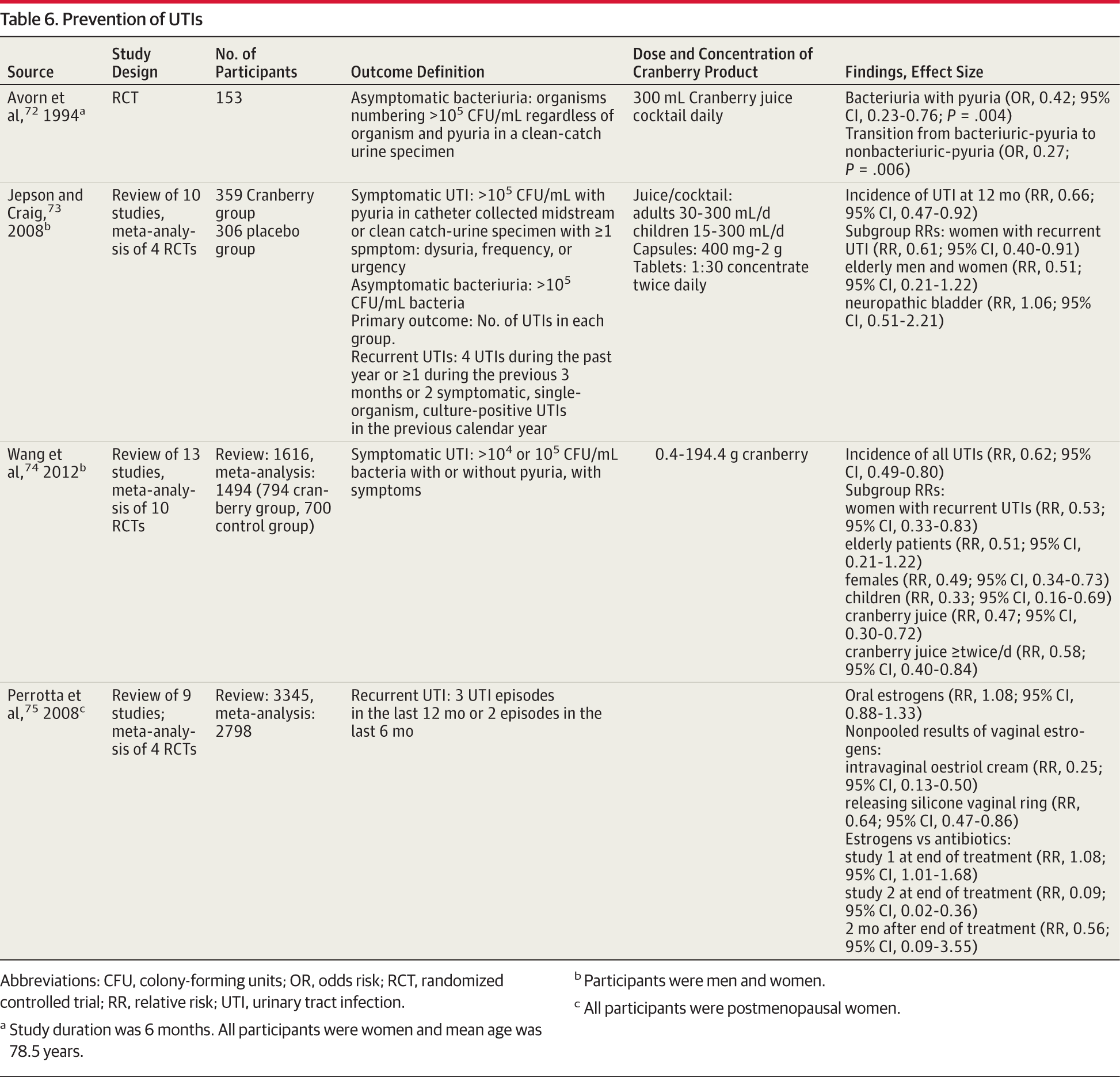
Older adults can help prevent UTIs by drinking plenty of fluids to flush the bacteria from their systems, Forciea says. She recommends older adults drink four to six 8-ounce glasses of water a day. Forciea further notes that drinking cranberry juice or taking cranberry tablets also can make urine less inviting for bacteria.
Use these strategies to help prevent UTIs in elderly women:
- Urinating promptly after the urge arises
- Wiping front to back
You May Like: Causes Of Urinary Frequency And Urgency In Females
Urinary Tract Infections In Elderly Patients: How Best To Diagnose And Treat
DALE P. MURPHY, MDSeries Editorand MARYJO CLEVELAND, MD
How is urinary tract infection best managed in elderly persons?
Genitourinary infection is the second most common type of infection in community-dwelling adults older than 65 years it occurs only slightly less frequently than upper respiratory tract infection. 1 The presentation of UTI in elderly patients may differ significantly from that in younger ones. Chronic urinary symptoms are common in elderly persons, and the classic triad of UTI-frequency, urgency, and dysuria-occurs routinely in older persons without infection.2 As many as one third of community- dwelling elderly women are incontinent, which can further confuse the presentation. A high index of suspicion is needed first to entertain the diagnosis and then to pursue a thorough evaluation.A variety of risk factors predispose older persons to UTIs . In those between ages 50 and 70 years, the most common are urinary tract surgery, incontinence, cystocele, high postvoid residual volume, and low estrogen levels. Neurogenic conditions of the bladderparticularly those associated with diabetes and with anticholinergic medicationalsopredispose to UTI.3 In patients older than 70 years, risk factors include the use of multiple antibiotics, the presence of an indwelling catheter, and a history of UTI.
Recommended Reading: Will A Urinary Tract Infection Go Away Without Antibiotics
What Is The Outlook
Most people improve within a few days of starting treatment. See a doctor if you do not quickly improve. If your symptoms do not improve despite taking an antibiotic medicine then you may need an alternative antibiotic. This is because some bacteria are resistant to some types of antibiotics. This can be identified from tests done on your urine sample.
You May Like: Mrx Rc Feline Urinary So
Uncomplicated Cystitis In Nonpregnant Patients
Uncomplicated cystitis occurs in patients who have a normal, unobstructed genitourinary tract who have no history of recent instrumentation and whose symptoms are confined to the lower urinary tract. Uncomplicated cystitis is most common in young, sexually active women. Patients usually present with dysuria, urinary frequency, urinary urgency, and/or suprapubic pain. Treatment regimens for uncomplicated cystitis in nonpregnant women are provided in Table 1, below.
References
Gupta K, Hooton TM, Naber KG, et al. International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: A 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 2011 Mar. 52:e103-20. . .
Wagenlehner FM, Schmiemann G, Hoyme U, Fünfstück R, Hummers-Pradier E, Kaase M, et al. . Urologe A. 2011 Feb. 50:153-69. . .
Abrahamian FM, Moran GJ, Talan DA. Urinary tract infections in the emergency department. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2008 Mar. 22:73-87, vi. .
Little P, Turner S, Rumsby K, Warner G, Moore M, Lowes JA, et al. Dipsticks and diagnostic algorithms in urinary tract infection: development and validation, randomised trial, economic analysis, observational cohort and qualitative study. Health Technol Assess. 2009 Mar. 13:iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-73. .
Foxman B. The epidemiology of urinary tract infection. Nat Rev Urol. 2010 Dec. 7:653-60. .
You May Like: Home Remedies For Urinary Urgency
Why Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections Are Most Common In Older Women
Urinary tract infections are an aggravation at any age, but theyre most common in older women. For senior women, UTIs can cause serious health problems and may not come with the usual symptoms.
At Alpenglow Gynecology, we help patients of all ages in Littleton, Colorado, treat the uncomfortable symptoms associated with UTIs. Rickie Guida, WHNP-BC and our entire care team are committed to helping older women understand and treat UTIs before they cause lasting damage. We offer a comprehensive line of womens health services to help you feel your best at every age.
Senior Uti Do You Know The Symptoms
Urinary tract infections, or UTIs, are the most common bacterial infection in older adults,affecting women more often than men.
UTIs can typically be treated effectively with antibiotics once diagnosed.Unfortunately, not all UTIs are treated quickly, and some aren’t even identified, particularly in seniors.
What is a UTI?
A UTI is an infection in the urinary tract. The urinary tract includes the kidneys, bladder, ureters and the urethra which carries urine out of the body. They are most commonly caused by bacteria but can also be a fungal infection.
A lower UTI is a common infection, affecting the lower part of the urinary tract, the urethra and urinary bladder. Infection of the urethra is urethritis while a bladder infection is cystitis. An upper UTI affects the kidneys.
What causes a UTI?
A typical bacterial UTI is caused by bacteria, often fecal bacteria, entering the urethra through the urethral opening where urine is released from the body. Usually, the body can fight off these bacteria and prevent infection. However, if the immune system is too weak, the bacteria multiply, causing infection.
Fungal UTIs usually stem from fungus in the bloodstream. Fungal UTIs are relatively uncommon, impacting mainly those with illnesses that compromised their immune system.
What are the symptoms of a UTI?
When typical, healthy adults get a UTI, the symptoms are usually easy to identify, and the infection is simple to diagnose:
If left untreated, a person may experience:
Also Check: Urinary Incontinence In Elderly Female
Can Uti Cause Permanent Dementia
There is no definitive answer to this question as the research on the matter is inconclusive. Some studies suggest that there is a link between UTIs and dementia, while other studies are not able to confirm this connection. It is possible that UTIs may contribute to the development of dementia, but further research is needed to determine if this is truly the case.
When bacteria enter the urethra through the urethra, they infect the bladder and kidneys, causing UTIs. Infection can cause serious health problems if left untreated. Urinary tract infections are commonly accompanied by fever, chills, or lower back pain. Despite this, dementia patients rarely succeed. UTIs can aggravate dementia symptoms, but they are not always indicative of dementia. Falls, recent incontinence, or a loss of appetite are all possible symptoms of a UTI infection. If left untreated, the infection can become life-threatening and spread to the blood stream.
Acute Uncomplicated Pyelonephritis : Symptoms And Remedies
It represents an upper urinary tract infection involving both the renal cavities and an involvement of the renal parenchyma .
Symptomatology is characterised by unilateral or bilateral low back pain, pain in the lumbar region, the classic Giordano ++ sign, hyperpyrexia with chills and sometimes nausea and vomiting.
The diagnosis is made by analysing the urinary sediment, where we find microhaematuria, pyuria, and sometimes cylindruria.
Here too, the bacterium most responsible for the infection is E.Coli, although to a lesser extent than in cystitis.
In the mild forms, therapy is based on the administration of targeted antibiotic therapy for 7 days, while in the more severe forms, the patient should be hospitalised in order to administer intravenous antibiotic therapy with the latest generation of drugs.
Recommended Reading: What To Take For Urinary Tract Infection
How To Prevent Uti Re
Following some tips can help you avoid getting another UTI:
- Empty your bladder often as soon as you feel the need to pee don’t rush, and be sure you’ve emptied your bladder completely.
- Wipe from front to back after you use the toilet.
- Drink lots of water.
- Choose showers over baths.
- Stay away from feminine hygiene sprays, scented douches, and scented bath products they’ll only increase irritation.
- Cleanse your genital area before sex.
- Pee after sex to flush out any bacteria that may have entered your urethra.
- If you use a diaphragm, unlubricated condoms, or spermicidal jelly for birth control, you may want to switch to another method. Diaphragms can increase bacteria growth, while unlubricated condoms and spermicides can irritate your urinary tract. All can make UTI symptoms more likely.
- Keep your genital area dry by wearing cotton underwear and loose-fitting clothes. Donââ¬â¢t wear tight jeans and nylon underwear they can trap moisture, creating the perfect environment for bacteria growth.
Show Sources
Strengths And Limitations Of The Review

The strengths of this review are mainly due to its methodological quality that it utilised a broad search strategy, with no limits to age or date applied. This allowed for studies that were representative of an elderly population and without the explicit aim of reporting the relationship between confusion and UTI to be identified. Another strength of this review was the registration of a protocol with pre-specified objectives and methods. The use of a second reviewer independently assessing the quality of selected studies also increases the quality of the review. Limitations included limiting articles to English and being unable to assess the eligibility of the unobtainable full-texts. This review also did not attempt to include studies from the unpublished literature, introducing possible publication bias.
Read Also: Best Way To Clean Urinary Tract
How Is It Diagnosed
If doctors suspect that a UTI is present, they will test a urine sample in the office or send it to a laboratory for a urinalysis.
A urine culture can confirm which bacteria are causing the infection. Knowing the specific type of bacteria allows the doctor to determine a suitable treatment plan.
A condition called asymptomatic bacteriuria is also common in older adults. ASB occurs when there are bacteria in the urine, but they do not cause any signs or symptoms of infection.
Although ASB is common in older adults, it does not typically require treatment, unless it causes other clinical symptoms.
The standard treatment for a UTI is antibiotics, which kill the bacteria causing the infection. Doctors will prescribe an antifungal medication instead if a fungus is causing the UTI.
It is essential that people take the antibiotic or antifungal medication precisely according to the prescription, even if they begin to feel better. Completing the entire prescription will help to destroy all of the infectious bacteria.
How Urinary Tract Infections Affect The Elderly
Elderly patients who need catheters to urinate are at increased risk for urinary tract infections, especially if they recently had surgery for urinary dysfunction.
Older people who have a depressed immune system, like diabetes, may also not be able to naturally protect themselves against the bacteria. This can lead to current urinary tract infections.
Elderly men who have an enlarged prostate can suffer complications that increase their risk for urinary tract infections. The abnormal prostate can trap urine inside the bladder, which leads to recurrent urinary tract infections.
Read Also: How Long To Get Rid Of Urinary Tract Infection
Why Do Utis Affect Older People Mentally
You can explain this as part of normal aging because your immune response changes over time. According to Dr. Pearson, any type of stress, physical or emotional, can cause an older adult to become confused.
Delirium From A Uti Can Worsen Quickly: Get Prompt Medical Attention
Antibiotics can be used to treat UTIs, which are common. When someone is experiencing delirium from UTI, their condition may quickly deteriorate. When someone is inrium, they are unable to comprehend what is happening around them and can engage in dangerous behaviors. If a person is suffering delirium as a result of their UTI, their condition can quickly deteriorate. If you or a loved one is experiencing delirium from a UTI, the best thing you can do is seek medical attention as soon as possible. It is critical that patients receive prompt treatment in order to improve their condition and prevent the infection from spreading.
Immunostimulants Studied In Humans
Strovac comprises ten strains of heat-killed uropathogens administered by intramuscular injection. This product was subsequently replaced by a vaginal preparation known as Urovac vaginal vaccine owing to considerable adverse reactions at the administration site. A meta-analysis of three randomized, placebo-controlled phase II studies consisting of 220 women demonstrated a modest effect that supports the need for further investigation of this immunostimulant . Benefits were highest in those patients receiving booster doses of the vaccine at monthly intervals,, but data are from small studies. Large, randomized phase III trials are required to establish the efficacy of this therapeutic option.
Recommended Reading: Malignant Genital Or Urinary Neoplasm
The Urinary Tract Infection Risks Factors For Male Seniors May Include:
- Kidney Stones and Bladder Stones: Kidney stones and bladder stones along the urinary tract can occur among older men. This obstruction of the urine outflow tract often causes pooling of urine and provides a suitable medium in which organisms can grow and thrive.
- Urethral Strictures: Narrowing of the outflow tract can cause a full bladder, and difficulty in voiding urine. Stones occluding the urinary tract may cause urethral strictures.
- Enlarged Prostate: This is an age-related condition, as prostates usually increase in size as a man ages. This may be due to the increase in the levels of sex hormones, however, causing difficulty in urination.
- Bacterial Prostatitis: The proximity of the prostate to the urinary bladder could easily transmit infections to the bladder when the prostate becomes infected by bacteria.
- Catheter Use: Prolonged use of a catheter to drain urine from the bladder is a risk factor for urinary tract infection.
You May Like: How To Treat Urinary Urgency
Other Ways To Prevent Some Utis Coming Back
If you keep getting a bladder infection , there is some evidence it may be helpful to take:
- D-mannose a sugar you can buy as a powder or tablets to take every day
- cranberry products available as juice, tablets or capsules to take every day
Speak to your doctor before taking any of these during pregnancy.
Be aware that D-mannose and cranberry products can contain a lot of sugar.
If you’re taking warfarin, you should avoid cranberry products.
Page last reviewed: 22 March 2022 Next review due: 22 March 2025
Also Check: What Is The Best Medicine For Urinary Tract Infection
Simple Ways To Prevent A Uti In Elderly Women
Urinary tract infections, or UTIs, are more than a painful medical condition. Left untreated, these infections can spread through the body. The leading cause of sepsis, an untreated UTI can ultimately result in death. For caregivers of elderly patients, learning how to recognize a UTI can be tricky as the symptoms are varied. Fortunately, there are three easy ways to avoid the onset of the infection to begin with.
Recommended Reading: Hollister Vented Urinary Leg Bag
Prevention Of Urinary Tract Infections In Elderly Adults

Preventive measures can be adopted to reduce the risk of urinary tract infections. It is worthy of note that not all urinary tract infections are preventable. Precautionary steps are usually advised, especially for the elderly adults who are at a higher risk of getting infected.
Consider the following strategies to help your elderly parent prevent a urinary tract infection:
- Stay Hydrated: Water is said to be a cleansing solvent, and water helps in staying hydrated. We are recommended to drink eight 8-ounce glasses of water daily.
Water keeps the body system active, and also flushes small stones that may later calcify to form bigger stones, which could then obstruct the outflow tracts. Staying hydrated could also help clear the mind and reduce the frequency of confusion.
- Drink Cranberry Juice: Some urologists believe that an ingredient in cranberry juice helps senior citizens prevent the growth or adherence of bacteria to the bladder, reducing the chance of getting infected. However, there is no scientific-proven evidence for this belief.
- Avoid Alcohol and Caffeine: Alcohol and Caffeine are referred to as bladder irritants in the elderly adults. Alcohol is detrimental to a seniors health. Alcohol use can lead to more confusion, hallucinations, or change in typical behaviors. Chronic use of alcohol could damage vital organs of the body, which further worsen a seniors immunity.
Dont Miss: Natural Remedies For Urinary Incontinence
Recommended Reading: How Treat Urinary Tract Infection Naturally