When You Should Call Your Healthcare Provider
-
Symptoms that do not improve within 48 hours of starting treatment
-
Fever
-
A fever that goes away but returns after starting treatment
-
Increased abdominal or back pain
-
Signs of dehydration
-
Vomiting or inability to tolerate prescribed antibiotics
-
Child begins acting sicker
-
If a urine culture was done, make sure to get the results from the healthcare provider. Make an appointment to follow up about a week after your child has finished antibiotics.
Causes Of Urinary Tract Infection In Toddler Boys
Urinary tract infections are a result of bacterial growth in the urinary tract. Urinary tract infection in toddler boys may occur due to one of the following reasons:
- Male babies are more likely to experience a urinary tract infection than older boys because of the proximity and duration of wearing soiled diapers. For toilet trained toddler boys, the chief cause of urinary tract infections is incontinence. When urine pools on the diaper/underwear, bacteria are able to enter the urethra
- In the case of toilet trained toddlers, poor hygiene could lead to a urinary tract infection. Chances are once your toddler is left to his own devices he won’t wash his hands thoroughly. Parents should make sure hands are thoroughly cleaned after every trip to the bathroom and the genital area is properly cleaned when bathing.
- At times frequent and persistent urinary tract problems may hint at a deeper urinary system disorder. If your toddler has over three UTI’s in a year, consult your doctor.
Urinary Tract Infections In Boys
- Urology
Urinary tract infections in boys are the result of bacteria getting into the bladder and staying there. UTIs are common in kids, especially girls and uncircumcised boys. E. Coli, responsible for over 75% of UTIs, doubles every 20 minutes in the bladder. That means if there are 100 bacteria of E. Coli in the bladder and you wait three hours to go to the bathroom, you will have over 50,000 bacteria in your bladder. The more bacteria in the bladder and the longer it stays there, the more likely you are to get a UTI.
There are many things that can be done to both treat urinary tract infections in boys and prevent them in the future.
Also Check: Urinary Incontinence After Prostate Removal
How To Treat A Urinary Tract Infection In Babies
Before a treatment is prescribed for babies or young children, doctors often recommend a urine culture to determine if bacteria are present in the urine. It is critical to treat UTIs as infections in the urethra and bladder can lead to pyelonephritis and kidney damage. Recurrent infections can also lead to kidney damage. First signs of uti in babies can be difficult to pinpoint at first.
Obviously, babies cannot give a urine sample on command. The doctor may obtain a urinalysis by drawing a sample via a catheter. It may take a day or so to get the result of a urine culture. Until then, attempt to alleviate any discomfort that your baby is feeling.
When a UTI has been diagnosed by a doctor, a baby will be given oral antibiotics to combat the infection . Aside from antibiotics, there are other remedies including the following:
How Are The Infections Diagnosed
The doctor will give your child a physical examination and ask about his or her symptoms. Your child also will have lab tests, such as a urinalysis and a urine culture, to check for germs in the urine. It takes 1 to 2 days to get the results of a urine culture, so many doctors will prescribe medicine to fight the infection without waiting for the results. This is because a child’s symptoms and the urinalysis may be enough to show an infection.
After your child gets better, the doctor may have him or her tested to find out if there is a problem with the urinary tract. For example, urine might flow backward from the bladder into the kidneys. Problems like this can make a child more likely to get an infection in the bladder or kidneys.
Recommended Reading: Cystex Plus Urinary Pain Relief
Urinary Tract Infections In Children: Why They Occur And How To Prevent Them
See related article on urinary tract infections.
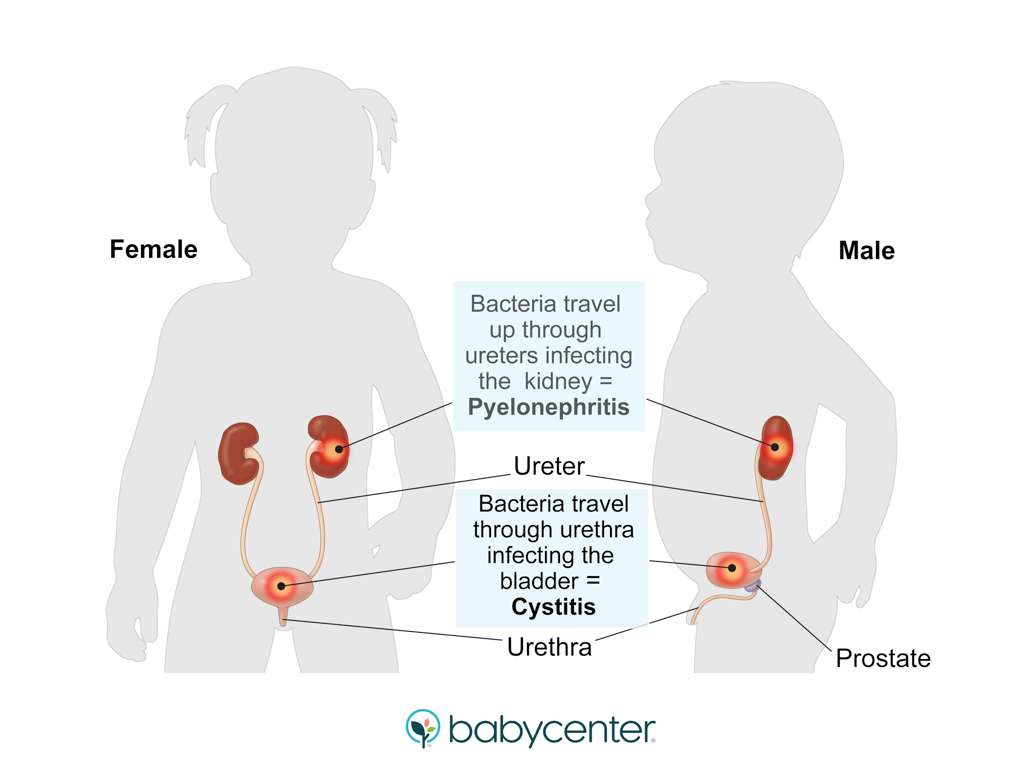
The urinary tract has these parts:
The kidneys, where urine is made.
The ureters, tubes that carry urine from each kidney to the bladder.
The bladder, where urine is stored.
The urethra, a tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. The opening is at the end of the penis in boys and near the vagina in girls.
What Are Symptoms Of A Urinary Tract Infection In Babies
Urinary Tract Infection In Babies Once the first signs of uti in babies are apparent, parents should seek prompt treatment. It may be more difficult to detect a urinary tract infection in babies as they cannot communicate what they are experiencing . Here are a few symptoms of which parents should remain vigilant:
Read Also: Labs For Urinary Tract Infection
When May My Child Need To Be Hospitalized For A Uti
Your child may need to be hospitalized for the following reasons:
- If theyre a young infant or child.
- If they have a high fever.
- If they have back pain.
- If theyre dehydrated .
- If he or she is unable to tolerate oral antibiotics.
- When there is a concern that the infection has spread to their bloodstream.
What Causes Utis In Children
When bacteria enters the urinary tract and multiplies, it can cause a UTI. The bacteria most frequently come from the gut, usually in the faeces , and this can infect the urinary tract. In some children, constipation can increase the risk of developing an infection.
Sometimes, UTIs are caused by a condition called urinary reflux. This condition develops when there is a problem with the bladder valve and urine flows in the wrong direction, back up into the kidneys from the bladder. If you suspect your child has a UTI, its important that they see their doctor and have this investigated, to prevent complications such as kidney scarring.
Read Also: How To Take Azo Urinary Tract Defense
Suggestions That May Help Some Children
Parents often want to know what they can do to prevent UTIs. Not all UTIs can be prevented, but here are some suggestions that may help some children:
- treat any constipation
- encourage your child to go to the toilet regularly when they feel the need
- encourage your child to sit properly on the toilet with their feet on a stool so that they empty their bladder completely
- make sure your child drinks plenty of water with meals, and during hot weather
- teach girls to wipe their bottoms from front to back rather than back to front
There is a suggestion in studies of UTI in boys that circumcision might slightly reduce the incidence of UTI. But the benefit is small. Most specialists would not recommend circumcision for this reason unless there are repeated UTIs which are causing major health problems.
Virulence Factors Of Pathogens
Virulence factors of pathogens increase the likelihood that a specific bacterial strain will colonize and subsequently invade the urinary tract. These factors include -hemolysin, M hemagglutinin, endotoxin, cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1, K capsular antigen, a rigid cell wall, serum resistance ability due to the outer membrane protein TraT, aerobactin which supports growth by chelating iron, and adhesive capacity . The three different types of adhesins identified on uropathogenic E. coli include type 1 pili , P-fimbriae and X-adhesins . These adhesins facilitate adherence of the bacteria to mucosal receptors in the uroepithelium in spite of the flushing action of urine flow . Once the uroepithelium is invaded, an intracellular biofilm is formed . The biofilm can protect the uropathogenic E. coli from the host immune system .
You May Like: Royal Canin Vet Diet Urinary S O
What Puts My Child At Risk Of Getting A Uti
UTIs are common. They are most common in babies under the age of 12 months but can affect children of any age.
There are some conditions which put babies and children at higher risk of UTIs:
- constipation
- an abnormality of the urinary tract
- neurological conditions where the bladder doesn’t empty properly
Treatment Of Uti In Children
Your childs UTI will require prompt antibiotic treatment to prevent kidney damage. The type of bacteria causing your childs UTI and the severity of your childs infection will determine the type of antibiotic used and the length of treatment.
The most common antibiotics used for treatment of UTIs in children are:
- nitrofurantoin
- sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim
If your child has a UTI thats diagnosed as a simple bladder infection, its likely that treatment will consist of oral antibiotics at home. However, more severe infections may require hospitalization and IV fluids or antibiotics.
Hospitalization may be necessary in cases where your child:
- is younger than 6 months old
- has a high fever that isnt improving
- likely has a kidney infection, especially if the child is very ill or young
- has a blood infection from the bacteria, as in sepsis
- is dehydrated, vomiting, or unable to take oral medications for any other reason
Pain medication to alleviate severe discomfort during urination also may be prescribed.
If your child is receiving antibiotic treatment at home, you can help ensure a positive outcome by taking certain steps.
During your childs treatment, contact their doctor if symptoms worsen or persist for more than three days. Also call their doctor if your child has:
- a fever higher than 101F
- for infants, a new or persisting fever higher than 100.4F
You should also seek medical advice if your child develops new symptoms, including:
- pain
Don’t Miss: How To Treat E Coli Urinary Tract Infection
A Pharmacist Can Help With Utis
You can ask a pharmacist about treatments for a UTI. A pharmacist can:
- offer advice on things that can help you get better
- suggest the best painkiller to take
- tell you if you need to see a GP about your symptoms
Some pharmacies offer a UTI management service and can prescribe antibiotics if they’re needed.
Urinary Tract Infections In Babies
It can be hard to figure out whats wrong with babies when all they can do to communicate pain is cry. A fussy infant may have any number of health problems, from colds to rashes, but some medical problems are harder to identify than others. For example, many parents may not know that babies can get infections in their urinary tract. In fact, childhood urinary tract infections account for more than 1 million pediatrician visits each year in the US.
UTIs are usually caused by bacteria in the kidneys, ureters , or bladder. Sometimes the body can rid itself of this bacteria but when it cannot, the bacteria can build up and cause an infection. Bacteria and other infection-causing microbes may enter the urinary tract when an infant has a dirty diaper or when babies are wiped from back to front. Good hydration enabling frequent urination and maintaining proper hygiene can help prevent UTIs.
Don’t Miss: Hollister Vented Urinary Leg Bag
Local Patterns Of Antibiotic Resistance Should Determine Choice Of Empiric Therapy
Empiric therapy for neonatal UTI and sepsis are similar because of common etiology. Traditionally parental antibiotics such as ampicillin and gentamicin are started once appropriate cultures are obtained. Within the US, the incidence of ampicillin resistance in neonatal E. coli isolates has been reported to be as high as 75% and gentamicin resistance as high as 12%17%.54,55 In spite of approximately 90% resistance against ampicillin among the E. coli isolates from a neonatal ward, Taheri and colleagues56 reported that clinical response was obtained in 50% of the patients, suggesting that that there is a discordance between in vitro and in vivo activity of these drugs. This may be because the urinary concentration of ampicillin is much higher than the plasma level since it is excreted through the kidneys which may allow it to overcome the minimum inhibitory concentration of certain pathogens.57
How To Prevent Urinary Tract Infections In Babies
How to prevent urinary tract infections in babies starts in first understanding the why this occurs. The causes of urinary tract infections in babies differ from those of an adult. As we age, urinary problems may become more prevalent. The bladder muscles may fail, and bladder control is lost. Bladder stones, bladder cancer, an overactive bladder or the eventual need for a catheter are frequent causes of urinary tract infections in adults. However, the causes are different for infants, and often, the only sign is an unexplained fever. Therefore, it is important to prevent UTIs from occurring as much as possible.
Drink plenty of fluids. Make sure your baby is drinking enough water as this helps to flush the toxins from their bladder and kidneys. This reduces the risk of UTIs significantly .
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Urinary Tract Infection At Home
Key Points To Remember About Urinary Tract Infections
- a urinary tract infection is an infection in the urine
- UTIs are common in children
- UTIs can cause children to have high temperatures and become unwell
- sometimes UTIs can make children seriously ill, especially babies and young children – see your doctor or after-hours medical centre urgently if that happens
- babies under 12 months need investigation after a UTI to see if there is anything wrong with their urinary tract
How Is A Urinary Tract Infection Diagnosed How Do Healthcare Providers Test For A Uti In Toddlers
After interviewing you about your childs history and performing a physical examination, the healthcare provider may order the following tests:
- Urine tests like the leukocyte esterase and a urine culture to test for the presence of bacteria or white blood cells.
- Blood tests looking for infection or kidney function.
- Ultrasound or CT of the kidneys and bladder.
- Voiding cystourethrogram , which evaluates the bladder and urethra to detect vesicoureteral reflux .
Also Check: How Does Kidney Failure Affect The Urinary System
What Are Risk Factors For Utis In Children
Risk factors predisposing for childhood UTIs include the following:
- urinary urgency , and
- loss of previously established urinary control .
Nonspecific but common symptoms include fever and abdominal pain. For some children less than 2 years of age, these more subtle problems may be the only indicator of a UTI. Associated symptoms of concern include flank pain, fever, and vomiting. Obvious blood in the urine as well as a positive family history for childhood urinary tract infections are also red flags and should raise the level of concern. Interestingly, the odor and color of the urine are not predictors of a UTI.
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection In Children

A UTI is when bacteria gets into your urine and travels up to your bladder. As many as 8 in 100 of girls and 2 in 100 of boys will get UTIs. Young children have a greater risk of kidney damage linked to UTI than older children or adults.
How Does the Urinary Tract Work?
The urinary tract is the organs in your body that make, store, and get rid of urine, one of the waste products of your body. Urine is made in the kidneys and travels down to the bladder through the ureters . The kidneys make about 1½ to 2 quarts of urine a day in an adult, and less in children, depending on their age. In children, the bladder can hold 1 to 1½ ounces of urine for each year of age. For example, a 4-year-old childs bladder can hold 4 to 6 ouncesa little less than a cup.
The bladder stores the urine until it is emptied through the urethra, a tube that links the bladder to the skin, when you urinate. The urethra opens at the end of the penis in boys and in front of the vagina in girls.
The kidneys also balance the levels of many chemicals in the body and check the blood’s acidity. Certain hormones are also made in the kidneys. These hormones help control blood pressure, boost red blood cell production and help make strong bones.
Normal urine has no bacteria in it, and the one-way flow helps prevent infections. Still, bacteria may get into the urine through the urethra and travel up into the bladder.
Don’t Miss: Myasthenia Gravis And Urinary Incontinence
What Is The Urinary Tract
The urinary tract gets rid of extra fluids and waste. The kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra are the organs that make up the tract. The kidneys filter blood and make the urine, the urine travels through the ureters to the bladder which stores the urine and then the urine passes through the urethra and out of the body.
Things You Can Do Yourself
To help ease pain:
- takeparacetamolup to 4 times a day to reduce pain and a high temperature for people with a UTI, paracetamol is usually recommended over NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or aspirin
- you can give childrenliquid paracetamol
- rest and drink enough fluids so you pass pale urine regularly during the day, especially during hot weather
It’s important to follow the instructions on the packet so you know how much paracetamol you or your child can take, and how often.
It may also help to avoid having sex until you feel better.
You cannot pass a UTI on to your partner, but sex may be uncomfortable.
Taking cystitis sachets or cranberry products has not been shown to help ease symptoms of UTIs.
You May Like: Treatment Of Urinary Tract Infection In Pregnancy