Drg Mapping Rules For C679
Diagnostic codes are the first step in the DRG mapping process.
The patients primary diagnostic code is the most important. Assuming the patients primary diagnostic code is C67.9, look in the list below to see which MDCs Assignment of Diagnosis Codes is first. That is the MDC that the patient will be grouped into.
From there, check the subsections of the MDC listed. The patient will be mapped into the first subsection for which the treatment performed on the patient meet the listed requirements of that subsection.
DRG grouping rules are adjusted each year, so make sure to check the rules for the fiscal year of the patients discharge date.
After Bladder Cancer Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Bladder Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out if cancer has spread within thebladder lining and muscle or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. The following tests and procedures may be used in the staging process:
What Is The Latest Treatment For Bladder Cancer
bladder cancertreatcancerDepending on the stage of the cancer and other factors, treatment options for people with bladder cancer can include:
- Bladder Cancer Surgery.
- Intravesical Therapy for Bladder Cancer.
- Chemotherapy for Bladder Cancer.
- Radiation Therapy for Bladder Cancer.
- Immunotherapy for Bladder Cancer.
You May Like: How Treat Urinary Tract Infection Naturally
Smoking Can Affect The Risk Of Bladder Cancer
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Talk to your doctor if you think you may be at risk for bladder cancer.
Risk factors for bladder cancer include the following:
- Using tobacco, especially smoking cigarettes.
- Having a family history of bladder cancer.
- Having certain changes in the genes that are linked to bladder cancer.
- Being exposed to paints, dyes, metals, or petroleum products in the workplace.
- Past treatment with radiation therapy to the pelvis or with certain anticancer drugs, such as cyclophosphamide or ifosfamide.
- Taking Aristolochia fangchi, a Chinese herb.
- Drinking water from a well that has high levels of arsenic.
- Drinking water that has been treated with chlorine.
- Having a history of bladder infections, including bladder infections caused by Schistosoma haematobium.
- Using urinarycatheters for a long time.
Older age is a risk factor for most cancers. The chance of getting cancer increases as you get older.
Treatment Of Recurrent Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of recurrentbladder cancer depends on previous treatmentand where the cancer has recurred. Treatment for recurrent bladder cancer mayinclude the following:
- Radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- A clinical trial of a new treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
You May Like: Can Urinary Tract Infection Cause Fever
What Are The Risk Factors For Bladder Cancer
Some factors increase the risk of bladder cancer:
- Cigarette smoking is the biggest risk factor it more than doubles the risk. Pipe and cigar smoking and exposure to second-hand smoking may also increase one’s risk.
- Prior radiation exposure is the next most common risk factor .
- Certain chemotherapy drugs also increase the risk of bladder cancer.
- Environmental exposures increase the risk of bladder cancer. People who work with chemicals, such as aromatic amines are at risk. Extensive exposure to rubber, leather, some textiles, paint, and hairdressing supplies, typically related to occupational exposure, also appears to increase the risk.
- Infection with a parasite known as Schistosoma haematobium, which is more common in developing countries and the Middle East.
- People who have frequent infections of the bladder, bladder stones, or other diseases of the urinary tract, or who have chronic need for a catheter in the bladder, may be at higher risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Patients with a previous bladder cancer are at increased risk to form new or recurrent bladder tumors.
Other risk factors include diets high in fried meats and animal fats, and older age. In addition, men have a three-fold higher risk than women.
Defining Radical Cystectomy Using The Icd
No consensus list of ICD-10-PCS codes to identify radical cystectomy exists.
-
We developed and internally validated a list of ICD-10-PCS codes to identify RC.
-
Identified 222/225 in training cohort and 227/234 in validation cohort.
-
Codes may be useful to bladder cancer researchers working with administrative data.
Read Also: How To Do Bladder Training
Also Check: Urinary Tract Infection After Period
Specific Coding For Malignant Neoplasm Of Bladder
Non-specific codes like C67 require more digits to indicate the appropriate level of specificity. Consider using any of the following ICD-10 codes with a higher level of specificity when coding for malignant neoplasm of bladder:
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.0 for Malignant neoplasm of trigone of bladder
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.1 for Malignant neoplasm of dome of bladder
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.2 for Malignant neoplasm of lateral wall of bladder
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.3 for Malignant neoplasm of anterior wall of bladder
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.4 for Malignant neoplasm of posterior wall of bladder
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.5 for Malignant neoplasm of bladder neck
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.6 for Malignant neoplasm of ureteric orifice
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.7 for Malignant neoplasm of urachus
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.8 for Malignant neoplasm of overlapping sites of bladder
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.9 for Malignant neoplasm of bladder, unspecified
You Have Bladder Cancer
The tissue in the body is made up of cells. With cancer, the cells multiply uncontrollably, which leads to a malignant neoplasm developing. The cancer cells can destroy the healthy tissue and spread throughout the body.
The bladder sits low down in the abdomen and collects the urine. The urine is produced in the two kidneys. The urine flows from the kidneys into the bladder via the ureters. When you pass water, the urine flows from the bladder via the urethra and out.
Read Also: How To Prevent Urinary Tract Infections In The Elderly
Malignant Neoplasm Of Urethra
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- C68.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C68.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of C68.0 other international versions of ICD-10 C68.0 may differ.
type 1 excludes
Malignant Neoplasm Of Other And Unspecified Urinary Organsc68
Chapter 2 Neoplasms » Malignant neoplasms of urinary tract » Malignant neoplasm of other and unspecified urinary organs
ICD-10 Subcodes
7 indications for 794 drugs
Hierarchy Tree View
YOU AGREE THAT THE INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE IS PROVIDED AS IS, WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT OF ANY THIRD-PARTY PATENT, COPYRIGHT, OR ANY OTHER THIRD-PARTY RIGHT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE CREATORS OF THE WEBSITE OR WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF OR IN ANY WAY CONNECTED WITH THE WEBSITE, THE USE OF THE WEBSITE, OR THIS AGREEMENT, WHETHER IN BREACH OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, EVEN IF SUCH PARTY IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Center for Research Innovation in Biotechnology 4240 Duncan Avenue, Suite 110 Saint Louis, MO 63110
Also Check: Is Urge Incontinence The Same As Overactive Bladder
You May Like: Foods For Urinary Tract Health
Does Bladder Cancer Spread Quickly
cancergrowspread rapidlybladder cancergrowspread quicklycancersThe 3 main types of bladder cancer are:
- Urothelial carcinoma. Urothelial carcinoma accounts for about 90% of all bladder cancers.
- Squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cells develop in the bladder lining in response to irritation and inflammation.
- Adenocarcinoma.
There Are Different Types Of Treatment For Patients With Bladder Cancer
Different types of treatment are available for patients with bladder cancer. Some treatments are standard , and some are being tested in clinical trials. A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer. When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment. Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
You May Like: Why Do Males Get Urinary Tract Infections
Treatment Of Stage I Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage I bladder cancer may include the following:
- Transurethral resection with fulguration. This may be followed by one of the following:
- Intravesicalchemotherapy given right after surgery.
- Intravesical chemotherapy given right after surgery and then regular treatments with intravesical BCG or intravesical chemotherapy.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
What Is The Correct Code For A Patient With A Malignant Neoplasm Of The Lateral Wall Of The Bladder
4.5/5Malignant NeoplasmBladderLateral WallUrinary Bladder
Subsequently, one may also ask, what is malignant neoplasm of lateral wall of bladder?
C67. 2 – Malignant neoplasm of lateral wall of bladder. C67. 2 – Malignant neoplasm of lateral wall of bladder is a topic covered in the ICD-10-CM. To view the entire topic, please sign in or purchase a subscription.
One may also ask, what is the most aggressive type of bladder cancer? Tumor GradeHigh-grade tumor cells are very abnormal, poorly organized and more serious. They are the most aggressive and more likely to grow into the bladder muscle.
Beside this, what does malignant neoplasm of urinary bladder mean?
These tumors are called non-invasive papillary cancers. Very low-grade , non-invasive papillary cancer is sometimes called papillary urothelial neoplasm of low-malignant potential and tends to have a very good outcome. Flat carcinomas do not grow toward the hollow part of the bladder at all.
What is the base of the bladder called?
An internal sphincter â a type of muscular valve â helps prevent urine from leaking out. The triangle-shaped base of the bladder, known as the trigone, helps prevent stretching of the urethra or backflow into the ureters.
Don’t Miss: Burning Sensation In Urinary Tract
The Icd Code C679 Is Used To Code Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is any of several types of cancer arising from the epithelial lining of the urinary bladder. Rarely the bladder is involved by non-epithelial cancers, such as lymphoma or sarcoma, but these are not ordinarily included in the colloquial term bladder cancer. It is a disease in which abnormal cells multiply without control in the bladder.
| Specialty: |
Malignant Neoplasm Of Unspecified Lacrimal Gland And Duct
ICD-10 code C69.50 for Malignant neoplasm of unspecified lacrimal gland and duct
ICD-10
ICD-10 International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision
ICD-10
ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems , a medical classification list by the World Health Organization .
It contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or diseases.
ATC
The Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System is used for the classification of active ingredients of drugs according to the organ or system on which they act and their therapeutic, pharmacological and chemical properties.
It is controlled by the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology .
DDD
The defined daily dose is a statistical measure of drug consumption, defined by the World Health Organization .
It is used to standardize the comparison of drug usage between different drugs or between different health care environments.
Read Also: Causes Of Urinary Incontinence In Elderly Males
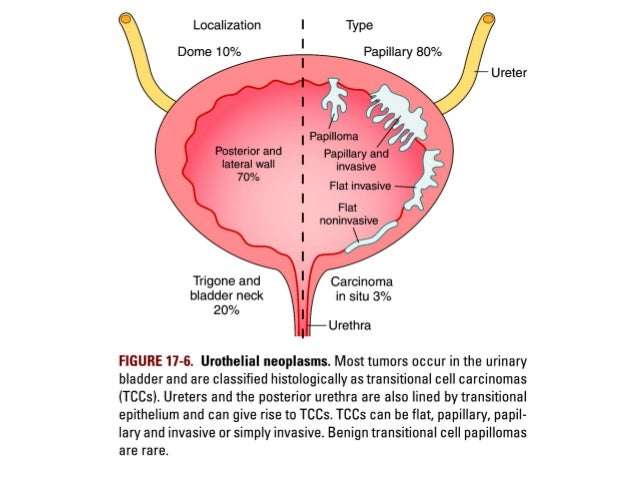
Papillary Vs Flat Cancer
Bladder cancers are also divided into 2 subtypes, papillary and flat, based on how they grow .
- Papillary carcinomas grow in slender, finger-like projections from the inner surface of the bladder toward the hollow center. Papillary tumors often grow toward the center of the bladder without growing into the deeper bladder layers. These tumors are called non-invasive papillary cancers. Very low-grade , non-invasive papillary cancer is sometimes called papillary urothelial neoplasm of low-malignant potential and tends to have a very good outcome.
- Flat carcinomas do not grow toward the hollow part of the bladder at all. If a flat tumor is only in the inner layer of bladder cells, it’s known as a non-invasive flat carcinoma or a flat carcinoma in situ .
If either a papillary or flat tumor grows into deeper layers of the bladder, it’s called an invasive urothelial carcinoma.
How Are Neoplasms Of Uncertain Behavior Coded In Icd
Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site mentioned, e.g., ectopic pancreatic malignant neoplasms are coded to pancreas, unspecified . Categories D37 D44, and D48 classify by site neoplasms of uncertain behavior, i.e., histologic confirmation whether the neoplasm is malignant or benign cannot be made.
Follow
Read Also: Guys Get Urinary Tract Infections
Secondary Malignant Neoplasm Of Bladder
ICD-10 code C79.11 for Secondary malignant neoplasm of bladder
ICD-10
ICD-10 International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision
ICD-10
ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems , a medical classification list by the World Health Organization .
It contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or diseases.
ATC
The Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System is used for the classification of active ingredients of drugs according to the organ or system on which they act and their therapeutic, pharmacological and chemical properties.
It is controlled by the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology .
DDD
The defined daily dose is a statistical measure of drug consumption, defined by the World Health Organization .
It is used to standardize the comparison of drug usage between different drugs or between different health care environments.
How Are Multiple Neoplasms Coded In Icd 10

For multiple neoplasms of the same site that are not contiguous, such as tumors in different quadrants of the same breast, codes for each site should be assigned. Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site mentioned, e.g., ectopic pancreatic malignant neoplasms are coded to pancreas, unspecified .
Don’t Miss: Hills Prescription Diet Urinary Care C D
Rare Forms Of Bladder Cancer
Adenocarcinomas account for less than 2% of primary bladder tumors. These lesions are observed most commonly in exstrophic bladders and are often associated with malignant degeneration of a persistent urachal remnant.
Other rare forms of bladder cancer include leiomyosarcoma, rhabdosarcoma, carcinosarcoma, lymphoma, and small cell carcinoma. Leiomyosarcoma is the most common sarcoma of the bladder. Rhabdomyosarcomas most commonly occur in children. Carcinosarcomas are highly malignant tumors that contain a combination of mesenchymal and epithelial elements. Primary bladder lymphomas arise in the submucosa of the bladder. Except for lymphomas, all these rare bladder cancers carry a poor prognosis.
Small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder is a poorly differentiated, malignant neoplasm that originates from urothelial stem cells and has variable expression of neuroendocrine markers. Morphologically, it shares features of small cell carcinoma of other organs, including the lung.
Here Are The Instructions From The Icd
Uncertain diagnosis
Do not code diagnoses documented as probable, suspected, questionable, rule out, or working diagnosis or other similar terms indicating uncertainty. Rather, code the condition to the highest degree of certainty for that encounter/visit, such as symptoms, signs, abnormal test results, or other reason for the visit.
Please note: This differs from the coding practices used by short-term, acute care, long-term care and psychiatric hospitals.
Primary malignancy previously excised
When a primary malignancy has been previously excised or eradicated from its site and there is no further treatment directed to that site and there is no evidence of any existing primary malignancy, a code from category Z85, Personal history of malignant neoplasm, should be used to indicate the former site of the malignancy.
Follow ICD-10 coding rules when reporting suspected or confirmed malignancy and personal history of malignant neoplasm. Remember, the codes that are selected stay with the patient.
Don’t Miss: Diflucan For Urinary Tract Infections
Other Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk Factors
Having bladder diverticula may increase an individuals chance of developing SCC. Rarely, bacillus Calmette-Guerin treatment for CIS has been reported to lead to development of SCC. Development of bladder cancer at a younger age has been associated with bladder exstrophy. SCC has also been described in urachal remnants.
Coffee consumption does not increase the risk of developing bladder cancer. Early studies of rodents and a minority of human studies suggested a weak connection between artificial sweeteners and bladder cancer however, most recent studies show no significant correlation.