Is It Possible To Prevent Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections With A Vaccine
Currently, there are no commercially available vaccines for UTIs, either recurrent or first-time infections. One of the problems in developing a vaccine is that so many different organisms can cause infection a single vaccine would be difficult to synthesize to cover them all. Even with E. coli causing about most infections, the subtle changes in antigenic structures that vary from strain to strain further complicate vaccine development even for E. coli. Researchers are still investigating ways to overcome the problems in UTI vaccine development.
How Utis Are Diagnosed
In most cases, if you think you have a UTI, you should visit a health care provider and give a urine sample for testing. A urinalysis is a test that looks for white blood cells, red blood cells, bacteria, and or other chemicals such as nitrites in your urine. A proper urinalysis can pinpoint an infection and a urine culture can help your health care provider choose the best antibiotic for treatment. It is vital to get a urinalysis and culture performed to make sure you have an infection and require care. Use of antibiotics when not needed, can be tricky, and can lead to greater rates of bacterial antibiotic resistance.
It should be noted that some individuals get a urinalysis result that shows bacteria, but the individuals are not having any symptoms of a UTI. This event is common in older adults. If the individual has bacteria in their urine, but has no symptoms, treatment is not right. Treatment should be given to individuls who have bacteria and associated UTI symptoms.
In closing, it should be noted that studies on cranberry juice and linked supplements are mixed. Some studies show that cranberry supplements can be helpful and other studies show that they don’t help stop UTIs before they happen. Be sure to read about the pros and cons of cranberry products, and decide if they’re right for you. For now, practice these tips to lower your risk of getting a UTI.
What Happens If A Uti Goes Untreated For An Older Person
UTI infections that go untreated can spread from your bladder to your kidneys and beyond. Especially in older adults or anyone with a lowered immune system, treating an infection earlier can keep it from spreading and overwhelming your system.
An infection that goes untreated can lead to , a serious form of infection. Dr. Slopnick says fear of sepsis is what causes some people to worry about asymptomatic bacteriuria. If you have a UTI, youll almost certainly show symptoms long before the infection spreads or sepsis sets in.
Also Check: How To Cure A Urinary Tract Infection In A Woman
Are Utis Caused By Bacteria Or Viruses
Most UTIs are caused by bacteria, and E. coli is the most common culprit. Some UTIs are fungal, in which case theyre usually caused by the Candida fungus. UTIs can also be viral, but viral UTIs are rare.
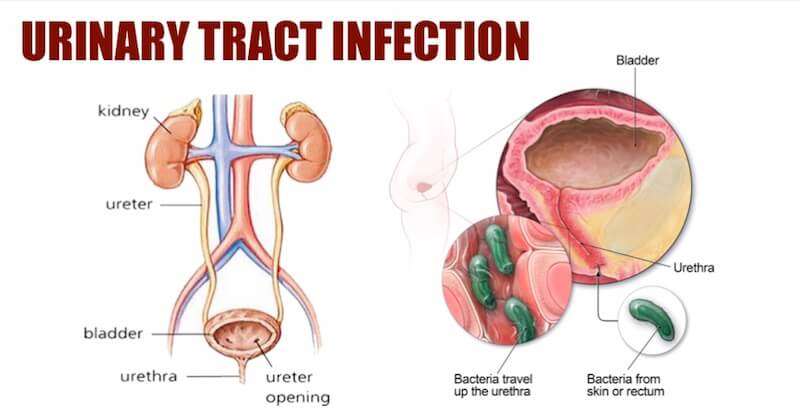
Since the urethra is open to the outside of your body, bacteria or other germs can enter your urethra and travel up the urinary tract to your bladder.
Symptoms of a bladder infection can include:
-
A constant urge to pee
-
A painful, burning sensation when urinating
-
Peeing only small amounts of urine at a time
-
Bloody or cloudy urine
You May Like: Herbs For Urinary Tract Health
How Do I Know If The Treatment Isnt Working
If the treatment isnt working, your symptoms will stay the same, get worse, or you will develop new symptoms. Call your doctor if you have a fever , chills, lower stomach pain, nausea, and vomiting. You should also call your doctor if, after taking medicine for 3 days, you still have a burning feeling when you urinate. If you are pregnant, you should also call your doctor if you have any contractions.
You May Like: Probiotic Supplements For Urinary Tract
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection occurs when fecal bacteria enter the urethra, the tube through which urine is excreted from the bladder. Sexually transmitted bacteria can also enter the urethra and cause an infection.
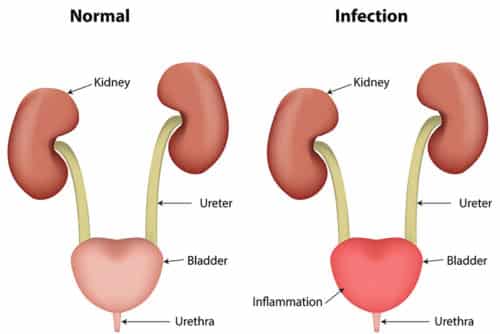
There are three types of urinary tract infections. The first, urethritis, is an infection localized to the urethra. When an infection spreads from the urethra to the bladder, it is known as cystitis. These two infections are the most common and easily cured, but it is possible for an infection to spread from the bladder to the kidneys. The kidneys filter waste from the blood, passing the waste on for collection in the bladder. A kidney infection is much more serious and rare.
How Are Urinary Tract Infections Diagnosed
Your doctor will usually be able to tell whats causing your pain by your description of your symptoms, along with a physical exam. Testing your urine can also help your doctor identify what type of infection you have. Usually, a sample of your urine is taken in your doctors office and sent to a lab to check for infection.
Don’t Miss: Does Urinary Infection Cause Back Pain
Cranberry Juice And Tablets
Cranberry juice and tablets have been shown to reduce RUTIs as they contain a compound called tannin, or proanthocyanidin, which reduces E. coli vaginal colonisation.65,66 Although earlier, smaller studies have shown that consuming cranberry juice or tablets can prevent RUTIs, an updated Cochrane review showed that evidence for its benefit in preventing UTIs is small therefore, cranberry juice cannot be recommended any longer for UTI prevention.21,6769
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection In Pregnancy
UTI is the most frequent medical complication of pregnancy. The risk factors of preterm delivery, low infant birth weight and abortions are most commonly associated with symptomatic and asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy.77 In pregnancy, factors that contribute to UTI risk are ureteric and renal pelvis dilation increased urinary pH decreased muscle tone of the ureters, and glycosuria, which promotes bacterial growth. Treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy reduces the risk of pyelonephritis. As RUTIs are common in pregnancy, they need prophylactic treatment if they occur. Screening for bacteriuria is recommended in all pregnant women at their first prenatal visit and then in the third trimester.82,83 They should subsequently be treated with antibiotics such as nitrofurantoin, sulfisoxazole or cephalexin.21,24,8284 Antibiotic prophylaxis for RUTI in pregnant women is effective using continuous or post-coital regimens. The causative organisms of UTI in pregnancy are similar to those found in non-pregnant patients, with E. coli accounting for 8090% of infections.85,86 Urinary group B streptococcal infections in pregnant women need to be treated and followed by intrapartum prophylaxis.21
Recommended Reading: Female Urinary Incontinence Treatment Options
After Youve Had One Your Risk For Having Recurrent Utis Increases With Each Uti You Have And 27 Percent Of Women Have More Than Two Utis Every Year
Story by: Kim Huston on April 16, 2018
Ladies: Most of us have had a urinary tract infection at least once. If you havent, theres a pretty good chance you will. The National Kidney Foundation states one in five women will have at least one UTI in her lifetime. After youve had one, your risk for having recurrent UTIs increases with each UTI you have. And 27 percent of women have more than two UTIs every year.
What Are Risk Factors For Recurrent Utis
-
Having had a UTI in the past
-
Incomplete emptying of the bladder, such as after menopause
-
A weakened immune system
The influence of these risk factors also differs for women depending on their age. In young, pre-menopausal women, the most common risk factor for recurrent UTIs is frequency of sexual intercourse. Having sex more than 9 times a month makes them twice as likely to have recurrent UTIs compared to having sex 4 to 8 times in a month.
In postmenopausal women, the strongest risk factor is related to the ability to empty the bladder. If you have urinary incontinence or a condition that keeps you from being able to completely empty your bladder, your risk of recurrent UTIs is higher.
If you have recurrent UTIs, your healthcare provider may suggest antibiotics for prevention. That means youd be taking an antibiotic regularly to prevent another UTI, rather than treat an existing one.
Also Check: How To Clear Urinary Tract Infection
Read Also: Azo Urinary Tract Health Gummies
How Can I Prevent A Uti
The No. 1 way to prevent a UTI is to empty your bladder completely and often. Dr. Slopnick suggests urinating every few hours, whether you feel the need to go or not.
She also recommends these tried-and-true prevention strategies:
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Utis
UTIs can cause such signs as:
- pain, burning, or a stinging sensation when peeing
- an increased urge or more frequent need to pee
- waking up at night a lot to go to the bathroom
- belly pain in the area of the bladder
- foul-smelling pee that may look cloudy or contain blood
If you have any symptoms of a UTI, you’ll need to go to a doctor right away. The sooner you begin treatment, the less uncomfortable you’ll be. Call your doctor’s office or clinic. If you can’t reach your doctor, you can visit an urgent care center or hospital emergency room. The most important thing is to take action as soon as possible.
Read Also: What Home Remedy Is Good For Urinary Tract Infection
Can You Have Sex If You Have A Uti
In general, it is recommended that you avoid having intercourse when you have an active urinary tract infection. When you get an antibiotic prescription, ask your doctor when the right time to resume sexual activity would be. Of course, you can still kiss and have other intimate and emotional connections.
Once you have completed a course of antibiotics and the UTI has cleared away, you should be able to resume sexual activity. But be sure to take the careful steps necessary to prevent the sex from putting you on the road to yet another one.
How Are Utis Treated And Prevented
A UTI is often a once-off illness that resolves quickly and responds to treatment with antibiotics if needed. However, for some people, UTIs are a recurring problem.
If you have repeated UTIs there are some self-help measures that may help prevent further infections:
- drink more fluids to help flush out bacteria
- urinate immediately after intercourse
- gently wipe from front to back after urinating
- wear cotton underwear and loose-fitting pants
- eat natural yoghurt to restore normal vaginal environment
- find an alternative method of birth control if you use spermicides
There is conflicting evidence for drinking cranberry juice to prevent UTIs. If you want to try cranberry products, ask your doctor for advice.
Read Also: Can A Urinary Tract Infection Cause Incontinence
Can Utis Be Prevented
A few things can help prevent UTIs. After peeing, girls should wipe from front to back with toilet paper. After BMs, wipe from front to back to avoid spreading bacteria from the rectal area to the urethra.
Also, go to the bathroom when needed and don’t hold the pee in. Pee that stays in the bladder gives bacteria a good place to grow.
Keep the genital area clean and dry. Girls should change their tampons and pads regularly during their periods. Bubble baths can irritate the vaginal area, so girls should take showers or plain baths. Avoid long exposure to moisture in the genital area by not wearing nylon underwear or wet swimsuits. Wearing underwear with cotton crotches is also helpful. Skip using feminine hygiene sprays or douches, as these can irritate the urethra.
If you are sexually active, go to the bathroom both before and within 15 minutes after sex. After sex, gently wash the genital area to remove any bacteria. Avoid sexual positions that irritate or hurt the urethra or bladder. Couples who use lubrication during sex should use a water-soluble lubricant such as K-Y Jelly.
Finally, drinking lots of water each day keeps the bladder active and bacteria-free.
UTIs are uncomfortable and often painful, but they’re common and easily treated. The sooner you contact your doctor, the sooner you’ll be able to get rid of the problem.
A Pharmacist Can Help With Utis
You can ask a pharmacist about treatments for a UTI.
A pharmacist can:
- offer advice on things that can help you get better
- suggest the best painkiller to take
- tell you if you need to see a GP about your symptoms
Some pharmacies offer a UTI management service. They may be able to give antibiotics if they’re needed.
Read Also: Urinary Tract Infection Vaginal Bleeding
Check If It’s A Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms of a urinary tract infection may include:
- pain or a burning sensation when peeing
- needing to pee more often than usual during the night
- pee that looks cloudy, dark or has a strong smell
- needing to pee suddenly or more urgently than usual
- needing to pee more often than usual
- lower tummy pain or pain in your back, just under the ribs
- a high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
Clinical Presentation And Diagnosis
Common symptoms of a UTI are dysuria, urinary frequency, urgency, suprapubic pain and possible haematuria. Systemic symptoms are usually slight or absent. The urine may have an unpleasant odour and appear cloudy.23 Diagnosis of RUTI depends on the characteristic of clinical features, past history, three positive urinary cultures within the previous 12-month period in symptomatic patients and the presence of neutrophils in the urine .7,8,21 Irritative voiding symptoms are present in 2530 % of women with RUTIs.25 The probability of finding a positive culture in the presence of the above symptoms and the absence of vaginal discharge is around 81%.26 In a complicated UTI, such as pyelonephritis, the symptoms of a lower UTI will persist for more than a week with systemic symptoms of persistent fever, chills, nausea and vomiting.25
Women with RUTIs should have an initial evaluation including a history-taking and a physical and pelvic examination the latter is important to detect pelvic organ prolapse and to assess the status of the vaginal epithelium.28 Urinalysis and urine culture with sensitivity are also valuable investigations. Women with a positive family history of DM, obesity or RUTI must be screened for DM.28,29 Women with suspected urine retention need to be evaluated for high post-void residual urine volume.
You May Like: What Can I Do To Prevent Urinary Tract Infections
How Do Women Get Utis
Women have a more than 50% chance of getting a UTI at some point. This is much more likely than men.
Women at higher risk include those who:
- Are pregnant .
- Are post-menopausal .
- Have pelvic organ prolapse, which makes it harder to empty the bladder.
- Use certain forms of birth control, such as diaphragms or spermicide.
- Have diabetes.
Do I Need To See A Doctor

Yes. Painful urination can be a symptom of a more serious problem. You should tell your doctor about your symptoms and how long youve had them. Tell your doctor about any medical conditions you have, such as diabetes mellitus or AIDS, because these could affect your bodys response to infection. Tell your doctor about any known abnormality in your urinary tract, and if you are or might be pregnant. Tell your doctor if youve had any procedures or surgeries on your urinary tract. He or she also need to know if you were recently hospitalized or stayed in a nursing home.
Read Also: Garden Of Life Urinary Tract Probiotics
Suggested Imaging Evaluation Of A Child With A Uti
Children who are to have a cystogram as part of the imaging evaluation for a UTI should receive therapeutic or suppressive doses of antibiotic until after the bladder imaging study. The following recommendations for the imaging evaluation of children following a UTI are based on a review of the literature, experience and reason.
-
In the neonate with urosepsis and in the infant, child or adolescent with a clinical diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis documented by urine culture:
Urinary tract ultrasound examination to identify an obstructive abnormality.
A contrast voiding cystourethrogram to evaluate the urinary bladder and urethra and detect vesicoureteral reflux.
Management of the acute illness is based on the clinical diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis. A significant obstructive abnormality will be disclosed by ultrasound examination. If vesicoureteral reflux is present, long-term suppressive antibiotic therapy may be indicated.30 Some clinicians recommend six months of suppressive antibiotic therapy for children who have pyelonephritis in the absence of vesicoureteral reflux . This is, however, an empiric recommendation related to the relatively high recurrence rate of UTIs in girls in the first months following a primary infection.
-
In the infant or child from about one to five years of age who has had one or several episodes of cystitis that responded promptly to therapy:
Urinary tract ultrasonography to identify structural abnormalities.
Imaging Evaluation Following A Uti
An algorithm for the management of children with the presumptive diagnosis of a UTI is presented in Figure 1. The literature describing various protocols for the imaging evaluation of the urinary tract following a UTI is extensive. Unfortunately, no prospective studies with long-term outcome data are available.21 Some experts recommend that all children with a UTI be investigated with urinary tract ultrasonography. With regard to children younger than one year, two years or five years, some experts recommend urinary tract ultrasonography and cystography.2226 Some would obtain only cortical imaging or cystography if these studies are normal. In addition, there are those who suggest that no imaging is needed in the child with cystitis who responds promptly to treatment.2729
Also Check: What Causes Urinary Urgency In Males