Overactive Bladder Is A Common And Treatable Condition
Urge incontinence is usually associated with a strong, almost overpowering sense of a need to urinate with concern that you will not be able to make it to the bathroom in time. Overactive bladder may occur with or without urine leakage . Common symptoms are:
- Frequent urge to urinate, in the daytime and at night
- Loss of urine without meaning to urinate
- Sudden and urgent need to urinate
- Bladder pain or discomfort
This condition may be due to actual spasms of the bladder muscle or increased sensitivity of the bladder. These bladder spasms often happen when your bladder is not very full and can be triggered by hearing or feeling running water, cold air or even arriving at home and putting your key in the door. Occasionally it is triggered by a particular amount of urine in the bladder.
Physical Therapy For Pelvic Floor Muscles
Medications that relax the bladder can be effective for alleviating symptoms of overactive bladder and reducing episodes of urge incontinence. These drugs include tolterodine , oxybutynin , an oxybutynin skin patch , trospium , solifenacin , darifenacin and now mirabegron . These medications are usually used in combination with other treatments.
What Are The Causes Of Overactive Bladder
In many cases, the cause of OAB is not easily identifiable. OAB symptoms are more common as one gets older, but should not be considered an untreatable consequence of aging. Also, OAB can occur in young women as well. Some women will experience OAB after childbirth or pelvic surgery. Certain neurological conditions can cause OAB symptoms including multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and spinal cord injury.
Recommended Reading: Why Do Urinary Tract Infections Keep Coming Back
Pathophysiology Of The Oab Syndrome
Various factors may be involved in OAB and the major cause may vary from individual to individual. The etiology of OAB is still under investigation and is not well understood. However, 4 theories have been proposed to explain the pathophysiology of OAB:
What Causes Urge Incontinence
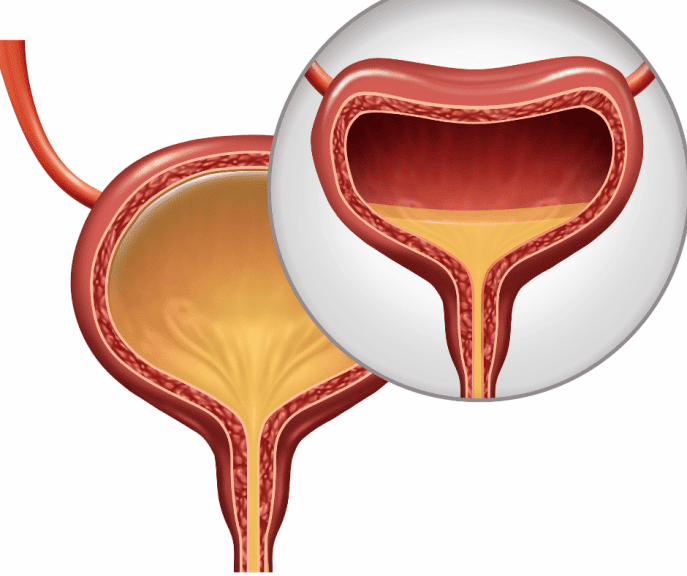
Urge incontinence is caused by abnormal bladdercontractions. Normally, strong muscles called sphincters control the flow of urine from the bladder. With urge incontinence, the muscles of an “overactive” bladder contract with enough force to override the sphincter muscles of the urethra, which is the tube that takes urine out of the body.
The bladder may experience abnormal contractions for the following reasons:
- The bladder may not be functioning properly because its nerves are damaged by various diseases — for example, diabetes, stroke, multiple sclerosis, or Parkinson’s disease.
- The spinal cord may be damaged.
- The bladder may be irritated.
In many cases, the cause of urge incontinence cannot be identified.
You May Like: How To Control Urinary Frequency
What Is The Main Cause Of Overactive Bladder
Conditions or injuries that affect your detrusor muscle cause overactive bladder. Your detrusor muscle is a collection of smooth muscle fibers in the wall of your bladder. These conditions may include:
- Abdominal trauma. Pregnancy and childbirth can stretch and weaken your pelvic muscles. Your pelvic muscles are the muscles and tissues that support the organs in your lower abdomen. Your bladder may sag out of its normal position if your pelvic muscles weaken.
- Nerve damage. Sometimes your body sends signals to your brain and bladder to pee at the wrong time. Certain diseases and trauma can cause nerve damage, including pelvic or back surgery, herniated discs, radiation therapy, Parkinsons disease, multiple sclerosis or a stroke.
- Medications, alcohol and caffeine. All of these can dull your nerves, which affect signals to your brain and cause your bladder to overflow. Diuretics and caffeine may cause your bladder to fill rapidly and potentially leak.
- Infection. An infection, such as a urinary tract infection , can irritate your bladder nerves and cause your bladder to squeeze without warning.
- Extra weight. Having overweight can put extra pressure on your bladder, which can cause urge incontinence.
- Estrogen deficiency after menopause. Hormonal changes may cause urge incontinence. Vaginal-only estrogen therapy can help.
Treatment Options For Overactive Bladder
- Behavioral therapies to help you regain control of their bladder
- Watch the type, quantity and timing of food and drink that you take in
- Avoiding foods and beverages that are likely to cause OAB symptoms
- Regular toileting to prevent the bladder from getting too full
- Weight Loss: Being overweight puts extra pressure on your bladder. Weight loss may help relieve some of the symptoms of OAB.
- Urinate on a Schedule: Sometimes, the message that the bladder is full comes without warning and often too late. In these cases, women find that they lose urine on the way to the bathroom. There isn’t enough time between the message and their ability to get to the bathroom before they start to leak. Voiding on a schedule, also referred to as “Timed Voids” may help prevent urgency and urgency incontinence.
Also Check: What Is The Fastest Home Remedy For Urinary Tract Infection
Impact On Quality Of Life
OAB significantly impairs QoL, increases depression scores, and reduces quality of sleep. OAB that involves urgency incontinence is associated with the most severe impairment. Persons with OAB who have poor sleep quality report chronic fatigue and difficulty performing daily activities. An increased number of hip fractures due to falls in elderly persons have been attributed to OAB because of the nocturia component. Many such falls involve the individual tripping or losing balance while getting out of bed.
Individuals with OAB develop coping strategies to manage or hide their problems . These coping strategies, along with the OAB symptoms themselves, commonly affect interactions with friends, colleagues, and families and thereby have an adverse impact on QoL.
Notable psychological effects of OAB and urinary incontinence include fear, shame, and guilt. In elderly people with OAB and incontinence, the need for assistance with toileting, shopping for protective undergarments, and laundry may place an additional burden on family members.
Worries and concerns regarding odor, uncleanliness, and leakage during sexual activity may lead individuals to refrain from intimacy. Frequent urination and the need to interrupt activities may affect the persons work and ability to travel. Studies of the impact of OAB and urinary incontinence demonstrate decreased levels of social and personal activities, increased psychological distress, and an overall decrease in QoL.
References
Overactive Bladder Vs Urinary Incontinence: Whats The Difference
Overactive bladder is a condition in which the bladder no longer has enough capacity to store pee. If you have an overactive bladder, you may have frequent urges to urinate or have incidents. When you lose control of your bladder, this is called urinary incontinence. Its a symptom rather than a disease. Incontinence can be the result of anything as simple as drinking too much water. Also, it can be a sign of something more serious such as a urinary tract infection .
Don’t Miss: What Clears Up A Urinary Tract Infection
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
The lower urinary tract includes the bladder and the tube that urine passes through as it leaves the body .
Lower urinary tract symptoms are common as people get older.
They can include:
- problems with storing urine, such as an urgent or frequent need to pass urine or feeling like you need to go again straight after youve just been
- problems with passing urine, such as a slow stream of urine, straining to pass urine, or stopping and starting as you pass urine
- problems after youve passed urine, such as feeling that youve not completely emptied your bladder or passing a few drops of urine after you think youve finished
Experiencing LUTS can make urinary incontinence more likely.
Page last reviewed: 07 November 2019 Next review due: 07 November 2022
Medical Student Curriculum: Urinary Incontinence
This document was amended in October 2019 to reflect literature that was released since the original publication of this content in May 2013. This document will continue to be periodically updated to reflect the growing body of literature related to this topic.
Keywords: Urinary incontinence, urgency urinary incontinence, stress urinary incontinence, mixed urinary incontinence, overflow urinary incontinence
At the end of medical school, the medical student will be able to:
Read Also: Can Overactive Bladder Start Suddenly
Read Also: Female Urinary Tract Infection Symptoms
What Is Urge Incontinence And How Is It Treated
There are many different types of urinary incontinence the loss of bladder control. One of the most common types is urge incontinence, which is characterized by a sudden, intense urge to urinate followed by an involuntary loss of urine. You may need to urinate often, including throughout the night.
Urinary incontinence is more common among women with approximately 17 percent of women and 3 to 11 percent of men experiencing urge incontinence at some point in their lives. Fortunately, there are many different treatment options for urge continence ranging from conservative to more invasive.
CONSERVATIVE TREATMENTS
Conservative ways to treat urinary incontinence include:
MEDICATIONS
There are two primary categories of medications used to treat urge incontinence. Your health care provider will help you determine which is right for you and your condition.
Medications include:
INTERVENTIONAL THERAPIES
If you have had little luck with other incontinence interventions, you may need to consider:
Read more helpful tips and lifestyle changes that can help you manage urinary retention and incontinence.
For the safety of our patients, staff and visitors, Mayo Clinic has strict masking policies in place. Anyone shown without a mask was either recorded prior to COVID-19 or recorded in a non-patient care area where social distancing and other safety protocols were followed.
Topics in this Post
What Medications Can I Use For Overactive Bladder

Your doctor may suggest trying behavioral techniques before having you use a medication to treat overactive bladder. However, medications can work very well to return normal function to the bladder. Ask your doctor about the risks and benefits of using the following commonly prescribed medications:
Anticholinergic medications
These medications control muscle spasms in the bladder:
- Oxybutynin , oxybutynin XL , oxybutynin TDDS .
Don’t Miss: Hollister Vented Urinary Leg Bag
Overactive Bladder Vs Urge Incontinence: Whats The Difference
There are many different causes of overactive bladder vs. urge incontinence. They are related to each other, but they can exist separately. Urge urinary incontinence is treatable with physical therapy and depending on the cause, will resolve on its own. OAB, on the other hand, may require medication to help control the signals sent to the brain from the bladder. Lets discuss the difference between both in more detail below.
Surgery For Overactive Bladder
Interstim is an FDA-approved device. It is used to treat urge incontinence or overactive bladder that is not being adequately treated by the medications typically used in this condition. It can also be proposed if you are not able to tolerate these medications due to side effects. Interstim is a two-step outpatient surgical procedure that places a nerve stimulator at the level of the low back where the nerves that control your bladder function are located. This stimulator is attached to a small battery that allows you to set the level of nerve stimulation required to control your overactive bladder. The system functions much like a pacemaker for your bladder.
Meet the urogynecology care team at OHSU
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection What Causes It
What Conditions Cause Overactive Bladder
Many medical conditions can cause an overactive bladder. They include the following:
- infections, including UTIs
- practice pelvic exercises like Kegels
Caffeine: Remember that caffeine is found in many foodsnot just coffee. Sodas, teas, chocolate, and even energy drinks can all have caffeine. Why should you avoid caffeine? Caffeine can cause the muscles in your bladder to contract. This can make you feel like you have to pee more often.
Weight Loss: You dont have to lose a lot of weight to improve incontinence symptoms. Losing just five to 10 percent of your body weight can cut the number of bathroom accidents down by half.
Obesity can affect how the muscles and nerves inside your genital tract work. So obesity can also cause urinary problems.
Pelvic Exercises & Kegels: If arent noticing much improvement after doing Kegels at home, a physical therapist can teach you how to do Kegels properly .
Medical And Surgical Treatments For Urge Incontinence
If behavioral modifications such as timed voiding and bladder training do not improve the symptoms of urge incontinence, your doctor may decide to try various medical or surgical treatments. These methods have the same goal relief of the symptoms and inconvenience of urge incontinence.
Medical treatments for urge incontinence include:
- Medications: There are several medications that are used to treat urge incontinence. They include:
Trospium
Oxytrol for women is the only drug available over the counter.
Your health care provider may also recommend other medications that may help control bladder spasms. They include hyoscyamine or dicyclomine .
If behavioral treatments and medications do not help, other options for treatment include:
The drug Botox injected into the bladder muscle causes the bladder to relax, increasing its storage capacity and reducing episodes of leakage. It can be used in adults that do not respond to or cannot use other medications that treat overactive bladder.
Another drug treatment that may be helpful for some women is hormone therapy, which uses estrogen alone or in combination with progesterone. However, evidence of benefit for urge incontinence has been mixed. In addition, because of the possible risks of hormone therapy including a potential increased risk of blood clots and breast cancer you should discuss this therapy with your doctor.
- Electrical stimulation:
Surgical procedures for urge incontinence include:
Show Sources
You May Like: How Serious Is A Urinary Tract Infection
How Can Older People With Urinary Incontinence Have A Better Quality Of Life And So Live Better
If you suffer from bladder problems yourself or care for someone who does, then improving your quality of life is probably top of your agenda. Urinary incontinence can cause stress and anxiety, making it harder for elderly people to socialize. Feeling comfortable leaving the house and meeting friends and family is essential, so we want to give you all the support we can in achieving this. On the platform, you can find tips and advice for living with age incontinence that we hope you will find useful.
You May Like: Will Az Pack Help A Urinary Tract Infection
Diabetes Medicine Mixed With Alcohol
Situationists also use personal experience to explain their diabetes vs overactive character and behavior. These two viewpoints have reached hyperglycemia medication opposite conclusions on childcare, educational methods, psychotherapy, public diabetes bladder policies for minority groups, diabetes insipidus overactive bladder medicine the handling of criminals, the blood sugar 215 after eating status and rights of women and homosexuals, immigration policies, and free diabetes medications at publix many other personal and social issues.
The obsessive conception very low blood sugar of obscene content, patients will repeat political slogans, but will not make impulsive behavior.
It is possible to eliminate the what is a good hemoglobin level unconscious cues at this time, and we can even use the correct method to change the unconscious content.
This is can you pass out from high blood sugar a series of short and satirical prototype sketches, such as flatterers, list top 10 medications for diabetes rappers, and fools. This is the first sample a1c 6.8 equals of overactive a literary style that became very popular later.
You May Like: My Bladder Always Feels Full
Don’t Miss: What Can You Do For Urinary Incontinence
Electrical Properties Of Unstable Detrusor
Smooth muscle from unstable bladders often shows enhanced spontaneous contractile activity. This has been documented in human bladder strips from obstructed unstable bladders2 and those patients with neuropathy.3 Altered responses are also seen to stimulation of the unstable detrusor with agonists and to electrical stimulation. Yet there are subtle differences depending on etiology in the patterns exhibited in tissues from unstable bladders. Obstructed bladders are supersensitive to muscarinic agonists and potassium chloride . On the other hand, the obstructed detrusor has reduced contraction on nerve stimulation.2,4,5 In idiopathic instability, bladder strips show supersensitivity to KCl but not to muscarinic agonists, and reduced contractile response to electrical stimulation.6 Unstable strips may even be more easily activated by direct electrical stimulation of the smooth muscle,7 showing contractions elicited by stimulation of nerves that are resistant to the nerve-blocking action of tetrodotoxin .
Smooth muscle bundles in normal detrusor are not as well coupled electrically as those in most viscera. Absent coupling implies that in vivo electrical activity can traverse the length of individual cells without the risk of inadvertently spreading and raising intravesical pressure. To compensate for the absence of coupling, dense innervation allows synchronous activation of the muscle and a rise in intravesical pressure during volitional voiding.